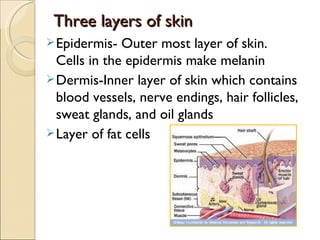
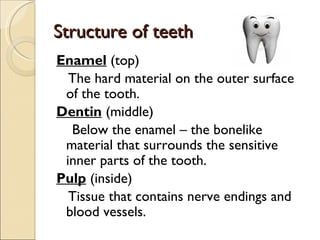
The document discusses personal hygiene and provides tips for maintaining hygiene in various areas of the body. It defines personal hygiene as maintaining cleanliness and grooming of the external body. It then covers hygiene practices for different body parts including hair, skin, teeth, ears, hands, nails, and feet. Key recommendations include regularly washing, brushing, and drying these areas to prevent issues like odor, acne, dental problems, and infections.