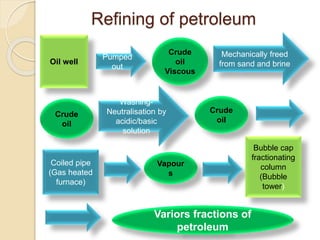
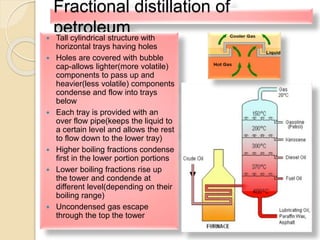
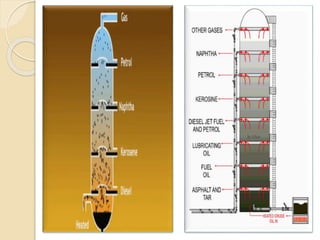
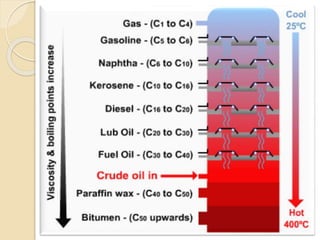
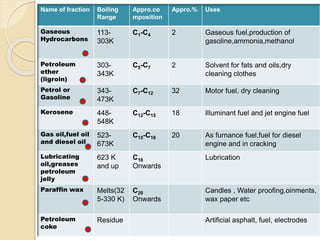
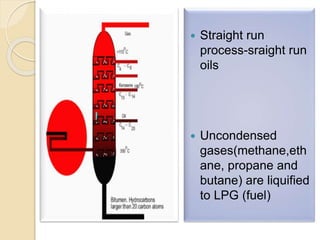
Petroleum is a dark colored, viscous liquid found below the earth's crust that is obtained through mining. It is a mixture of hydrocarbons that formed from the remains of ancient organisms over time under heat and pressure. Refining petroleum involves separating it into useful fractions through fractional distillation. This process involves heating crude oil in a tall distillation tower, which separates it into fractions with different boiling points like gasoline, kerosene, diesel and lubricating oil that are collected on different trays based on their volatility and used for various purposes. Straight run oils are also produced through this initial distillation process.