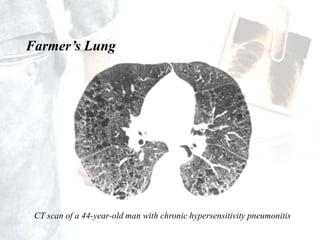
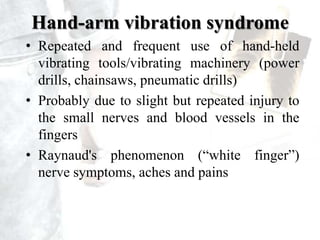
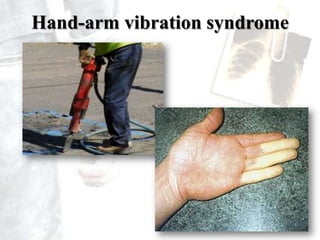
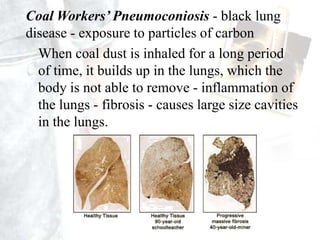
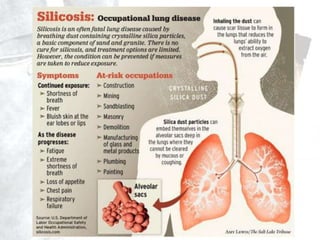
Occupational diseases are chronic ailments that occur as a result of work or occupational activity. They can develop instantly upon exposure to hazards like gases, or gradually over weeks, months, or decades from exposures like heavy metals or carcinogens. Globally, there are millions of occupational disease cases and deaths annually, costing countries 2-14% of GDP. Occupational diseases are classified into categories like those from physical, chemical, or biological agents. Examples of specific occupational diseases discussed are pneumoconiosis like black lung from inhaling dusts, occupational dermatitis from skin exposures, and hand-arm vibration syndrome from using vibrating tools. Prevention strategies include engineering controls, protective equipment, health monitoring, and legislation.