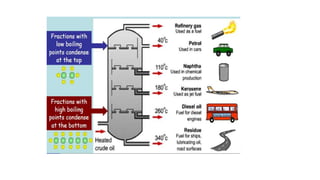
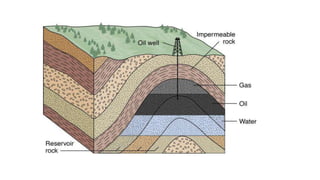
Crude oil, also known as black gold, is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons found in sedimentary rocks. It is believed to have formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals over millions of years. Crude oil is composed mainly of paraffin hydrocarbons, along with other components like naphthenes, aromatics, asphaltenes and various chemical elements. The four main categories of hydrocarbon types in crude oil are paraffins, olefins, naphthenes and aromatics, which have varying molecular structures and properties. Crude oil can also contain small amounts of sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen and heavy metal compounds.