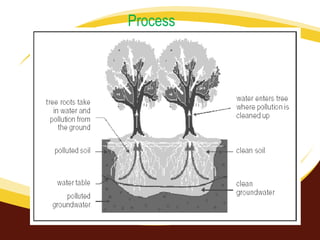
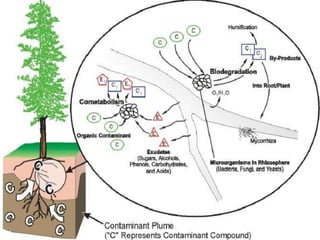
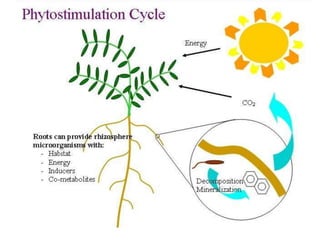
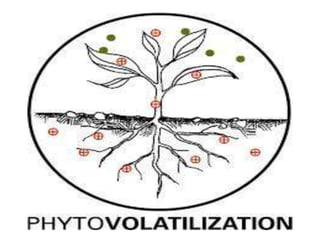
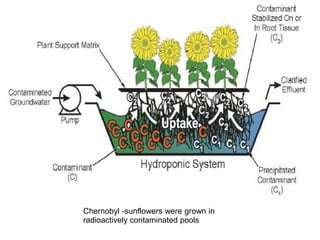
The document discusses the process of phytoremediation, which uses plants to remove pollutants from soil, sediment, surface water and groundwater. It describes various phytoremediation processes like phytoextraction, phytostabilization, and rhizofiltration. The document also covers the advantages of using phytoremediation compared to conventional remediation methods, as well as some limitations and challenges.