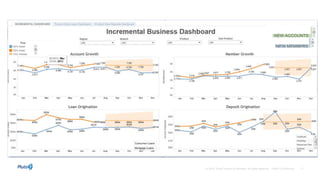
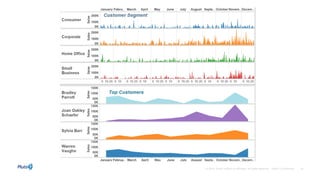
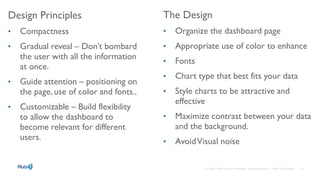
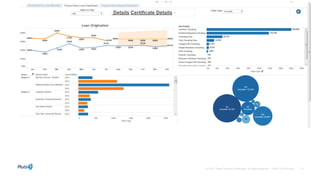
Governance involves ensuring data is current, accurate, and secure to support business decisions and outcomes. Effective governance combines IT and business approaches to protect sensitive information. Good governance provides competitive advantages through customer insights that inform various business functions. As data sources increase, organizations are integrating data more to gain insights from mobile and cloud-based sources. Dynamic collaboration and conversations around interactive data and dashboards are driving business decisions.