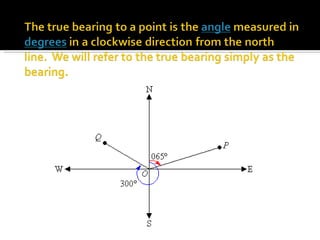
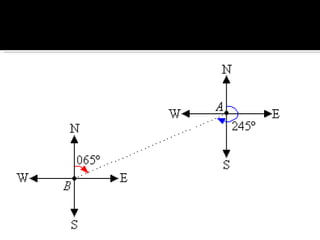
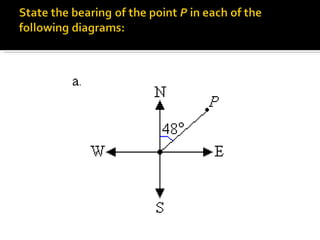
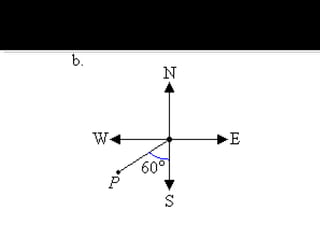
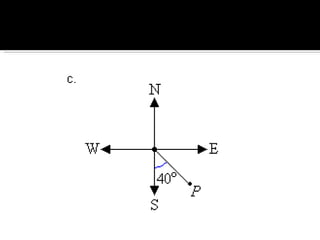
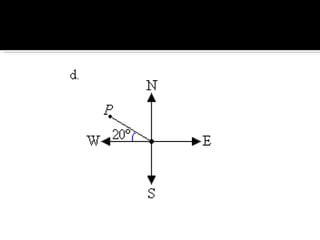
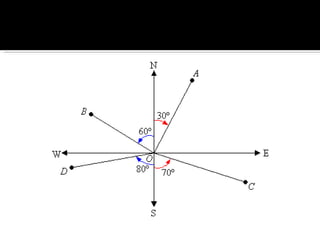
The document discusses compass bearings and directions. It defines bearings as the number of degrees measured clockwise from north to a point. Directions are similar but specify whether the bearing is east or west of north/south. It provides examples of converting bearings to directions.