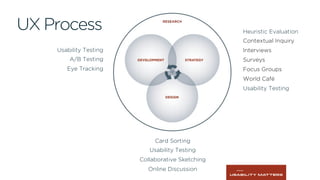
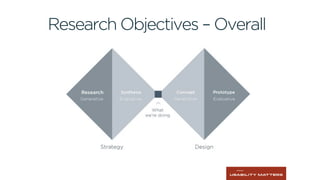
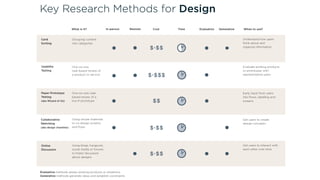
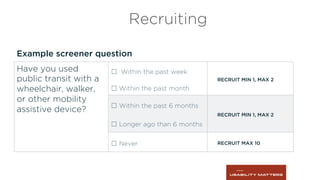
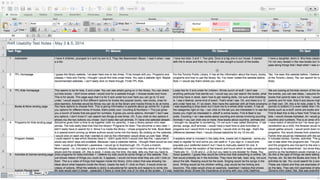
This document outlines the planning, execution, and analysis of user research in the UX process, emphasizing the importance of effective methodologies such as usability testing, interviews, and surveys. It highlights key steps in research including planning, recruiting participants, conducting interviews, and analyzing data to derive actionable insights. The document also stresses participant criteria and logistics necessary for successful research outcomes.