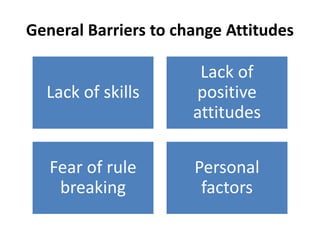
The document discusses individual values, ethics, and the impact of employee behavior on organizational credibility and relationships. It emphasizes the importance of moral principles in guiding actions and preventing unethical behavior while highlighting various personality traits and attitudes that influence work performance. Additionally, it outlines methods for fostering positive attitudes and the significance of effective training and realistic goal-setting for employees.