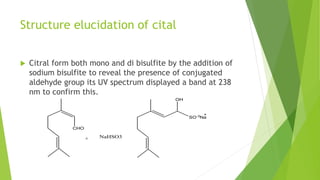
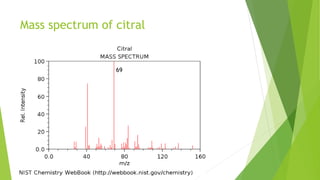
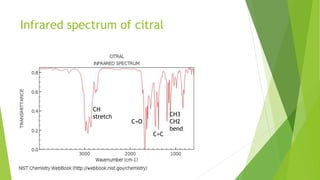
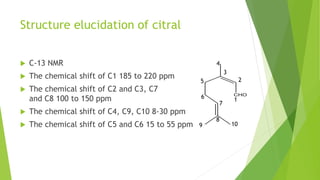
Citral is a mixture of terpenoid isomers found in plants like lemon grass, lemon myrtle, and lemon balm. It has a lemon odor and consists of two isomers, geranial and neral. Citral can be isolated from lemon grass oil via steam distillation. It undergoes reactions like reduction, aldol condensation, and rearrangements. Its structure was elucidated using techniques like NMR, mass spectrometry, and IR spectroscopy. Citral has applications as a flavoring and fragrance in perfumes due to its citrus smell.