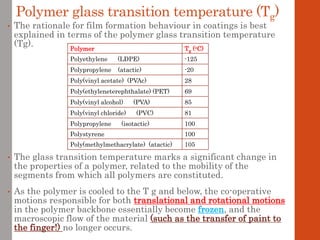
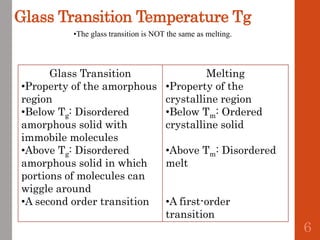
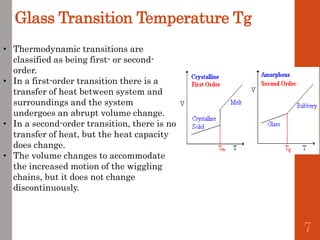
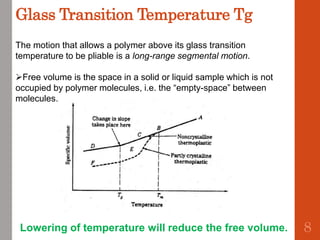
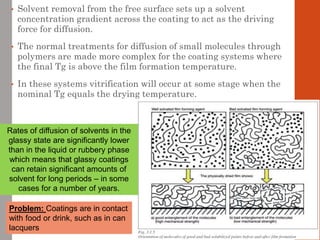
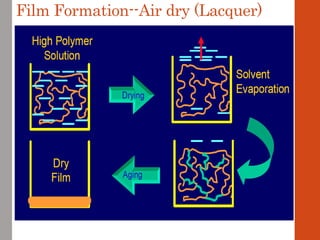
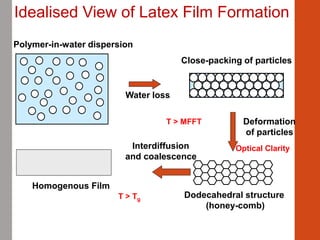
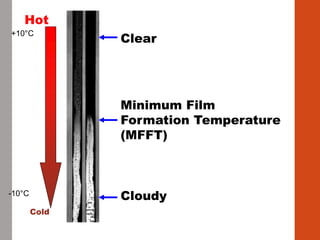
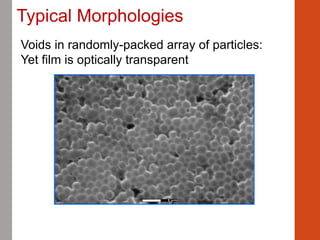
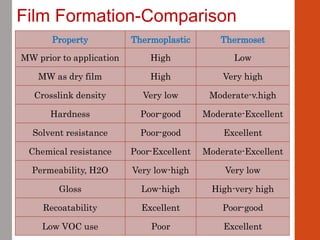
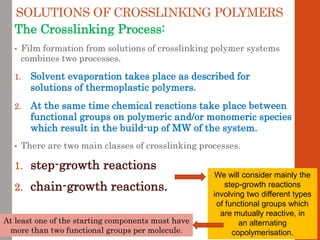
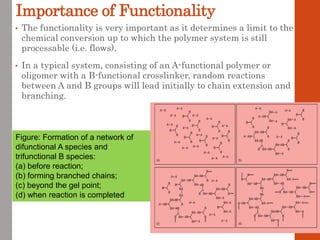
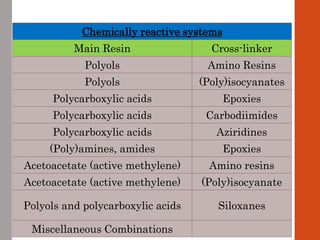
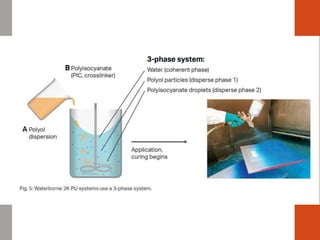
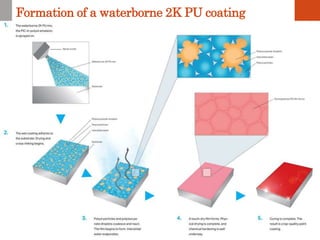
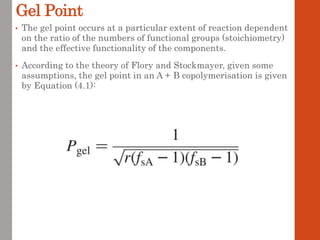
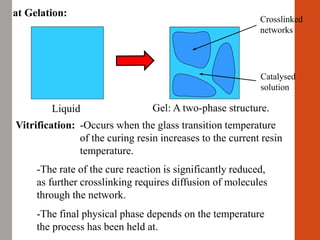
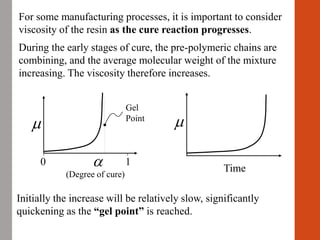
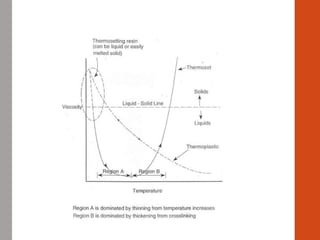
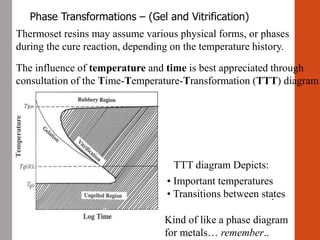
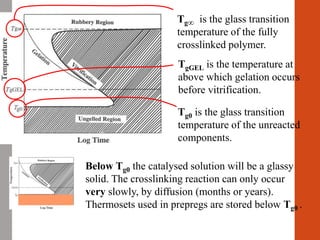
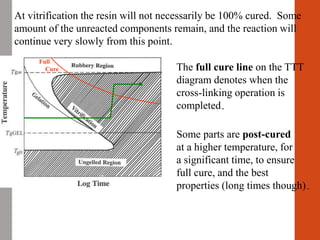
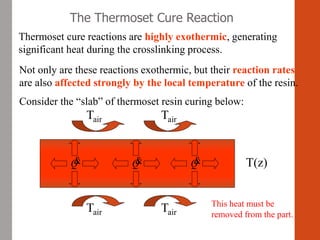
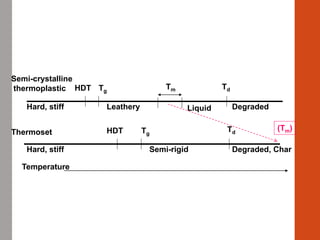
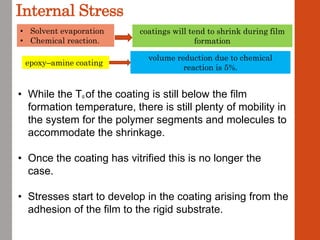
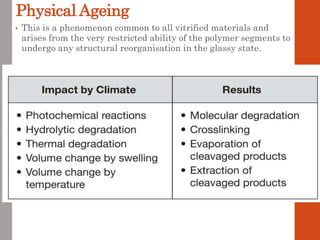
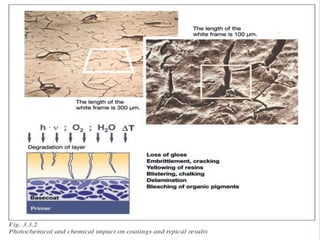
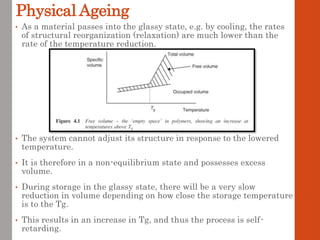
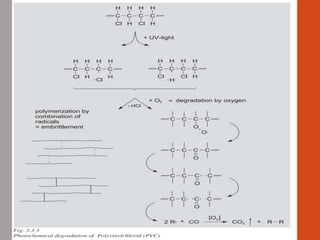
1. Film formation is the process by which a liquid coating is converted into a solid film after application. There are two main mechanisms for this - solvent evaporation and chemical crosslinking reactions.
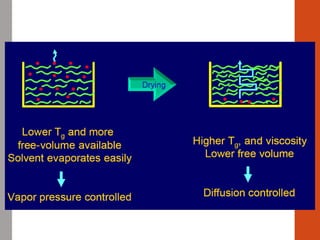
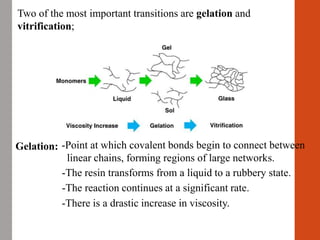
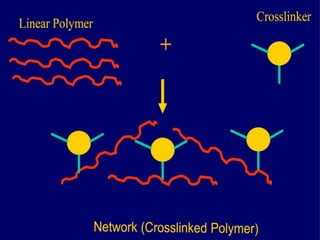
2. For thermoplastic coatings, film formation occurs as the solvent evaporates, causing an increase in the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the coating to match or exceed the ambient temperature. For crosslinking coatings, particles soften and coalesce during heating, then chemical reactions cause molecular weight and viscosity to increase until the surface sets.
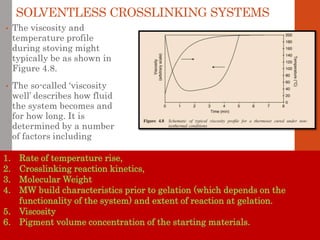
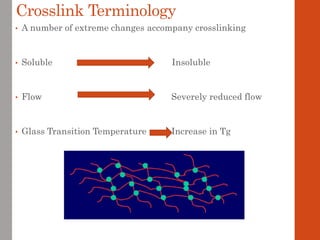
3. Both types of coatings aim to overcome issues like solvent retention, shrinkage stresses, and environmental pollution, though crosslinking systems are more thermally and chemically