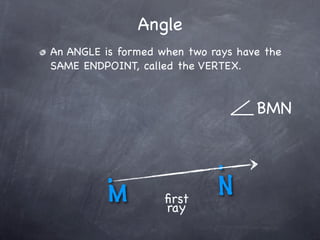
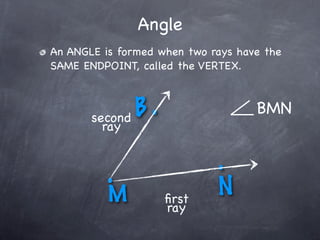
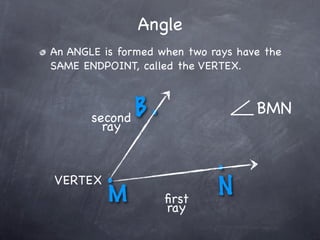
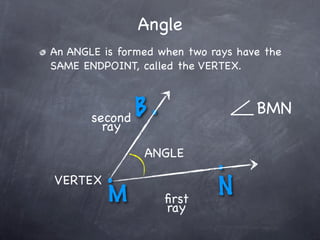
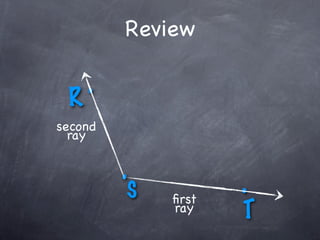
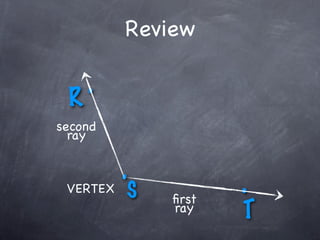
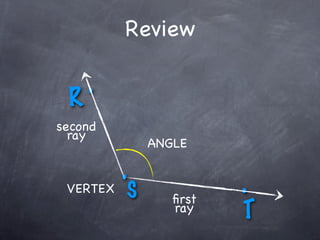
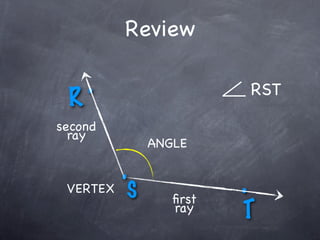
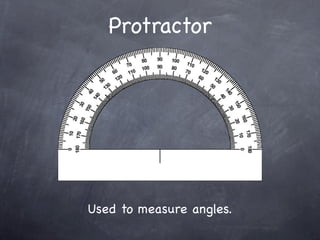
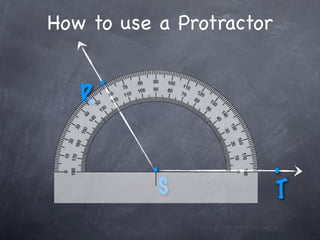
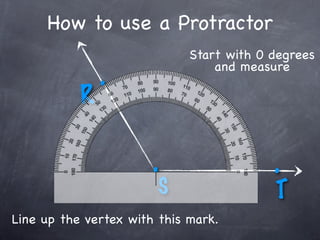
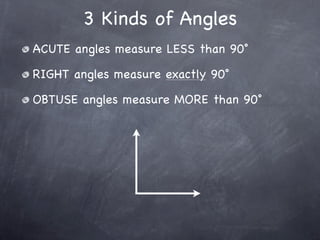
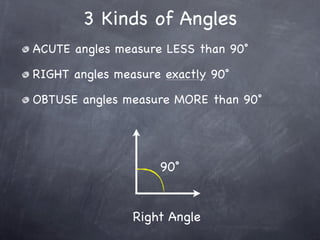
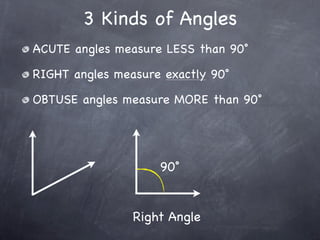
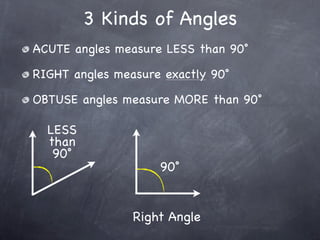
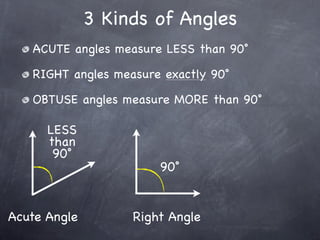
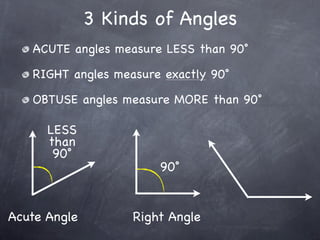
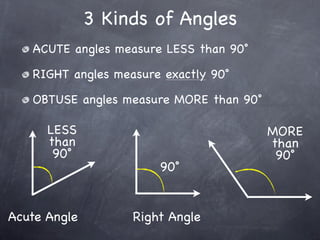
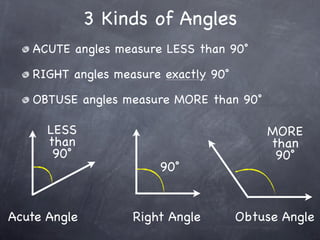
The document discusses angles and how to measure them. An angle is formed when two rays share an endpoint called the vertex. A protractor is used to measure angles by lining up the vertex with the 0 mark and reading the degree measure. There are three kinds of angles: acute angles measure less than 90 degrees, right angles measure exactly 90 degrees, and obtuse angles measure more than 90 degrees.