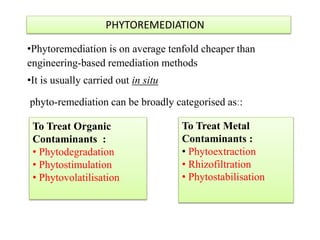
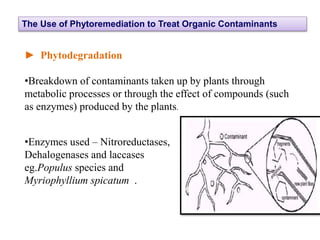
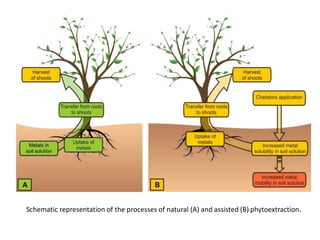
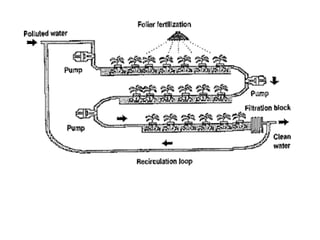
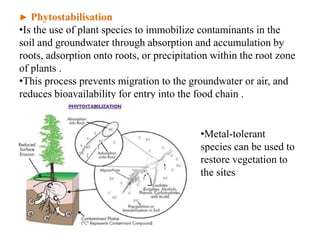
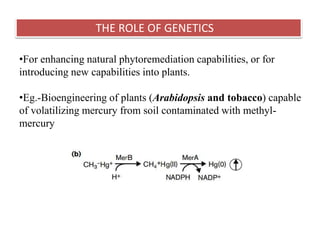
Phytoremediation is an eco-friendly method that utilizes plants to remediate contaminated soils, sediments, and water, offering a significantly cheaper alternative to traditional remediation techniques. It includes processes for treating both organic and metal contaminants, such as phytodegradation, phytoextraction, and phytostabilisation, which enhance the natural capabilities of plants for contaminant uptake and degradation. Despite its advantages, phytoremediation is slow and reliant on plant tolerance to pollutants, requiring large land areas and being affected by climatic variations.