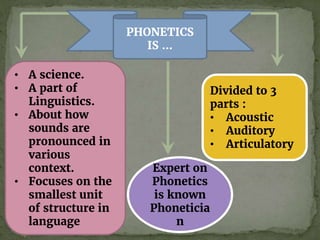
This document provides an overview of phonetics, which is the study of speech sounds and their production, perception, and physiology. It discusses phonetics as a science that focuses on the smallest units of language. The document then describes the three main branches of phonetics: acoustic (sound waves), auditory (perception), and articulatory (production). It goes on to explain places and manners of articulation, identifying different speech sounds based on where and how they are produced in the vocal tract. Various speech sounds are defined using phonetic symbols. In closing, the document provides references for further reading on linguistics and phonetics.





![Places of articulation are the places where
speech sounds are produced. They are :
Bilabial is a speech sound made by both upper and lower lip.
These speech sounds are represented by the symbol [p], [b],
[m].
Examples : Pie, buy, my
Labiodentals is a speech sound formed with upper teeth and
lower lip. The speech sound can be presented by the symbol
[f] and [v].
Examples : fan, van
Note : paragraph, cough, photo [f]
Dental is a s speech sound produced with tongue against the
upper front teeth. The speech sound can be presented by the
symbol [θ] and [ð].
Examples : [θ] : teeth, three, Thursday [ð]: the, there,
then](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phoneticsisunique-160326074013/85/PHONETICS-IS-UNIQUE-7-320.jpg)
![Alveolar is a speech sound formed with the tongue touching
behind upper front teeth. The speech sound can be
represented by the symbol [t], [d], [n], [s], [z].
Examples : tie, die, nut, see, zoo
Palatal is a speech sound produced with the tongue and the
palate. The speech sound can be represented by the symbol [ʃ]
“sh” and [tʃ] “ch”.
Examples : [ʃ] : brush, wash, wish [tʃ]: church,
chicken, teacher
Velar is a speech sound produced with back of the tongue
against the velum (soft palate). The speech sound can be
represented by the symbol [k] and [g].
Examples : [k] : kid, kill, kick, car [g] : bag, good,
goose, glass
Glottal is a speech sound produced without the active use of
the tongue and other parts of the mouth. This speech sound
can be represented by the symbol [h].
Examples : have, has, house, whom, whose, who.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phoneticsisunique-160326074013/85/PHONETICS-IS-UNIQUE-8-320.jpg)
![Manner of Articulation (how to produce sounds)
•Stop is the sound produced by some from of stopping the air
stream then releasing it suddenly. These sound can be
represented by the symbol [p], [b], [t], [d], [k], [g].
•Fricative is the sounds made by blocking the air stream and
having the air push through the very narrow opening. These
sounds can be represented by the symbols [f], [v], [], [ð], [s],
[z], [ʃ], [ʒ].
•Affricate is the sounds made by stopping the air stream then
followed immediately by fricative. In the other word, it’s
combination of “stop” and “fricative”. These sounds can be
represented by the symbol “[tʃ] as (ch)” and “[ʤ] as (j)”.
•Nasal is the sounds produced by sending the stream ir of air
through the nose. These sounds can be represented by the
symbol [m], [n], [ŋ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phoneticsisunique-160326074013/85/PHONETICS-IS-UNIQUE-9-320.jpg)
![•Liquid is the sounds produced when the tongue touches the
middle part of the alveolar ridge. These sounds can be
symbolized with [l] and [r]. when you pronounce the symbol
[r], your tongue tip will raise and curl back near the
alveolar ridge.
•Glide is the sounds by moving the tongue from one position
to another. These sounds are symbolized with [w] and [j].
•Glottal stop is the sound produced by closing the opening
the glottis (vocal cord). This sound is symbolized with [Ɂ].
You can produce the glottal stop if you try to say the word
“butter” and “bottle” without pronouncing the “-tt-ˮ part
in the middle.
•Flaps is the sound is produced by the tongue tip tapping the
alveolar ridge briefly. When you pronounce the word
“letter” that is close to “ladder”, it’s mean you are making
a flap.
Note: it should be better, if the reader also find and understand
International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phoneticsisunique-160326074013/85/PHONETICS-IS-UNIQUE-10-320.jpg)

