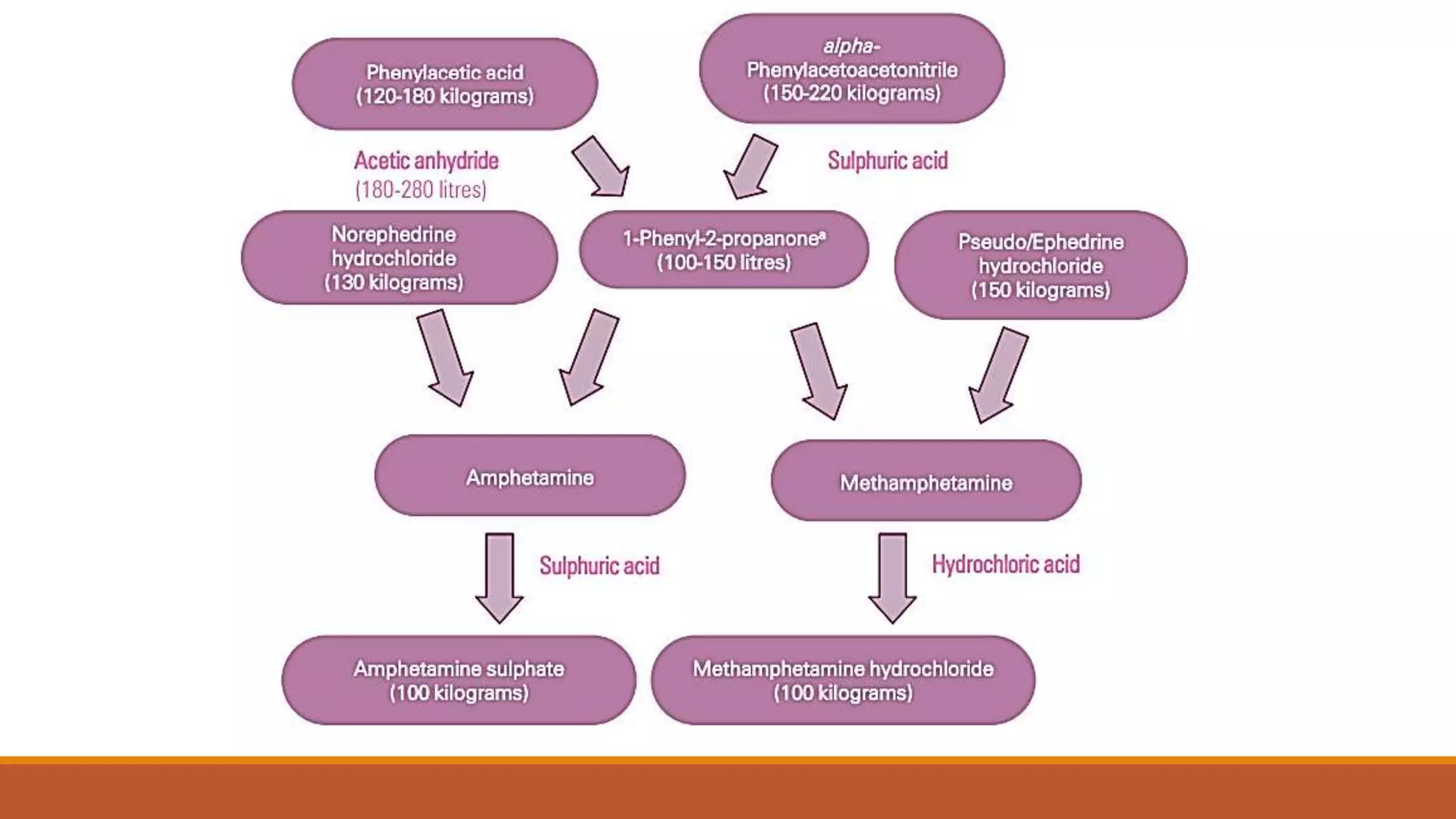
Precursor chemicals, also known as scheduled substances, are chemicals used in the illegal manufacture of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, while also having legitimate commercial uses. Legislation in Europe aims to prevent the diversion of these chemicals for illegal purposes, requiring monitoring of their trade and movement. There are 24 precursor chemicals categorized into four groups based on their risk and legitimate use, with specific regulatory requirements for each category.