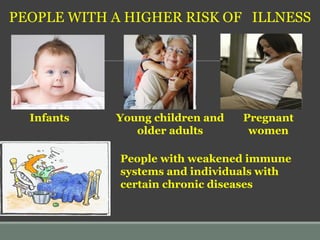
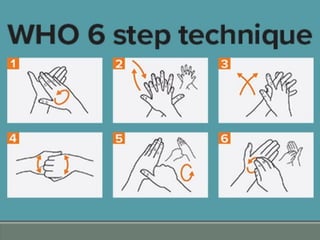
The document discusses the importance of personal hygiene. It defines hygiene as practices that help maintain health, including cleanliness and grooming. Proper hygiene includes regularly washing hands, bathing, cleaning teeth and nails, washing hair and clothes, and avoiding illness transmission. Key hygiene practices are washing hands thoroughly with soap and water, including under fingernails, before eating and after using the bathroom or touching animals. Maintaining hygiene helps prevent spread of disease.