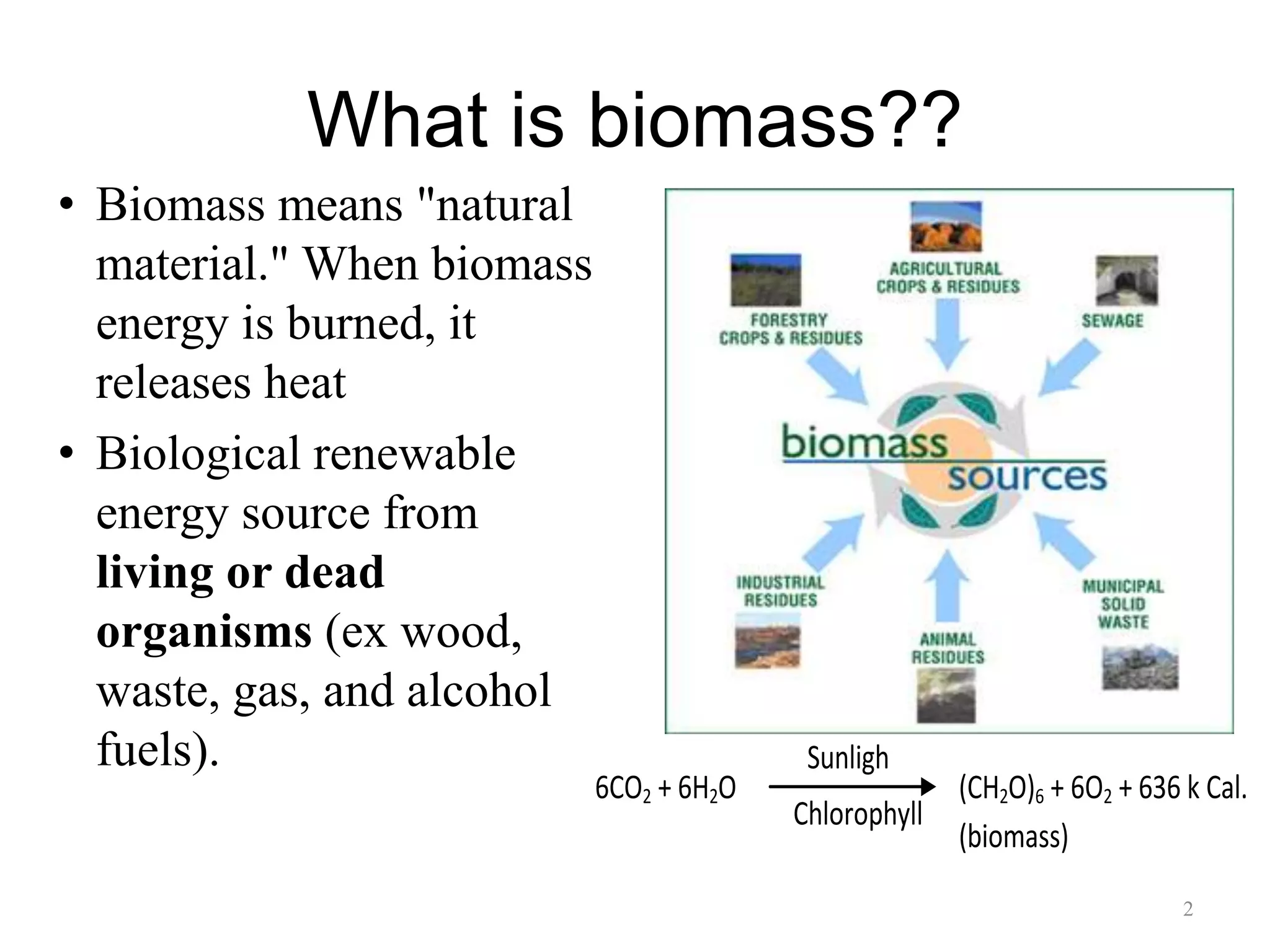
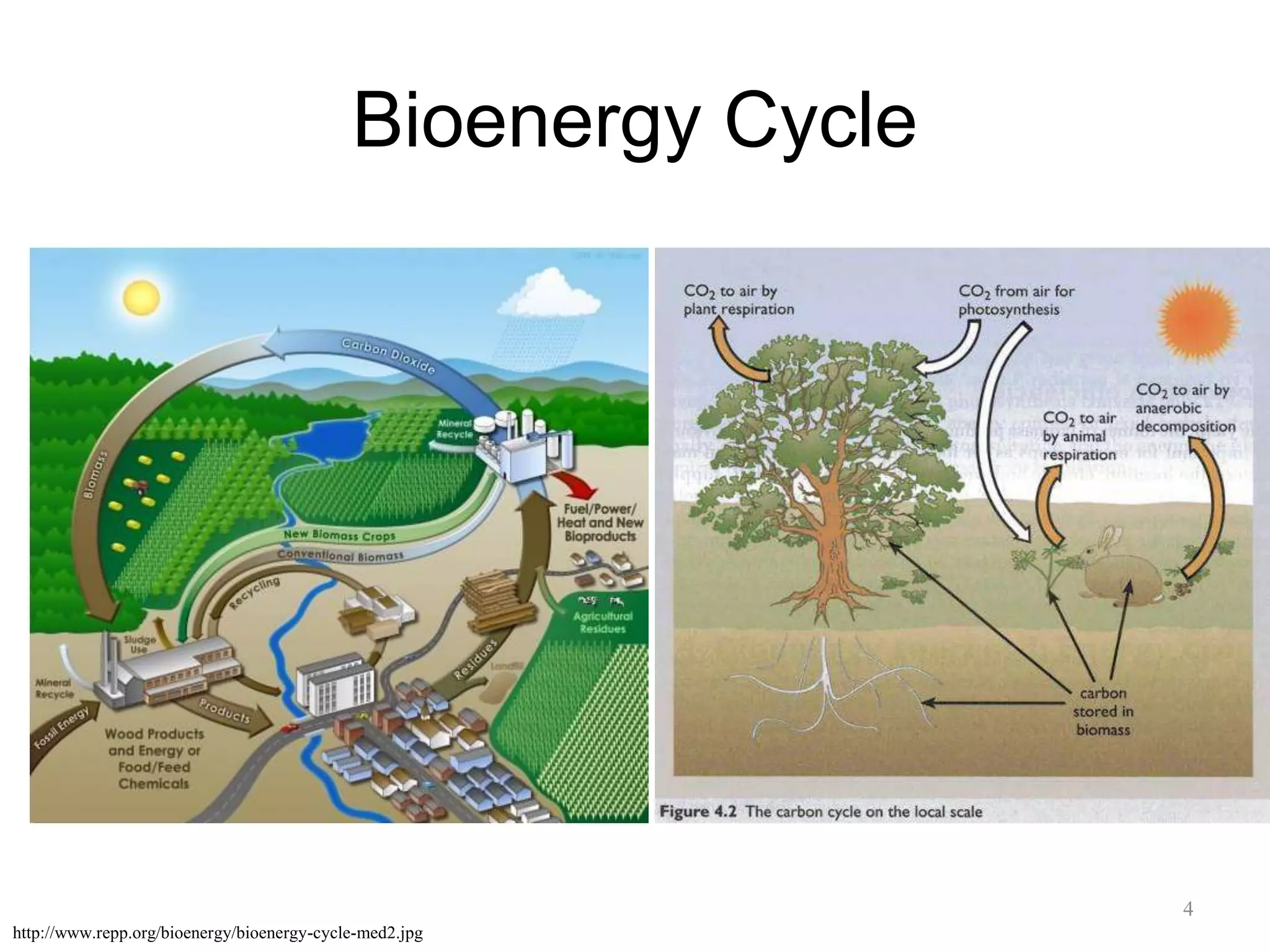
This document discusses biomass as a renewable energy source. It defines biomass as natural material from living or dead organisms that can be converted to energy. Biomass energy is stored in organic compounds that can be converted into heat, gases, solids, liquids or chemicals through combustion, gasification or pyrolysis. Examples of biomass feedstocks include wood, agricultural waste and municipal solid waste. The document also outlines the biomass energy cycle and various biomass conversion technologies and their processes.



























![Bioenergy Calculation
32
Composition Percent % kJ/kg Total
Paper 7.73 16,750 1,295
Plastic 18.29 32,500 5,944
Food waste 26.56 4,650 1,235
Wood and yard 8.52 18,600 1,585
*Others 14.92 15,000 2,238
Ferrous 2.47 0 0
Aluminium 0.06 0 0
Glass 1.93 0 0
Sand/fine materials 14.41 0 0
Other inorganics 5.11 0 0
Total 100.00 12,297kJ/kg
kJ --> kWh 0.000278
Throughput: 1800 tons/day
Thermal Power : 256 MW/hour
Electricity Efficiency : 7.5 % 5-10% for a "normal" design
Nomimal power gen : 19.2 MWe/hour [460 MWh/day]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biomass-180222053645/75/Biomass-32-2048.jpg)