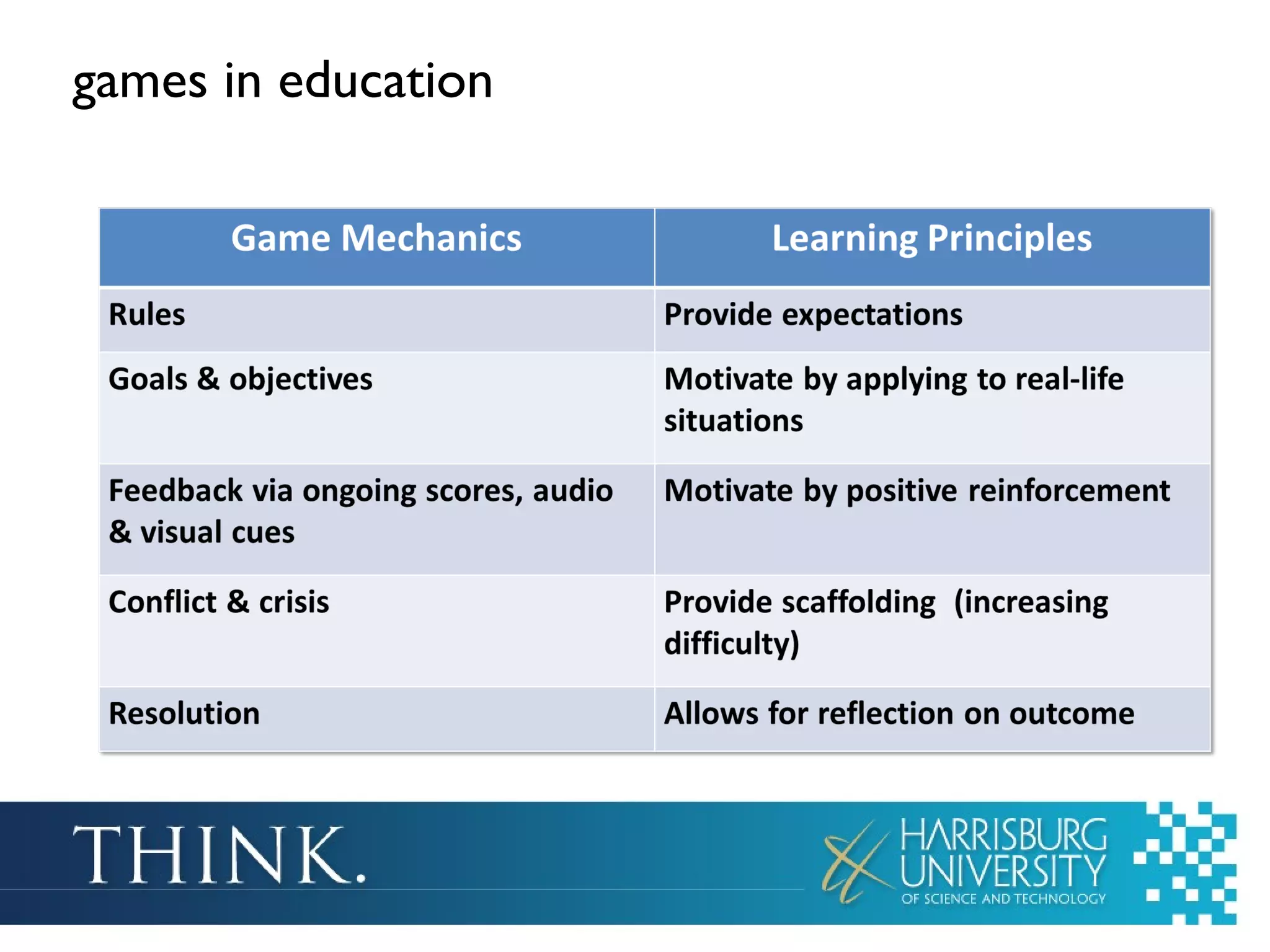
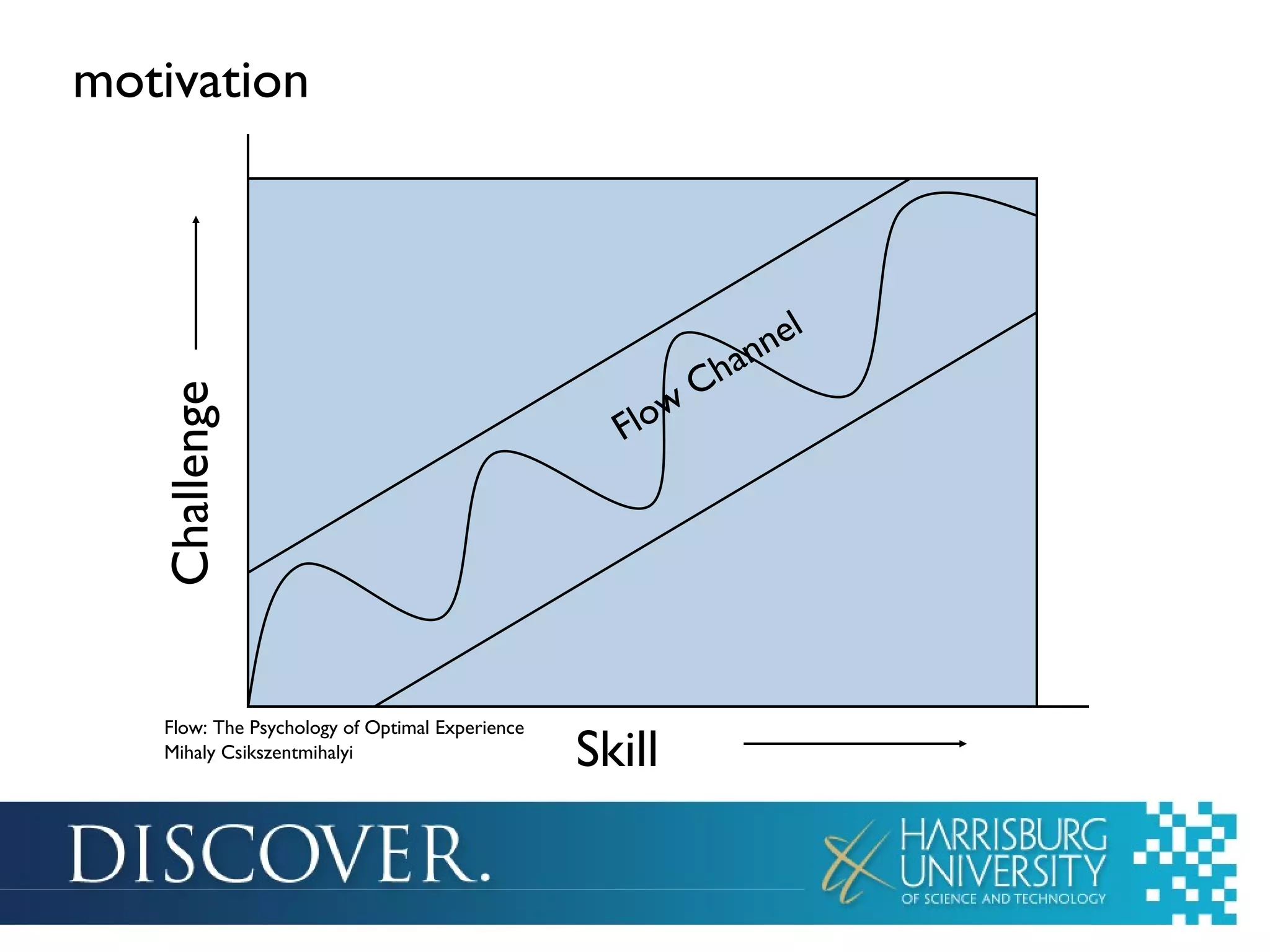
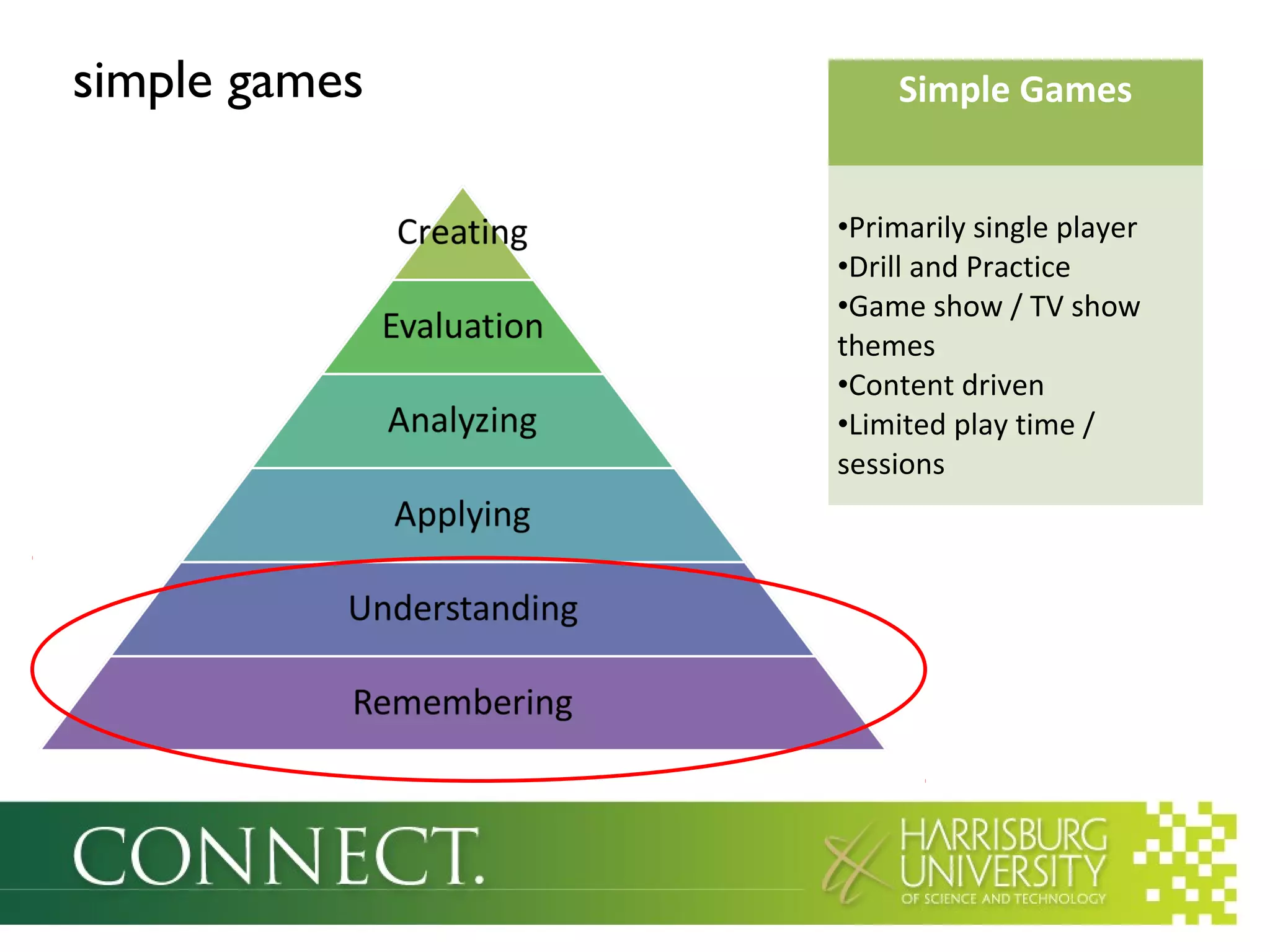
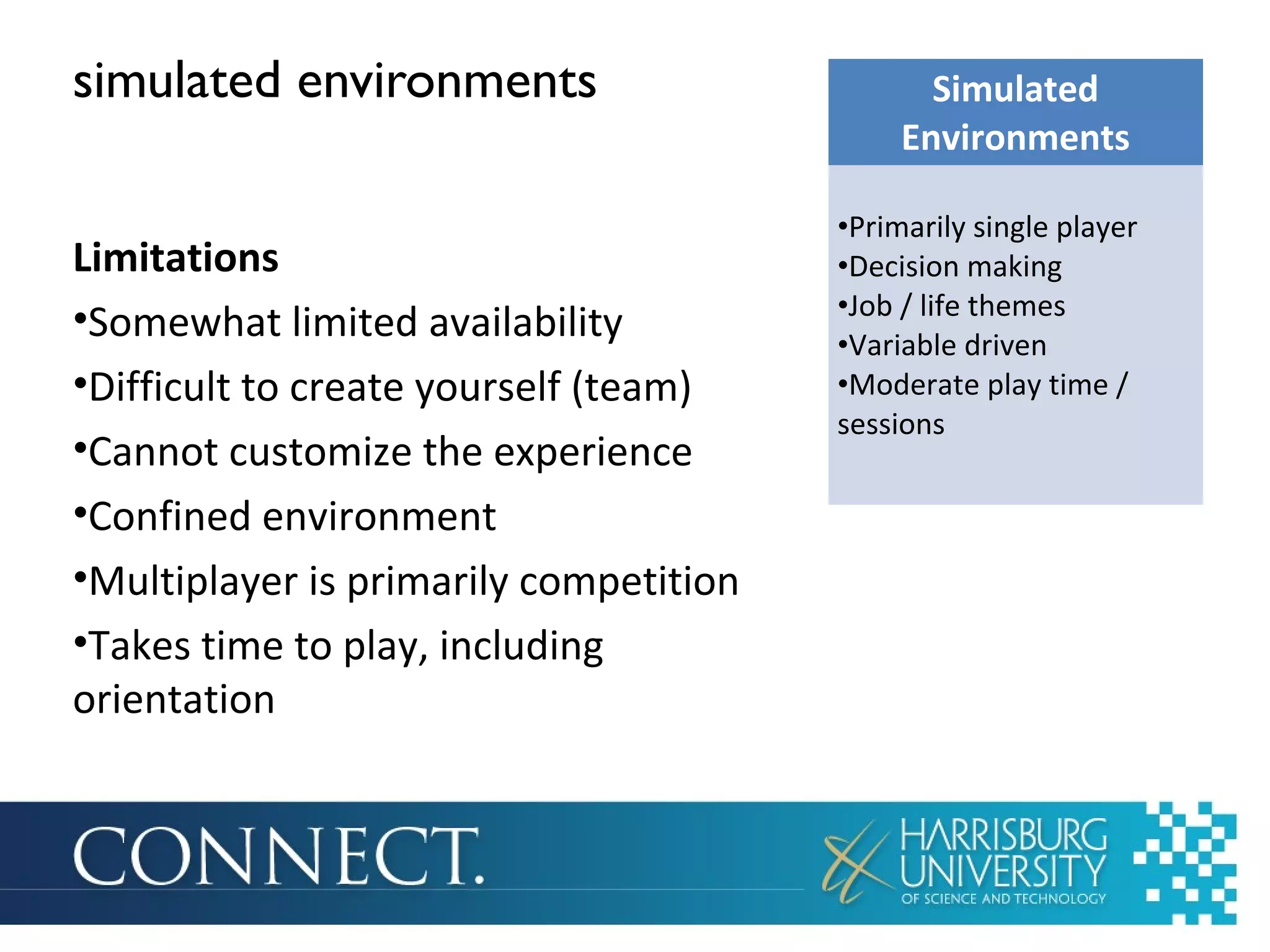
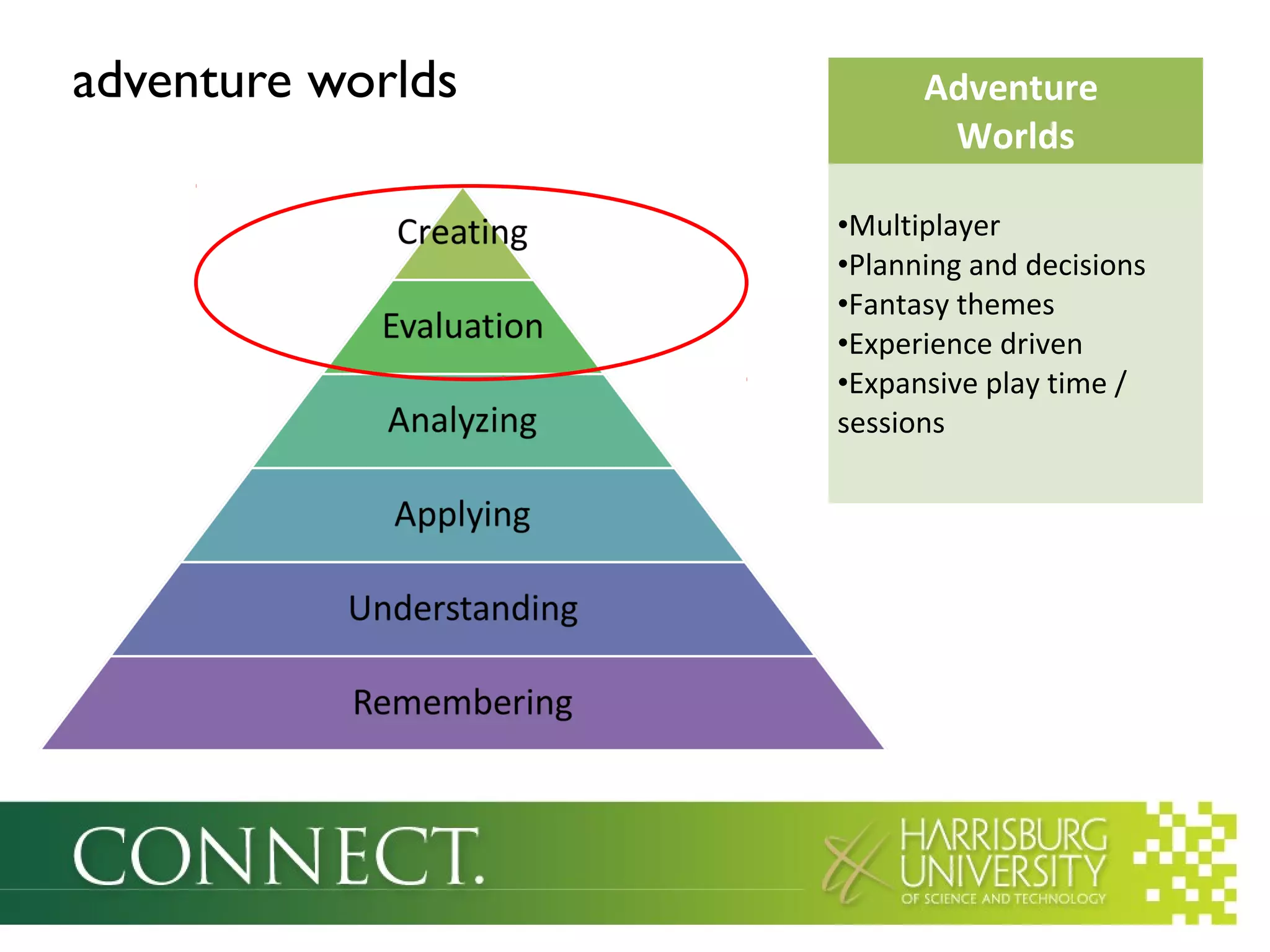
The document discusses the integration of games in education, highlighting their benefits such as enhanced motivation, personalized learning, and engagement. It categorizes educational games into three types: simple games, simulated environments, and adventure worlds, detailing their respective attributes, advantages, and limitations. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of teacher involvement in maximizing the effectiveness of these educational tools.