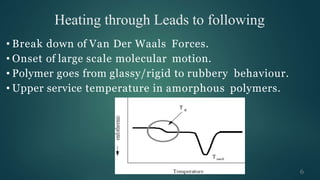
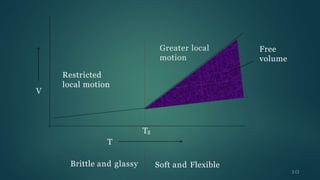
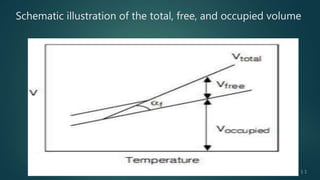
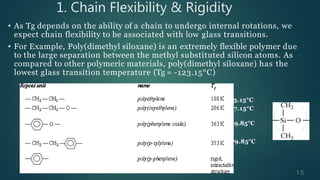
The document presents an overview of glass transition temperature (Tg) in polymers, detailing the transition between glassy and rubbery states and the implications for various polymers. It discusses the free volume theory which relates Tg to the molecular motion dependent on the availability of unoccupied volume, as well as factors affecting Tg, including chain flexibility, steric effects, intermolecular forces, copolymerization, cross-linking, and the use of plasticizers. Overall, the understanding of Tg is key for determining the appropriate applications of different polymers based on their thermal behavior.











![2. Steric Effects
17• The presence of bulky side groups hinders rotation of the
backbone atoms due to steric hindrance, and therefore results in
an increase in Tg. The magnitude of this effect depends on the
size of the side groups.
• This is illustrated in the following Table for vinyl polymers
having the general structure,
—[CH2 — CHX ]—
-93.15°C
-20.15°C
99.85°C
134.85°C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glasstransitiontemperature-200817065744/85/Glass-transition-temperature-16-320.jpg)
![3. Effect of Intermolecular Forces
18
• The presence of polar side groups leads to strong intermolecular
attractive interactions between chains which hinders molecular
motion thus causing an increase in Glass transition
temperature.
• This effect is illustrated in the following table for the polymers of
type −[CH2−CHX ]−
-20.15°C
80.85°C
84.85°C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glasstransitiontemperature-200817065744/85/Glass-transition-temperature-17-320.jpg)



