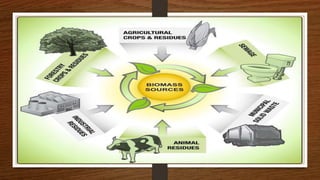
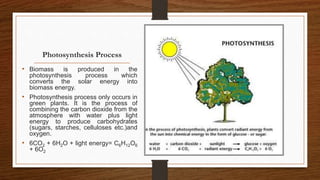
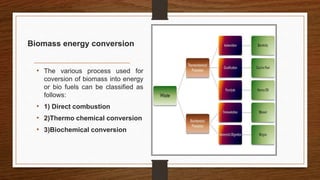
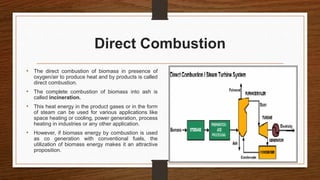
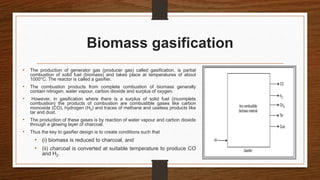
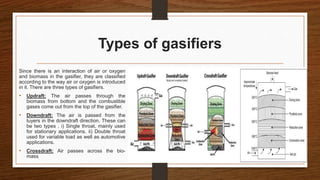
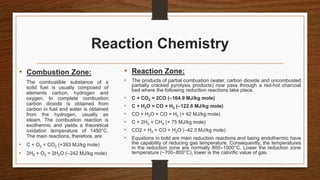
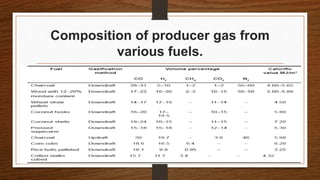
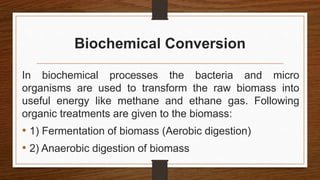
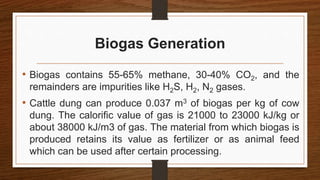
Biomass can be converted into energy through direct combustion, gasification, or biochemical processes. Direct combustion involves burning biomass to produce heat, while gasification converts it into a combustible gas mixture through incomplete combustion. Biochemical processes use bacteria and microorganisms to produce fuels like methane from raw biomass through fermentation or anaerobic digestion. Anaerobic digestion of wet biomass produces biogas, which is around 55-65% methane, through decomposition by anaerobic bacteria.