This document outlines Jun Zhu's Ph.D. dissertation on physical layer security in massive MIMO systems. The dissertation examines how to improve security in massive MIMO systems using artificial noise (AN). It analyzes the impact of pilot contamination on AN design and explores AN techniques under various precoding schemes and with hardware impairments. The dissertation addresses challenges in securing massive MIMO, including the complexity of null-space based AN and the effects of pilot contamination and hardware impairments on AN and wireless security.


![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
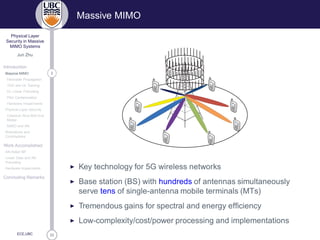
Massive MIMO
3Favorable Propagation
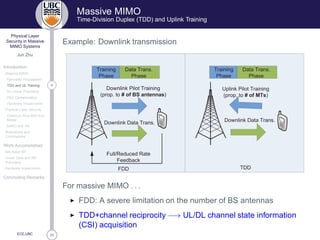
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
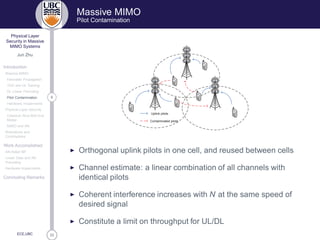
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
◮ Given channel matrix G = [gH
1 , . . . , gH
K ]H
∈ CK×N
1
N
gk gH
j → 0,
1
N
gk gH
k → 1 (N → ∞, K/N → 0)
◮ Favorable propagation: (channel hardening)
C = log2 IK +γGGH
≤
K
k=1
log2 1 + γ gk
2
= K log2(1 + γN).
◮ Simple processing, e.g., maximum ratio transmission/combining
(MRT/MRC) achieves optimal throughput](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-4-320.jpg)

![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
8Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve Model
Typical Scenario:
Alice
Bob
EveAlice-Bob-Eve Model
Multi-User Multi-Antenna Network
(Employing AN)
BSEve
MT Data
AN
CBob
CEve
Information Theory:
◮ Assume the channel between Alice and Bob is “better” than the
channel between Alice and Eve.
→ There are codes which allow Bob to decode error free while
Eve cannot extract any information about Alice’s message.
◮ Secrecy capacity:
C×
= [C Ó − C Ú ]+
Key question: How can we guarantee Bob’s channel is better
than Eve’s?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-9-320.jpg)
![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
9MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
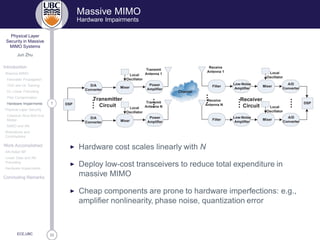
Physical Layer Security
Multi-User MIMO and AN
Enhancing Bob’s channel/Degrading Eve’s channel
◮ The key is to have more degrees of freedom at Alice/Bob than at
Eve (multi-antenna at Alice)
◮ Alice knows Bob’s CSI but not Eve’s −→ Artificial Noise (invisible
to Bob)
Lower Bound on Achievable Secrecy Rate for MISOME Channel
◮ Multi-Input Single-Output Multi-Eavesdropper (MISOME)
R×
≥ R×
= [R Ó − C Ú ]+
◮ Ergodic Secrecy Rate=Eh[R×
] (span over many independent
channel realizations):
◮ Secrecy Outage Probability=Pr(R×
≤ R0) (span only one
channel realization):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-10-320.jpg)



![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
13AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
Chapter 2
AN-Aided MF Precoding in
Secure Massive MIMO Systems
◮ Introduce AN-aided massive MIMO transmission
◮ Derive a tight analytical lower bound for achievable secrecy rate
and upper bound for secrecy outage probability for AN-aided MF
[J1]: J. Zhu, R. Schober, and V. K. Bhargava, “Secure transmission in multicell massive
MIMO systems,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 13, no. 9, pp. 4766-4781, Sept.
2014.
[C1]: J. Zhu, R. Schober, and V. K. Bhargava, “Secure transmission in multi-cell massive
MIMO systems,” in Proc. IEEE Globecom 2013, Atlanta, GA, Dec. 2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-14-320.jpg)

![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
15AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
AN-Aided MF
System Design
Options for Tx Data Precoding Matrix Fn
◮ MF: fnk = (ˆhk
nn)H
/ ˆhk
nn
◮ SZF/SRCI/CZF/CRCI
◮ POLY
Options for Tx AN Precoding Matrix An
◮ NS: ˆHnnAn = 0K×L
◮ Random: vni = ˜vni / ˜vni , ˜vni ∈ CN(0NT
, 1NT
)
◮ POLY
Power Allocation
◮ Define power allocation factor φ ∈ (0, 1] with
p =
φP
K
q =
(1 − φ)P
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-16-320.jpg)
![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
16AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
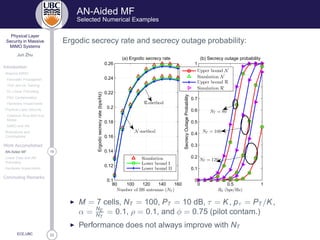
AN-Aided MF
Performance Evaluation
Achievable Ergodic Secrecy Rate
R×
nk = [Rnk − C Ú
nk ]+
with
◮ Rnk : Achievable ergodic rate of MT k in cell n
◮ C Ú
nk : Ergodic capacity of Eve with respect to message of MT k in
cell n
Tight Lower Bound on Achievable Ergodic Rate of MT k in cell n
Rnk ≥ Rnk = log2(1 + γnk )
where γnk =
desired signal
|E[
√
pgk
nnfnk ]|2
Ú Ö[
√
pgk
nnfnk ]
signal leakage
+
M
m=1
L
i=1
E[|
√
qgk
mnami |2
]
AN leakage
+
{m,l}={n,k}
E[|
√
pgk
mnfml |2
]
intra- and inter-cell interference
+ σ2
nk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-17-320.jpg)
![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
17AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
AN-Aided MF
Performance Evaluation
Achievable Ergodic Secrecy Rate
R×
nk = [Rnk − C Ú
nk ]+
with
◮ Rnk : Achievable ergodic rate of MT k in cell n
◮ C Ú
nk : Ergodic capacity of Eve with respect to message of MT k in
cell n
Ergodic Capacity of Eve
C Ú
nk = E log2
1 + pfH
nk GH
nE q
M
m=1
AH
mGH
mE GmE Am
−1
GnE fnk
We make the following pessimistic assumptions
◮ Eve can decode and cancel all other MTs successfully
◮ Eve has perfect CSI of all BS-Eve channels
◮ AWGN at Eve is negligible](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-18-320.jpg)

![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
21Linear Data and AN
Precoding
Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
Chapter 3
Linear Data and AN Precoding in
Secure Massive MIMO Systems
◮ Derive a tight analytical lower bound for achievable secrecy rate
for different types of linear data and AN precoders
◮ Propose low-complexity POLY data and AN precoders
[J2]: J. Zhu, R. Schober, and V. K. Bhargava, “Linear precoding of data and artificial noise
in secure massive MIMO systems,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 15, no. 3, pp.
2245-2261, Mar. 2016.
[C2]: J. Zhu, R. Schober, and V. K. Bhargava, “Secure downlink transmission in massive
MIMO system with zero-forcing precoding,” in Proc. IEEE EW 2014, Barcelona, Spain,
May 2014. (Invited Paper)
[C3]: J. Zhu, R. Schober, and V. K. Bhargava, “Secrecy analysis of multi-cell massive MIMO
systems with RCI precoding and artificial noise transmission,” in Proc. IEEE ISCCSP
2014, Athens, Greece, May 2014. (Invited Paper)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-22-320.jpg)



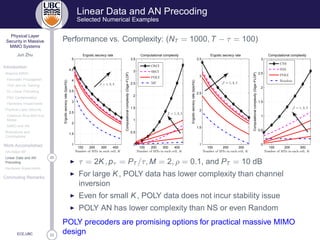
![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
26Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
Chapter 4
Hardware Impairments in Secure
Massive MIMO Systems
◮ Introduce hardware impaired secure massive MIMO
◮ Derive a tight analytical lower bound for achievable secrecy rate
for generalized hardware impairment model for AN-aided MF with
general uplink pilots and downlink AN
[J3]: J. Zhu, D. W. K. Ng, N. Wang, R. Schober, and V. K. Bhargava, “Analysis and design of
secure massive MIMO systems in the presence of hardware impairments,” submitted
to possible journal, Feb. 2016.
[C4]: J. Zhu, R. Schober, and V. K. Bhargava, “Physical layer security for massive MIMO
systems impaired by phase noise,” submitted to possible conference, Feb. 2016.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-27-320.jpg)

![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
28Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
Hardware Impairments
Performance Evaluation
Achievable Ergodic Secrecy Rate
R×
k =
1
T
t∈{B+1,...,T}
[Rk (t) − CE (t)]+
with
◮ Rk (t): Achievable ergodic rate of MT k at time t
◮ CE (t): Ergodic capacity of Eve w.r.t. message of MT k at time t
Tight Lower Bound on Achievable Ergodic Rate of MT k
Rk (t) ≥ Rk (t) = log2(1 + γk (t))
where γk (t) =
p E gH
k
ΘH
k
(t)fk
2
K
l=1
pE gH
k
ΘH
k
(t)fl
2
− p E gH
k
ΘH
k
(t)fk
2
+ E gH
k
ΘH
k
(t)(qAAH + Υ Ët
)ΘH
k
(t)gk + E υÅÌk,r
(t) + ξ Ä](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-29-320.jpg)
![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
29Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
Hardware Impairments
Performance Evaluation
Achievable Ergodic Secrecy Rate
R×
k =
1
T
t∈{B+1,...,T}
[Rk (t) − CE (t)]+
with
◮ Rk (t): Achievable ergodic rate of MT k at time t
◮ CE (t): Ergodic capacity of Eve w.r.t. message of MT k at time t
Ergodic Capacity of Eve
CE = E[log2(1 + pfk GE GH
E (qAAH
+ Υ Ë
t )GE
−1
(fk GE )H
)]
We make the following pessimistic assumptions
◮ Besides, Eve can completely remove the phase noise, and the
only remaining hardware impairment is additive distortion noise
at BS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-30-320.jpg)
![33
Physical Layer
Security in Massive
MIMO Systems
Jun Zhu
Introduction
Massive MIMO
Favorable Propagation
TDD and UL Training
DL Linear Precoding
Pilot Contamination
Hardware Impairments
Physical Layer Security
Classical Alice-Bob-Eve
Model
MIMO and AN
Motivations and
Contributions
Work Accomplished
AN-Aided MF
Linear Data and AN
Precoding
30Hardware Impairments
Concluding Remarks
ECE,UBC
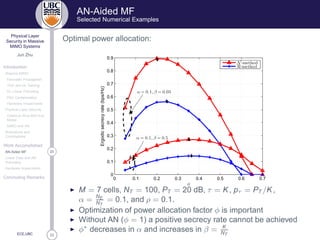
Hardware Impairments
Performance Evaluation
Lower Bound on Achievable Ergodic Secrecy Rate
R×
k ≥ R×
k =
1
T
t∈{B+1,...,T}
[Rk (t) − CE ]+
Lower Bound on Achievable Rate
Rk (t) = log2
1 +
λk e−(σ2
φ+σ2
ψ)|t−B|
φN
(ak + ck − βµk )φ + βµk + β(κÅÌr + κ Ë
t + ξ Ä/βk /PT )
◮ λk ∈ (0, 1)-desired signal
◮ ak -interference, scales with N, ck -signal leakage
◮ µk -AN leakage under Generalized-NS (G-NS) AN with Mo
◮ Mo = No −→ phase noise removed (L = N/No − K)
◮ Mo = 1 −→ reduce to NS (L = N − K)
Upper Bound on Eve’s Capacity
CE ≤ CE = log2 1 +
pNE
qL + κ Ë
t PT − χNE
q=0
−→ log2 1 +
α
κ Ë
t (β − α)
where χ depends on κ Ë
t , p, q, K, L.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/af72bfb2-f4e5-40dc-a1ba-0a7087548b6e-160317220517/85/PhySec_MassiveMIMO-31-320.jpg)