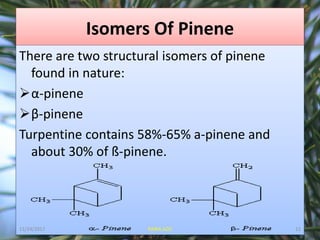
Pinene (C10H16) is a colorless, volatile bicyclic monoterpene found in essential oils from pine trees and various other plants. It has applications as a solvent, in resin manufacturing, and possesses health benefits such as anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator effects. The two isomers, α-pinene and β-pinene, are derived from geranyl pyrophosphate through specific cyclization processes.