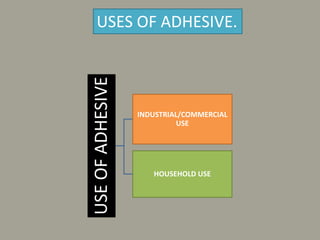
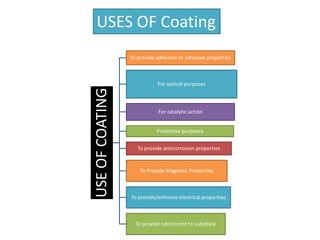
The document discusses adhesives and coatings, defining adhesives as substances that bind materials together and coatings as protective or decorative coverings for surfaces. It details various applications of adhesives in industrial, commercial, and household contexts, as well as the numerous purposes of coatings, ranging from protective to decorative functions. Specific examples include the use of polyurethane adhesives in the automotive industry and diverse coating types for optical, protective, and functional enhancements.