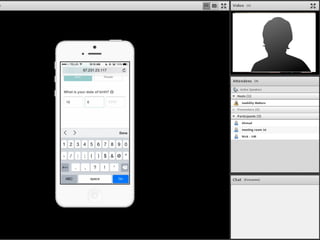
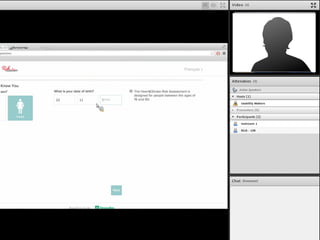
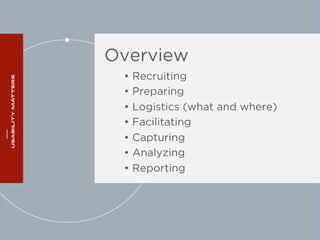
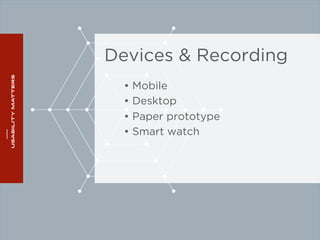
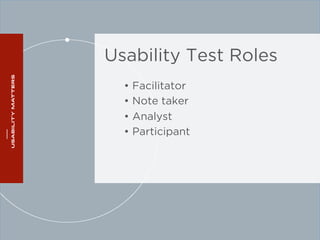
The document outlines a workshop on usability testing discussing key concepts such as user experience, the importance of usability, and methods for evaluating it. It also details the steps involved in conducting usability tests, including recruiting participants, defining research objectives, and analyzing results. The workshop emphasizes the necessity of accessibility in usability and provides a structured approach to facilitating and reporting on usability tests.