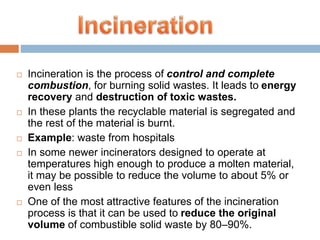
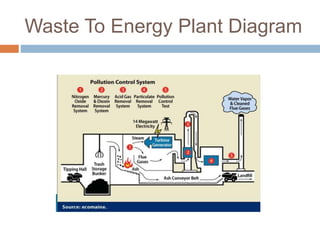
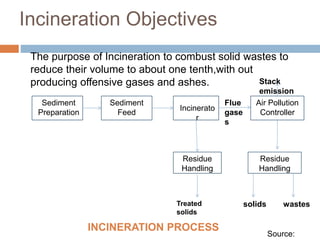
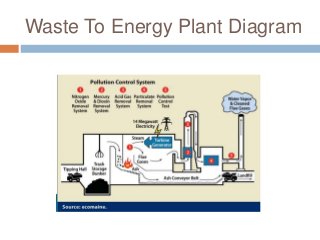
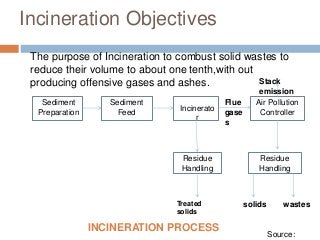
The document discusses solid waste management through incineration methods. It explains that solid waste management aims to minimize environmental impacts through collection, disposal, and utilization of wastes. Incineration is described as a process that burns solid wastes to reduce their volume while recovering energy and destroying toxic materials. The document outlines the incineration process and notes its advantages of volume and weight reduction as well as energy recovery, but also disadvantages like toxic emissions and ash disposal challenges. It provides examples of incineration practices and challenges in India.