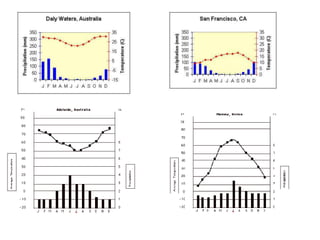
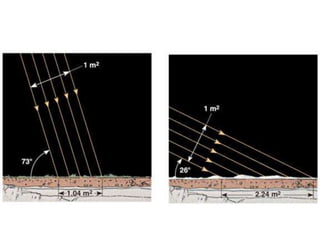
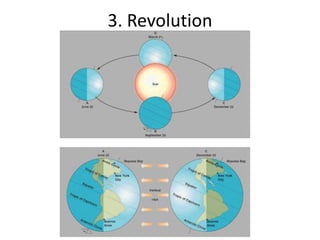
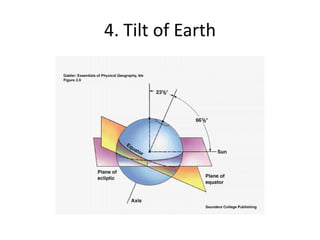
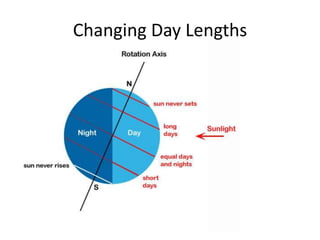
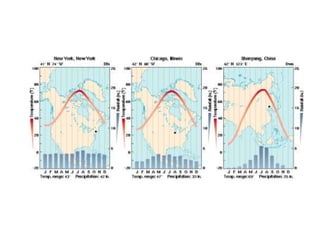
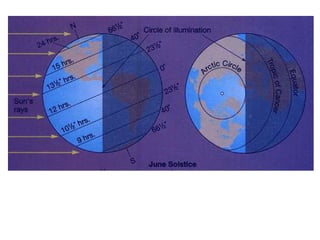
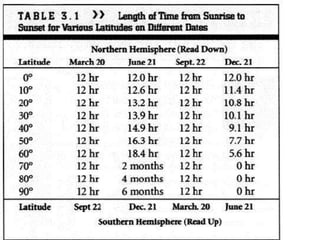
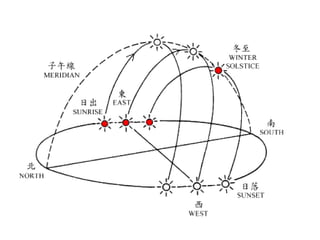
The document discusses the causes of Earth's seasons. It explains that the seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis of rotation relative to its orbit around the Sun, and not by variations in Earth's distance from the Sun. Specifically, as the Earth revolves around the Sun, its tilted axis stays pointed in the same direction, causing the Northern and Southern hemispheres to alternately face more and less directly towards the Sun, creating summer in one and winter in the other. The amount of direct sunlight and daylight hours varies by latitude and season due to this tilt, with more extreme seasonal variations at higher latitudes.