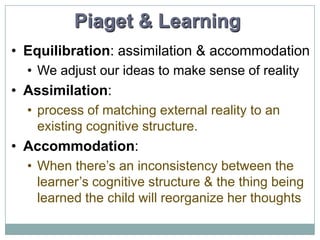
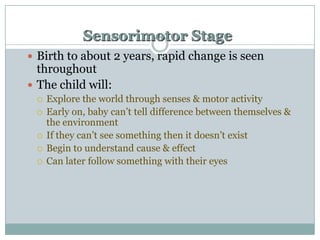
Piaget was a Swiss psychologist who developed one of the most influential theories of cognitive development. He believed that children construct an understanding of the world through active learning rather than passive absorption of information. Piaget identified four main stages of cognitive development - sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational - which he believed all children progress through in the same sequence as they interact with their environment. Piaget's theory emphasizes that cognitive development must occur through these stages and cannot be hurried by education.