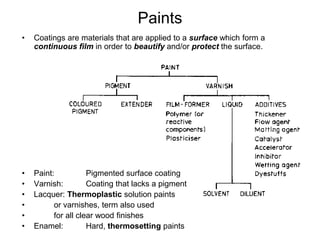
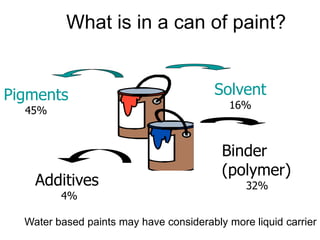
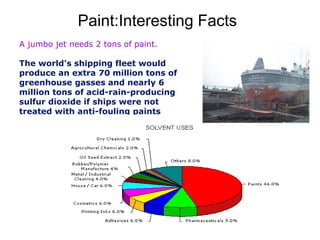
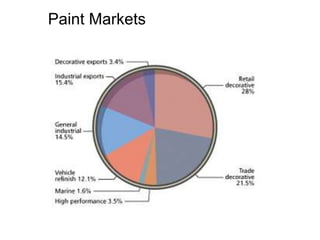
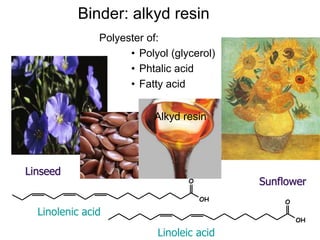
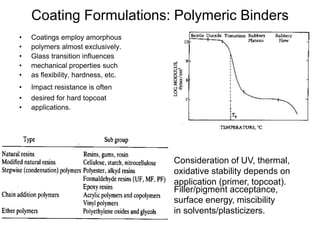
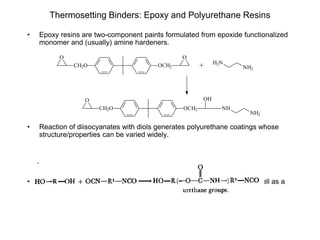
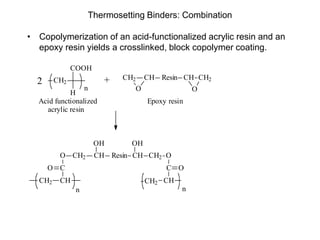
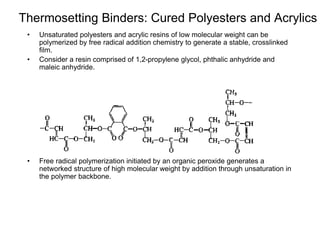
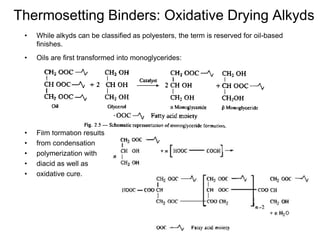
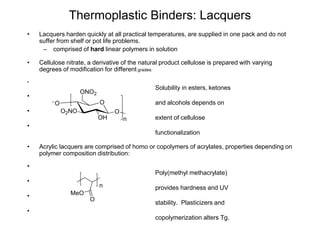
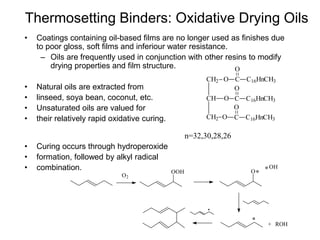
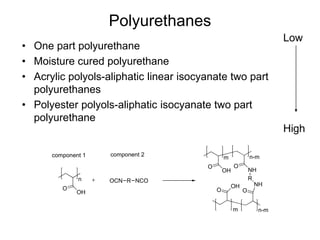
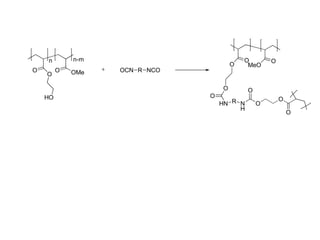
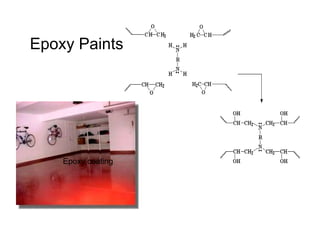
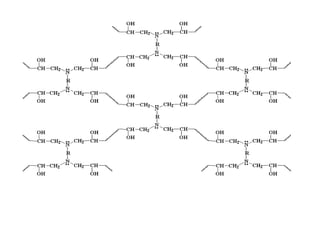
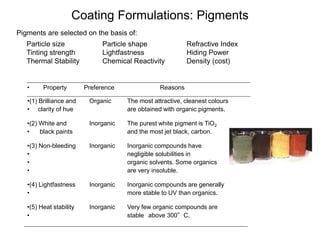
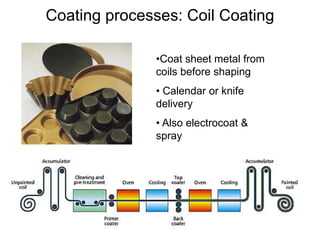
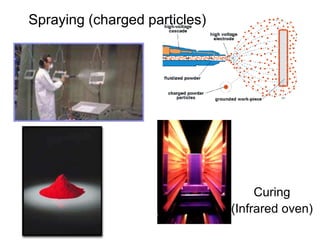
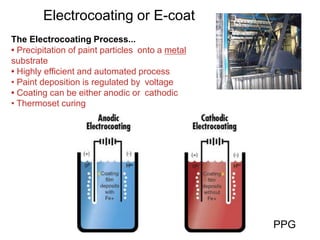
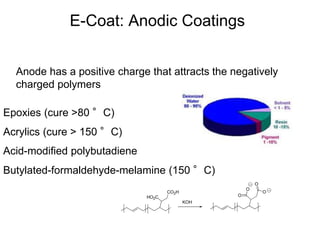
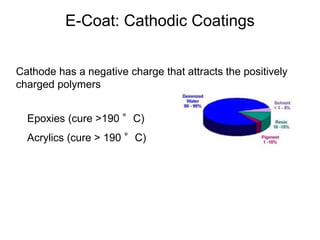
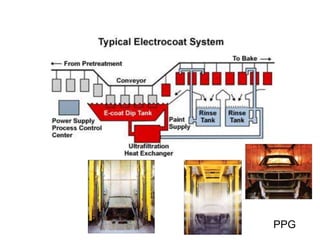
The document provides an overview of paints and coatings, detailing their composition, types, applications, and market segments. It explains the differences between paints and stains, the role of binders, pigments, additives, resins, and solvents in paint formulation, and the various methods of applying coatings. Additionally, it discusses the market dynamics, including the architectural, OEM/product, and specialty segments of the anti-corrosive epoxy coatings market.