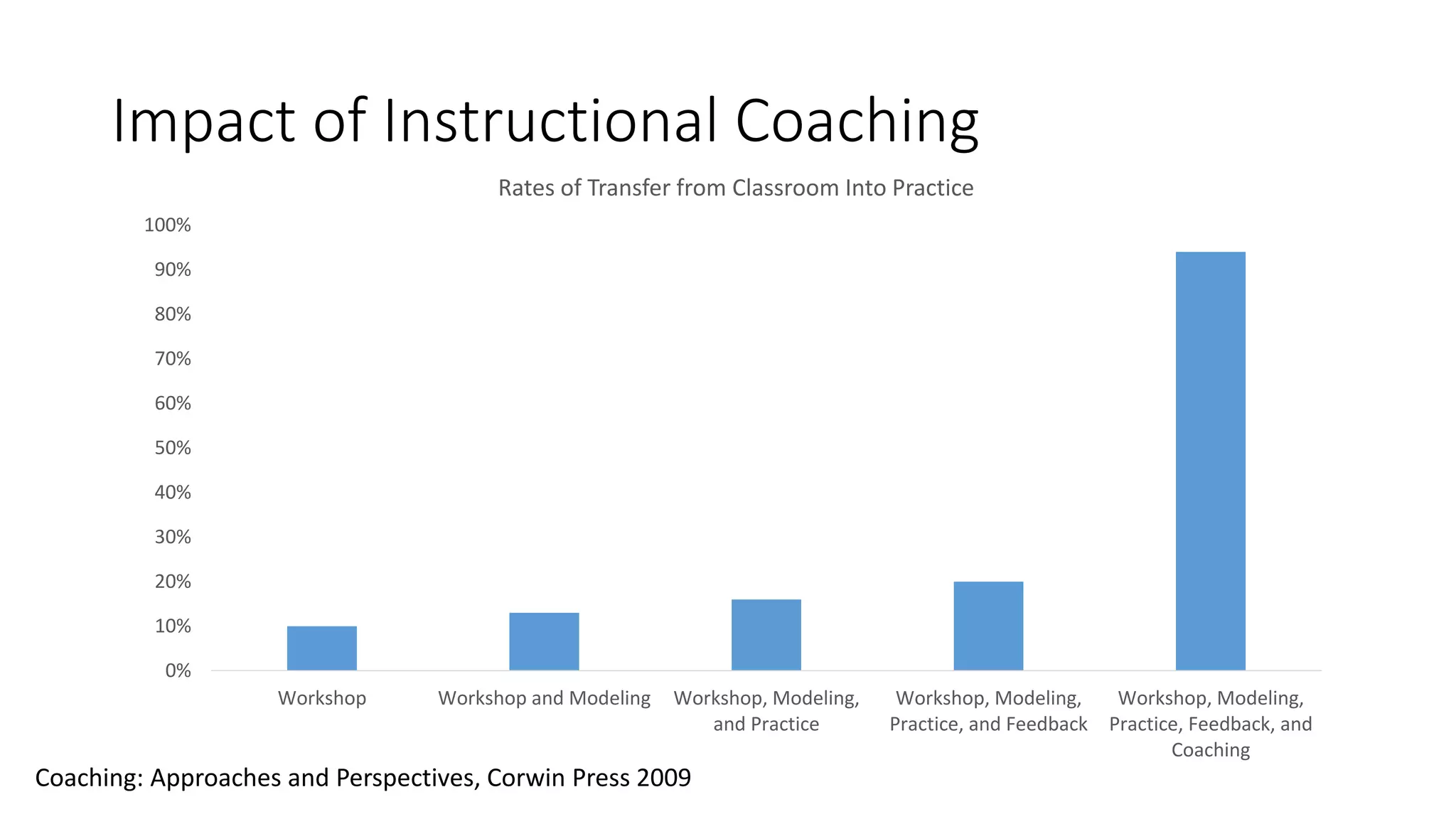
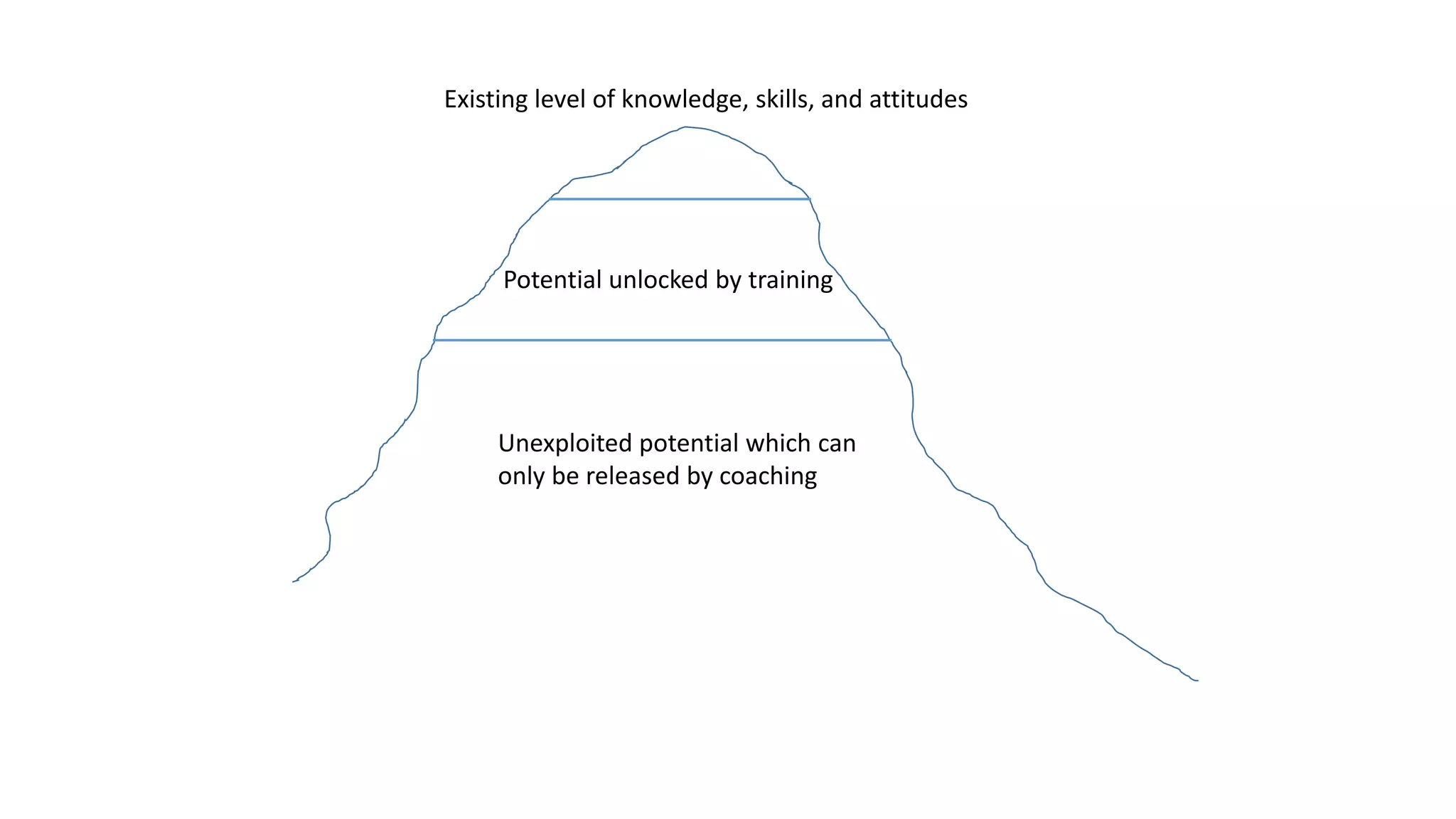
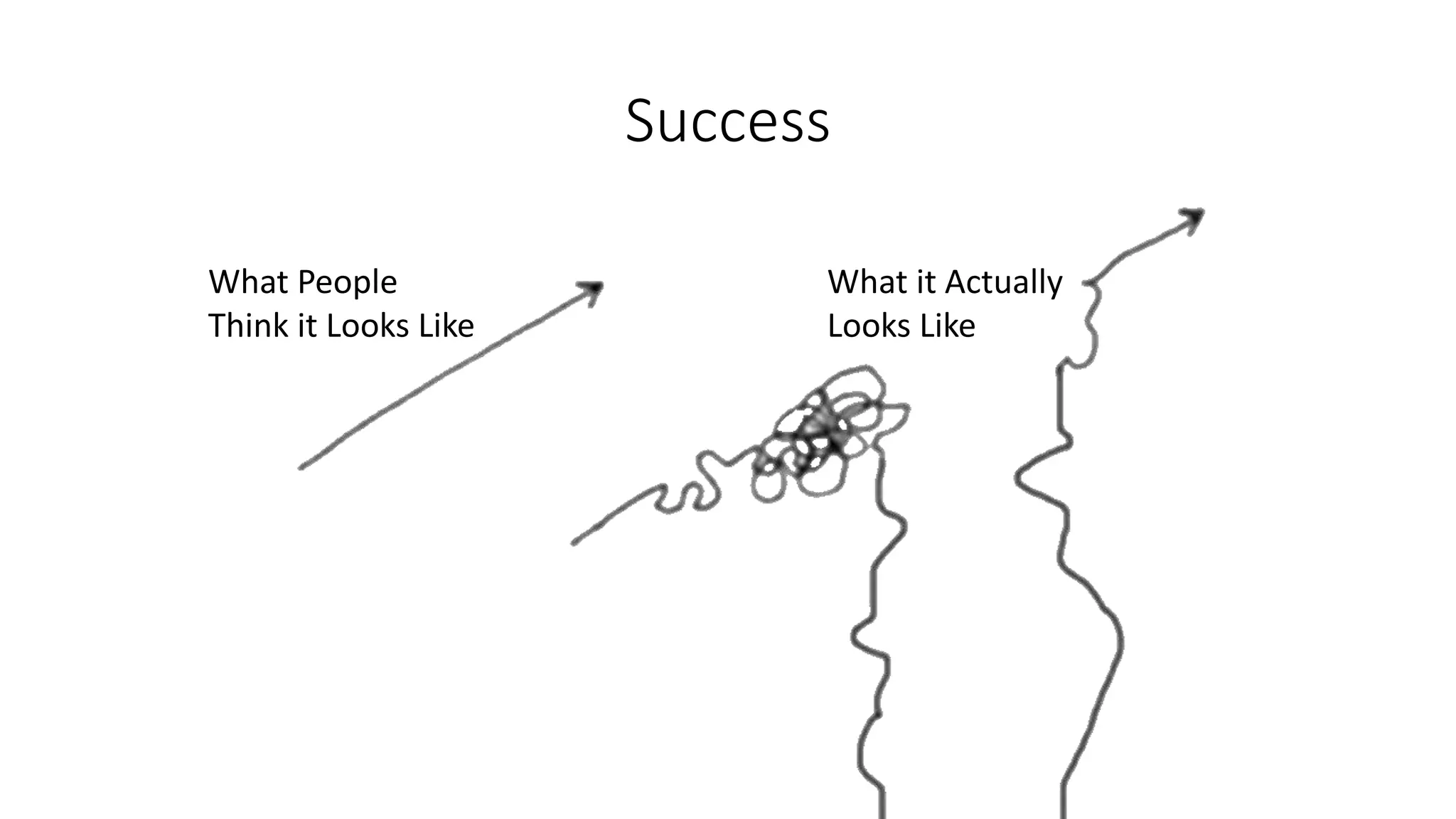
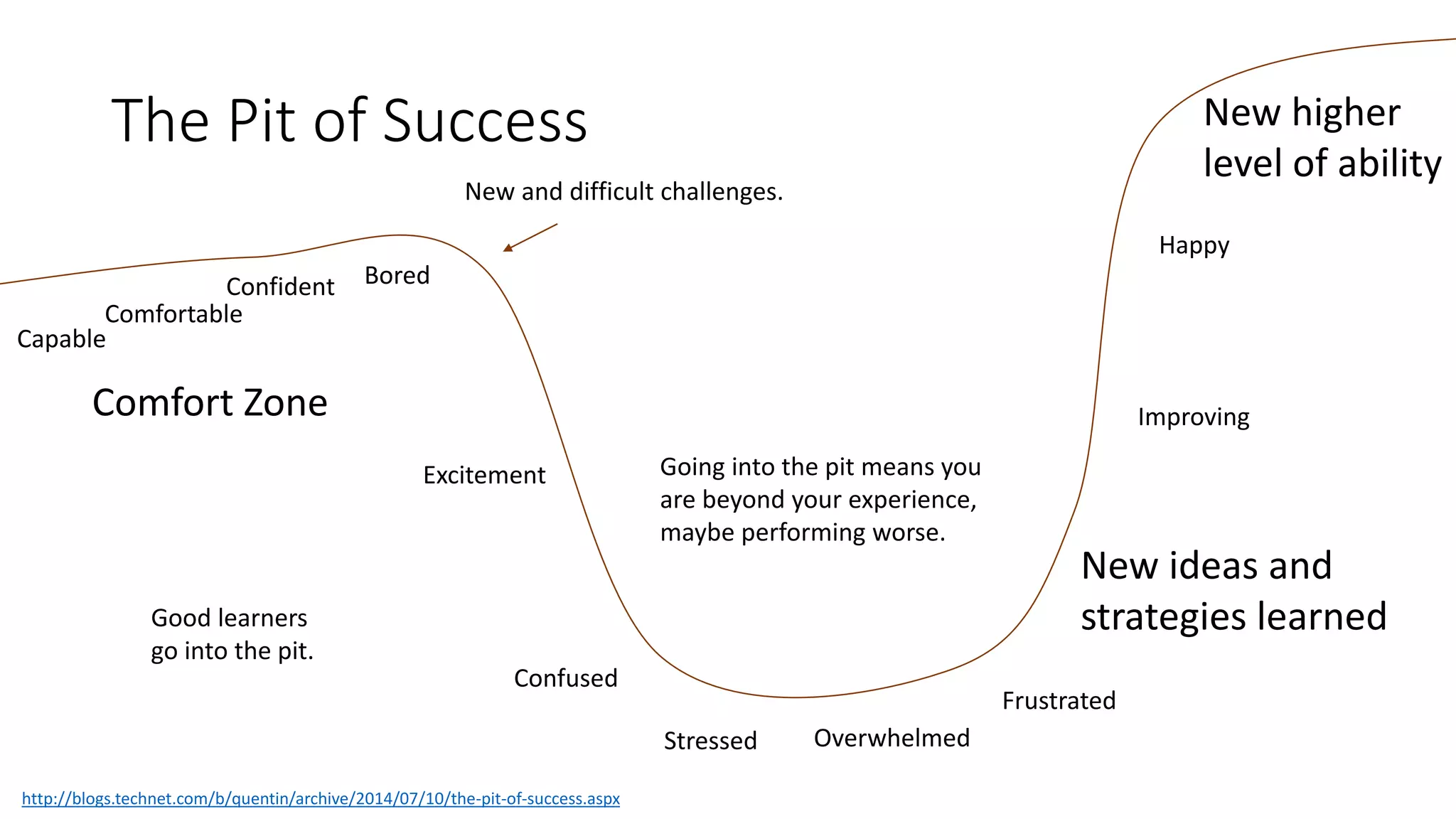
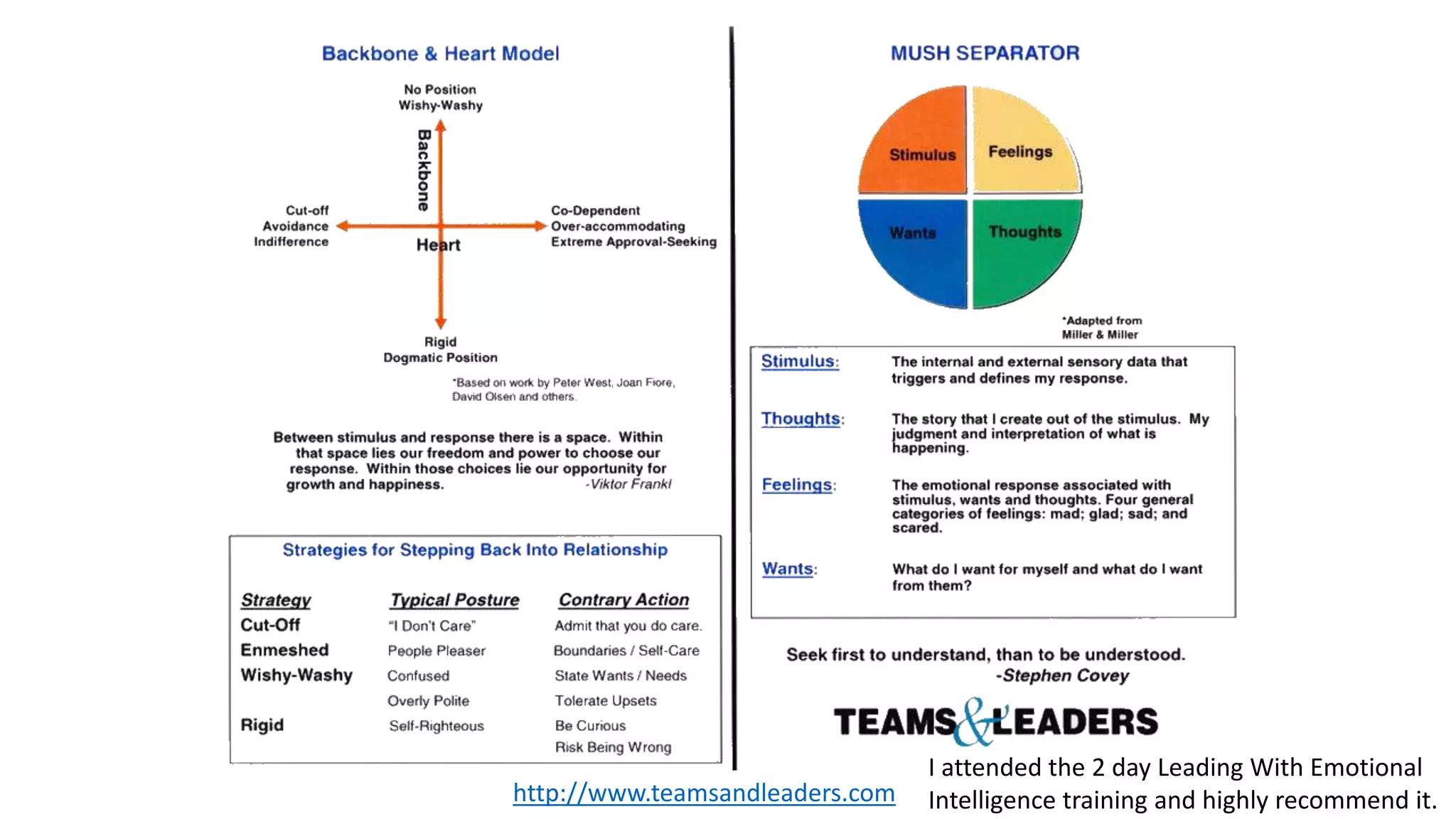
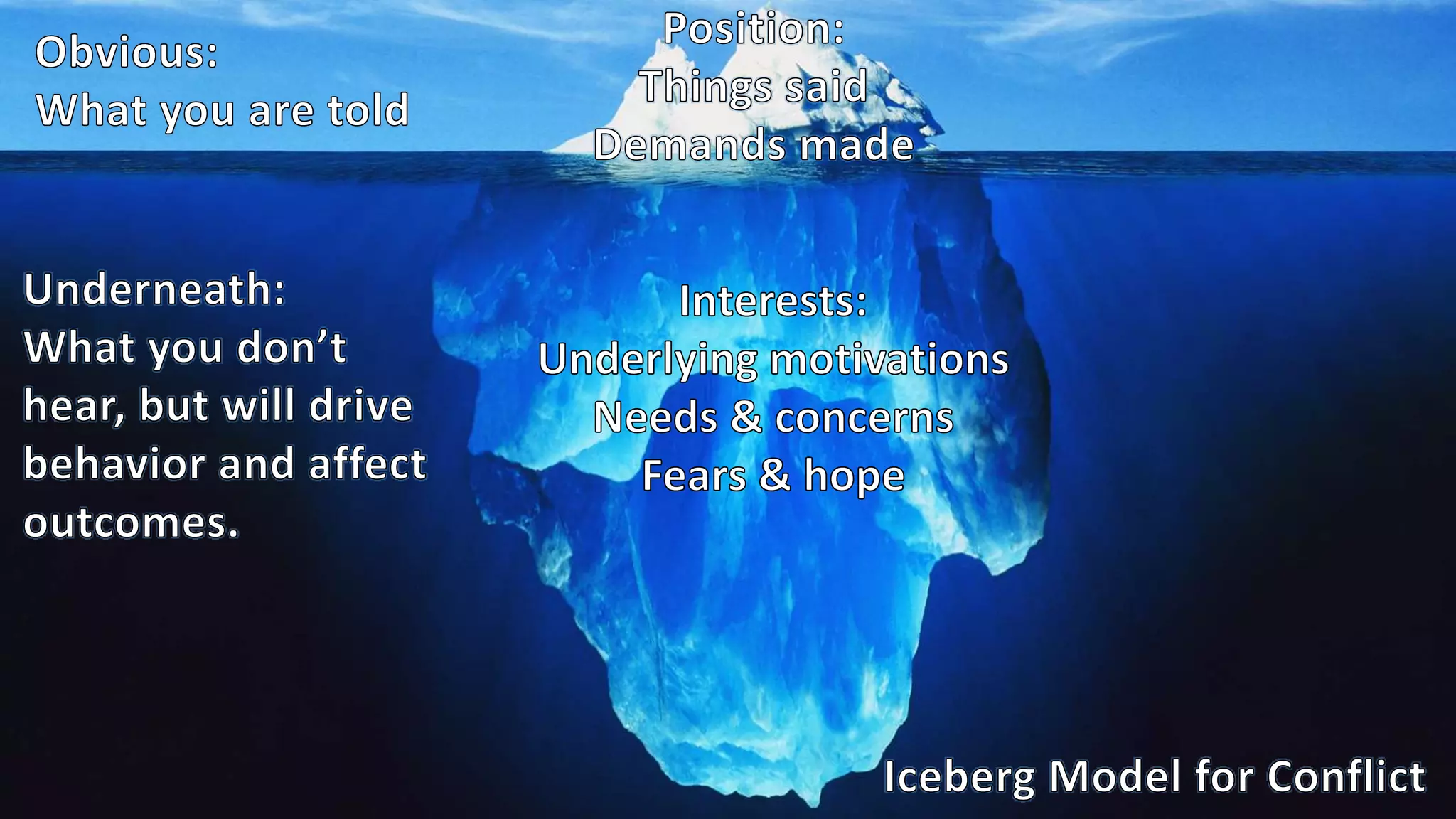
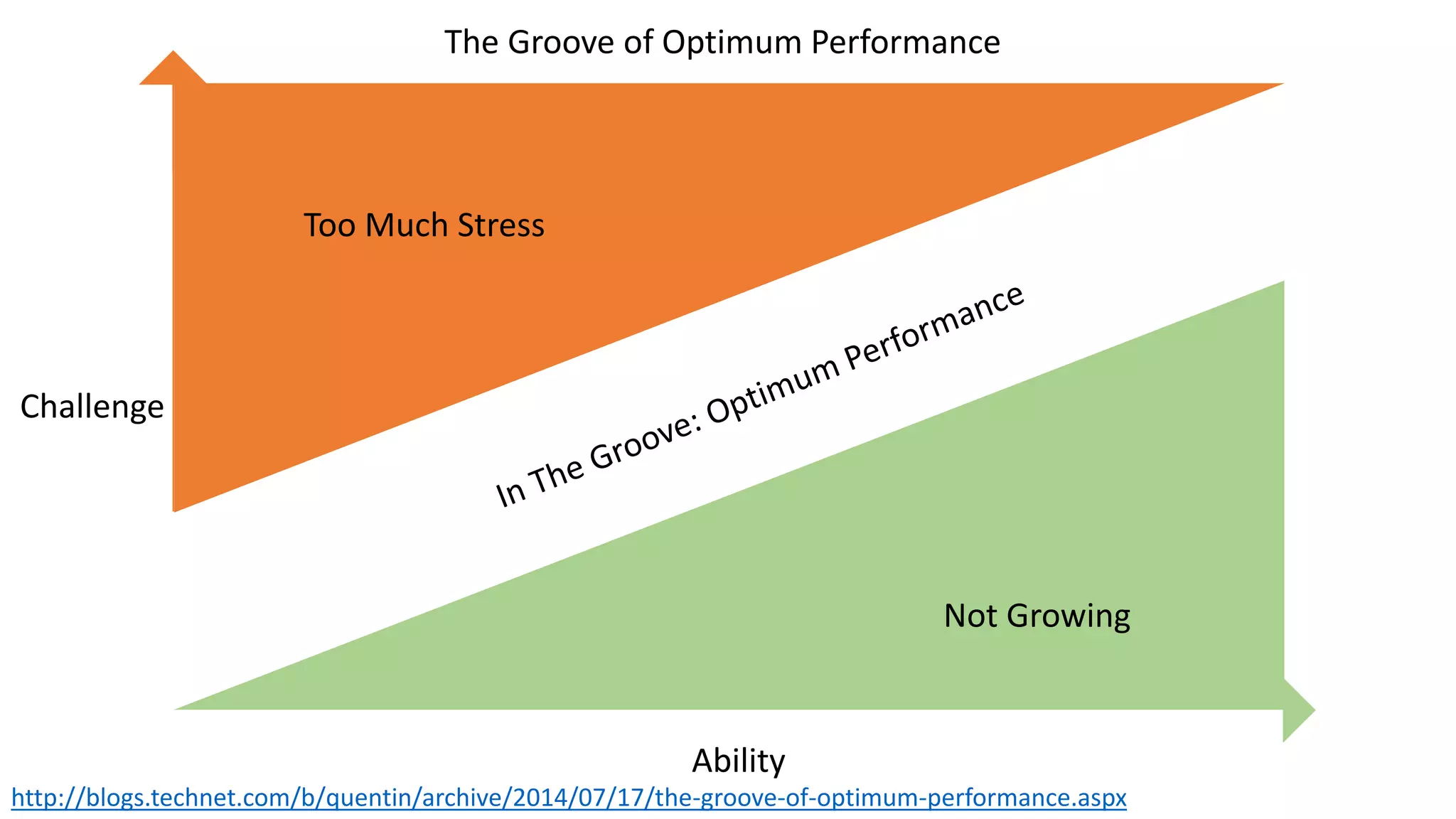
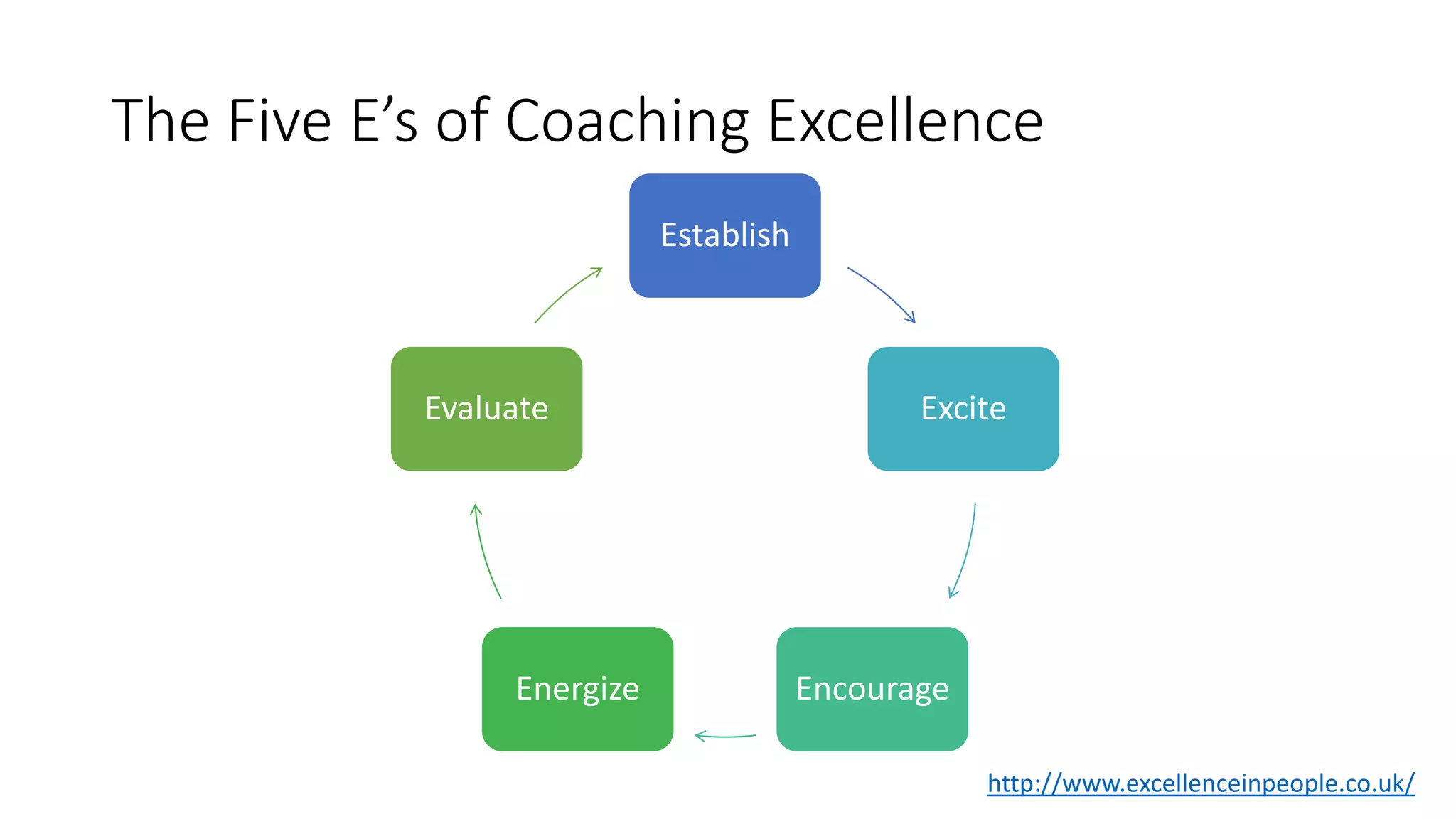
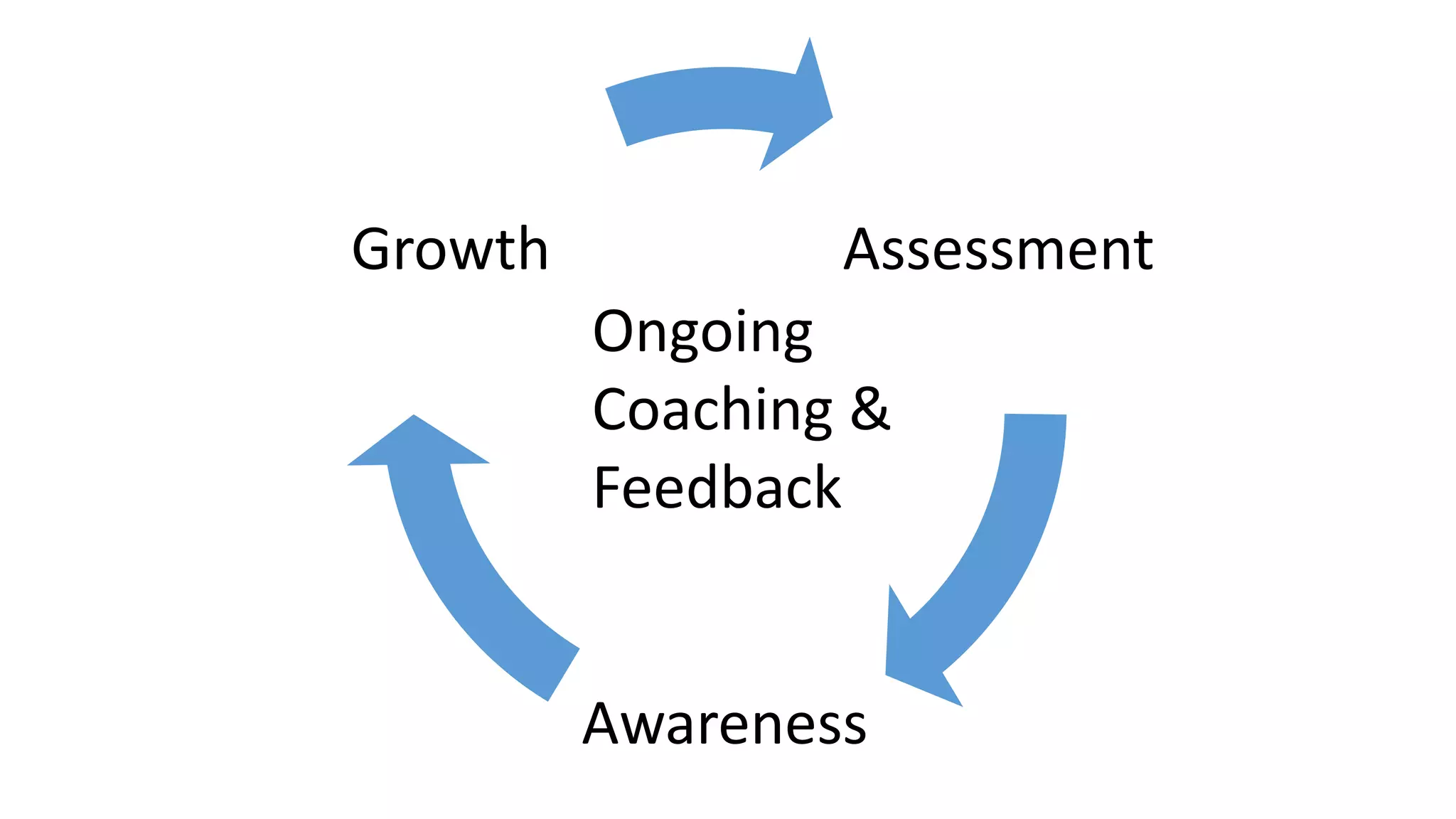
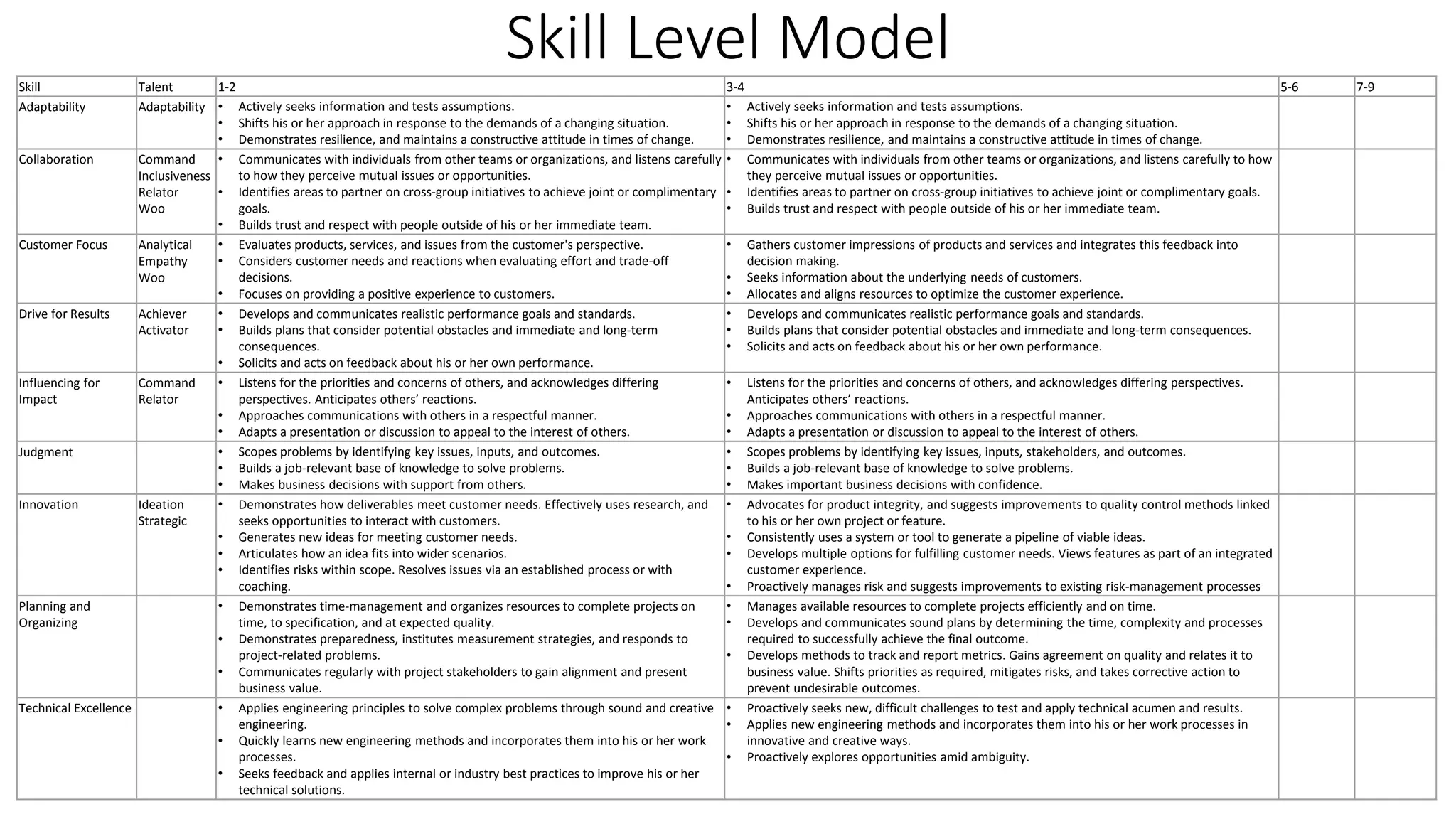
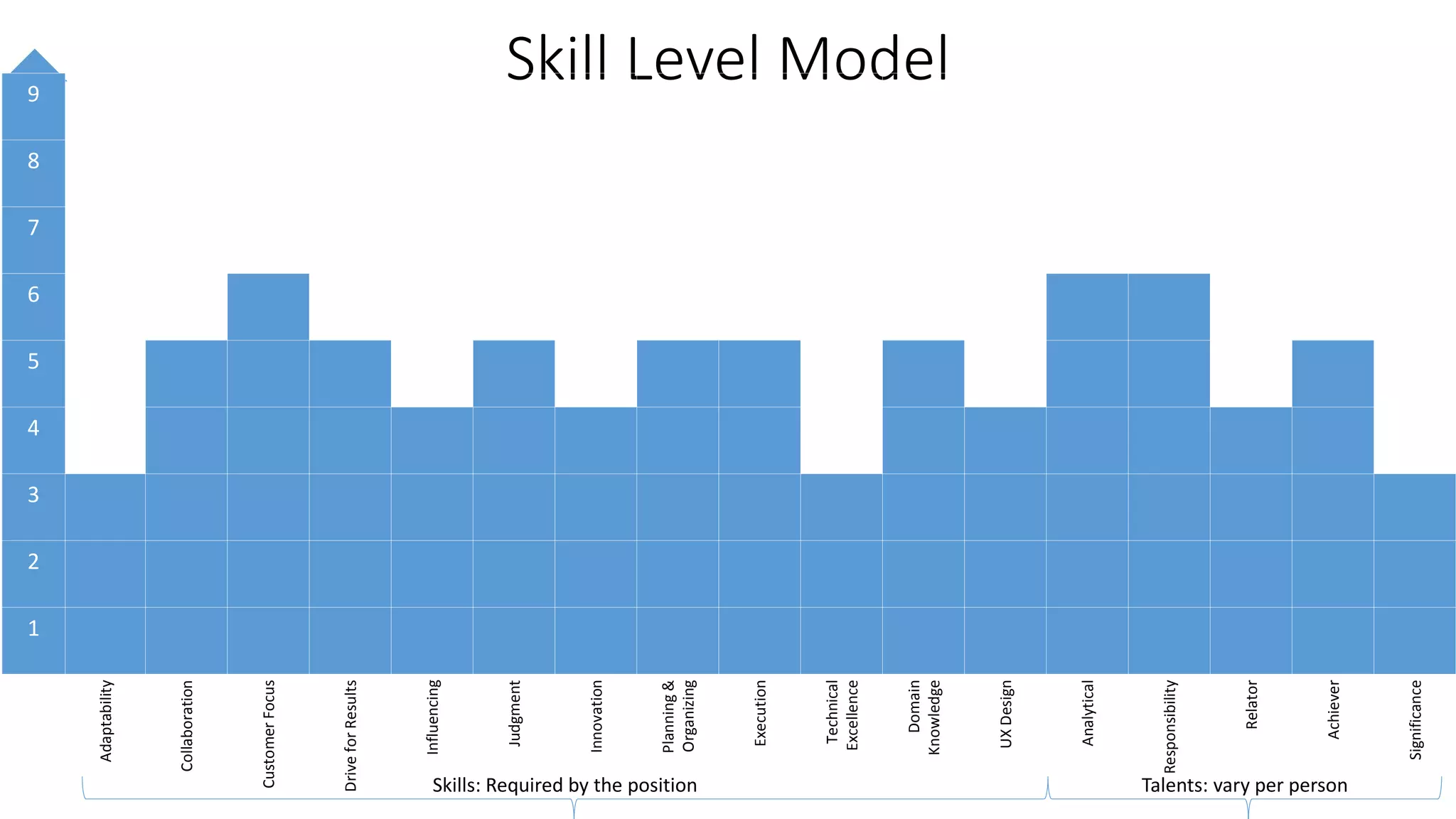
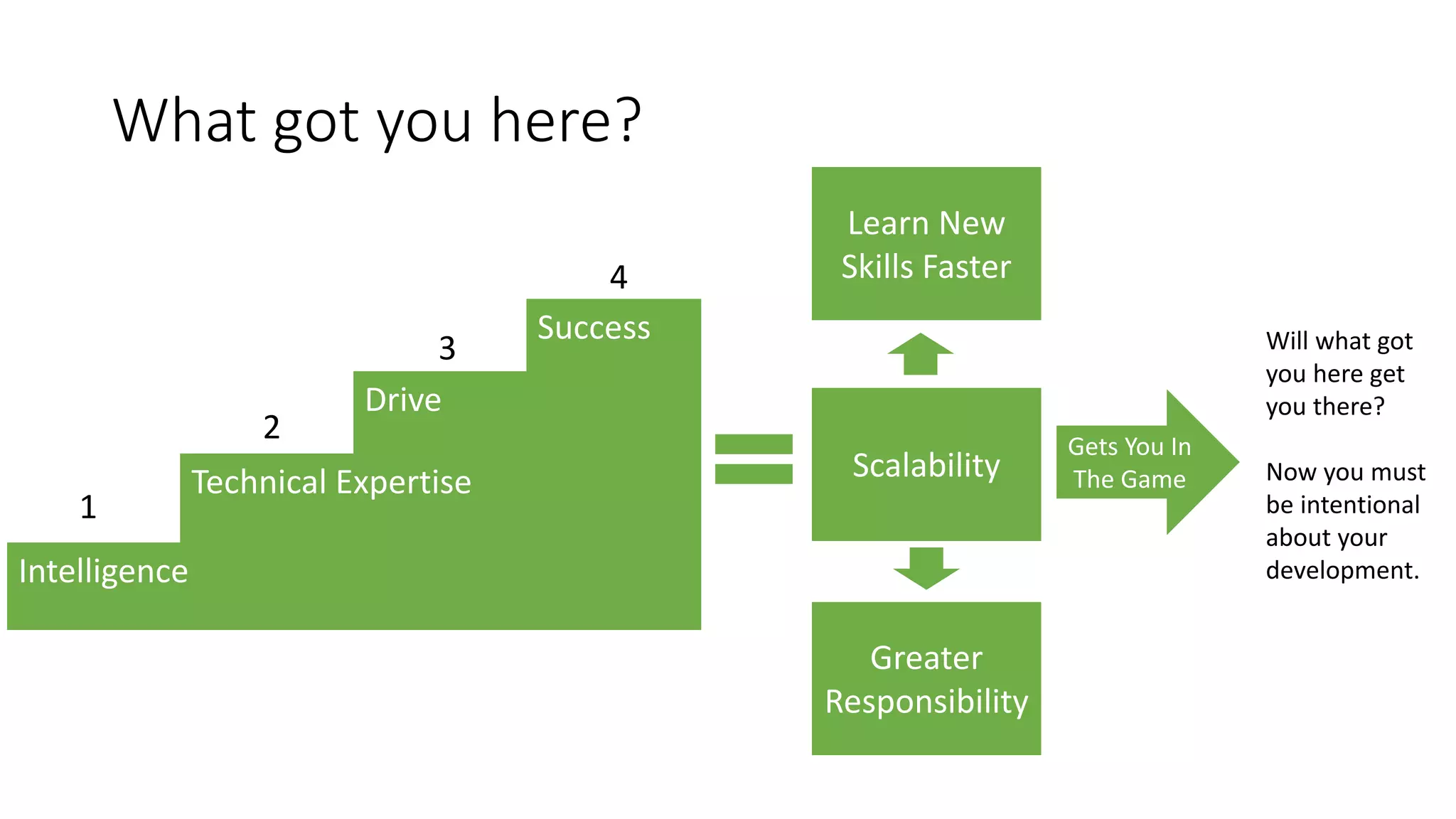
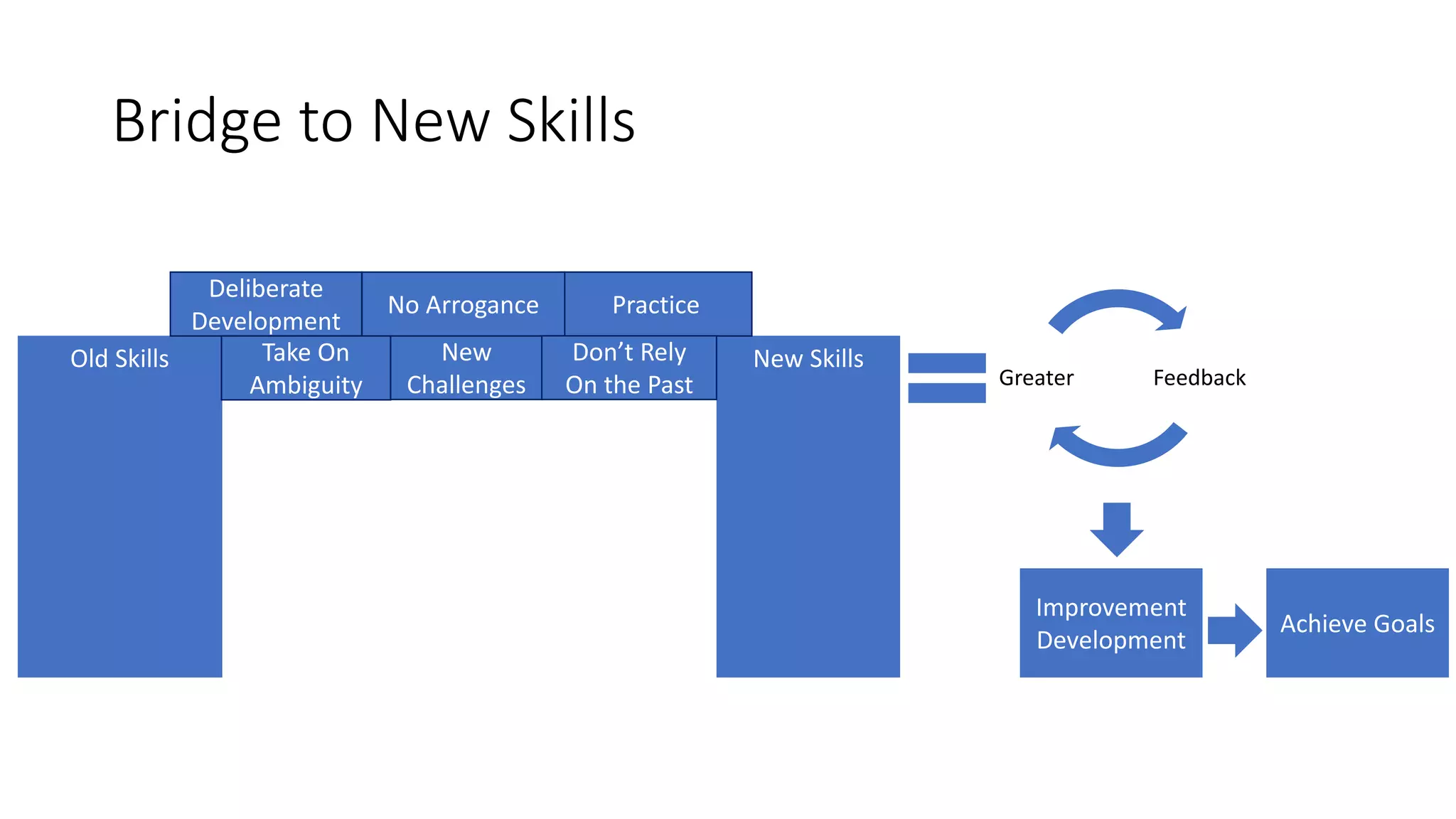
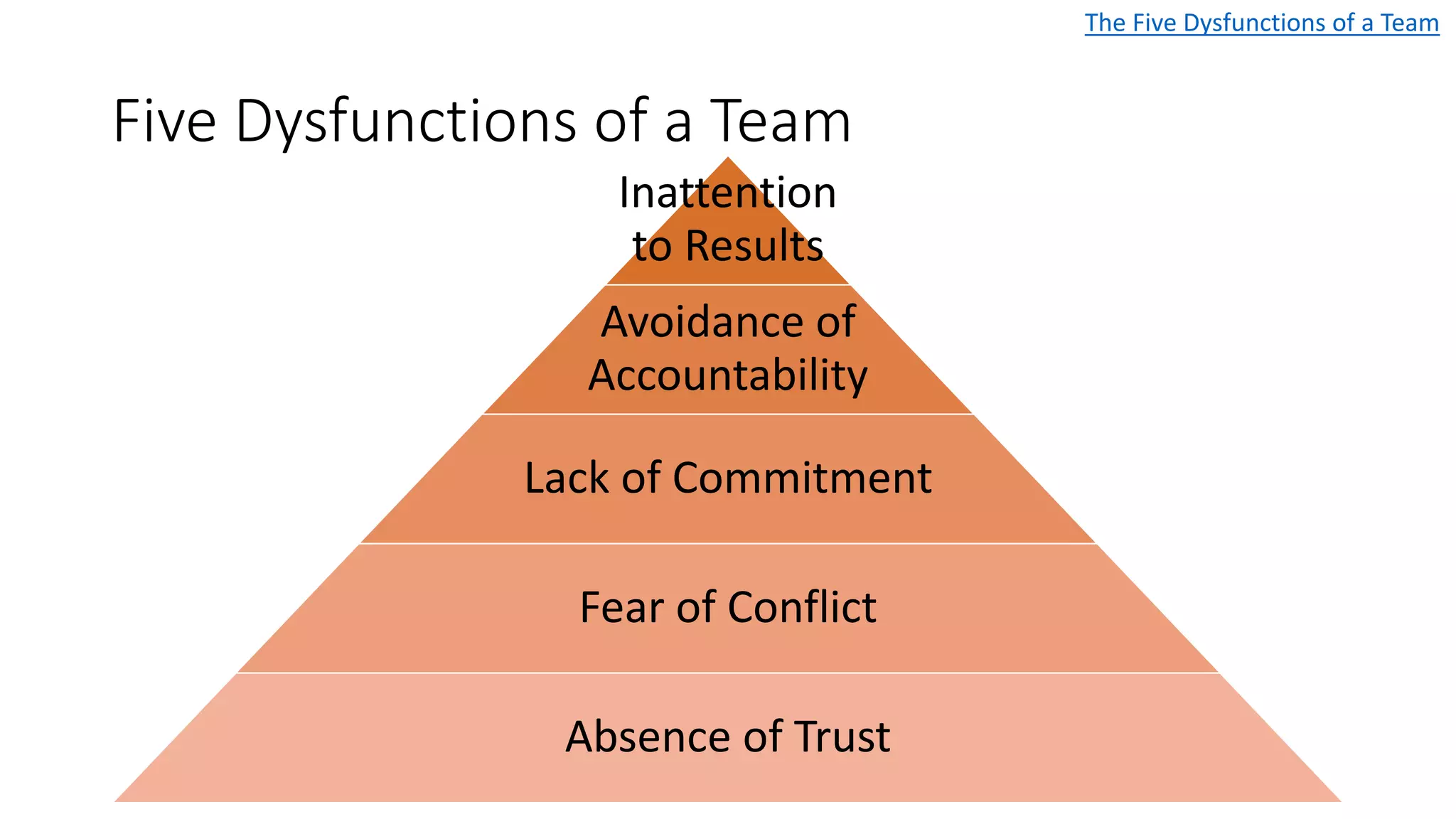
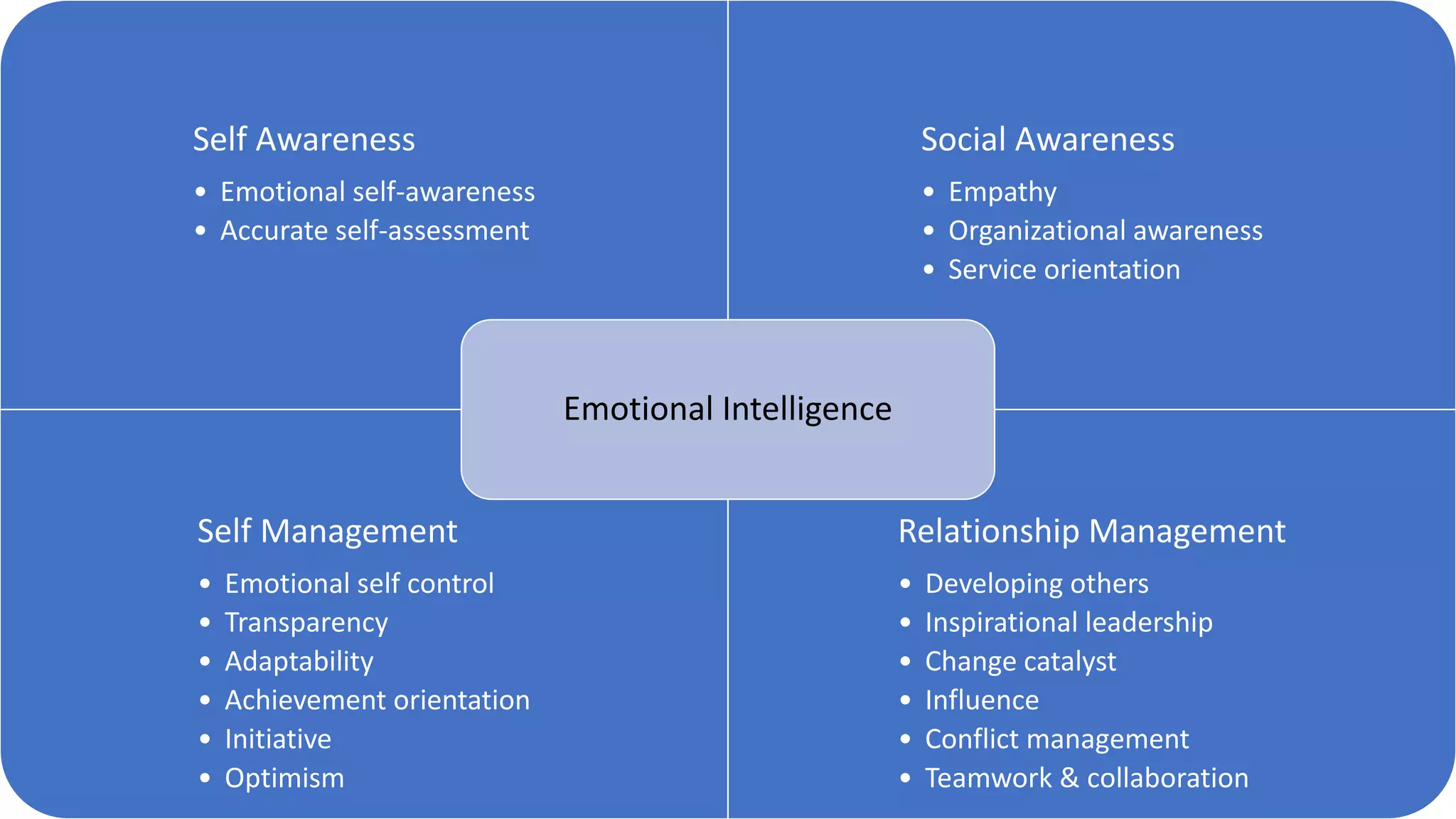
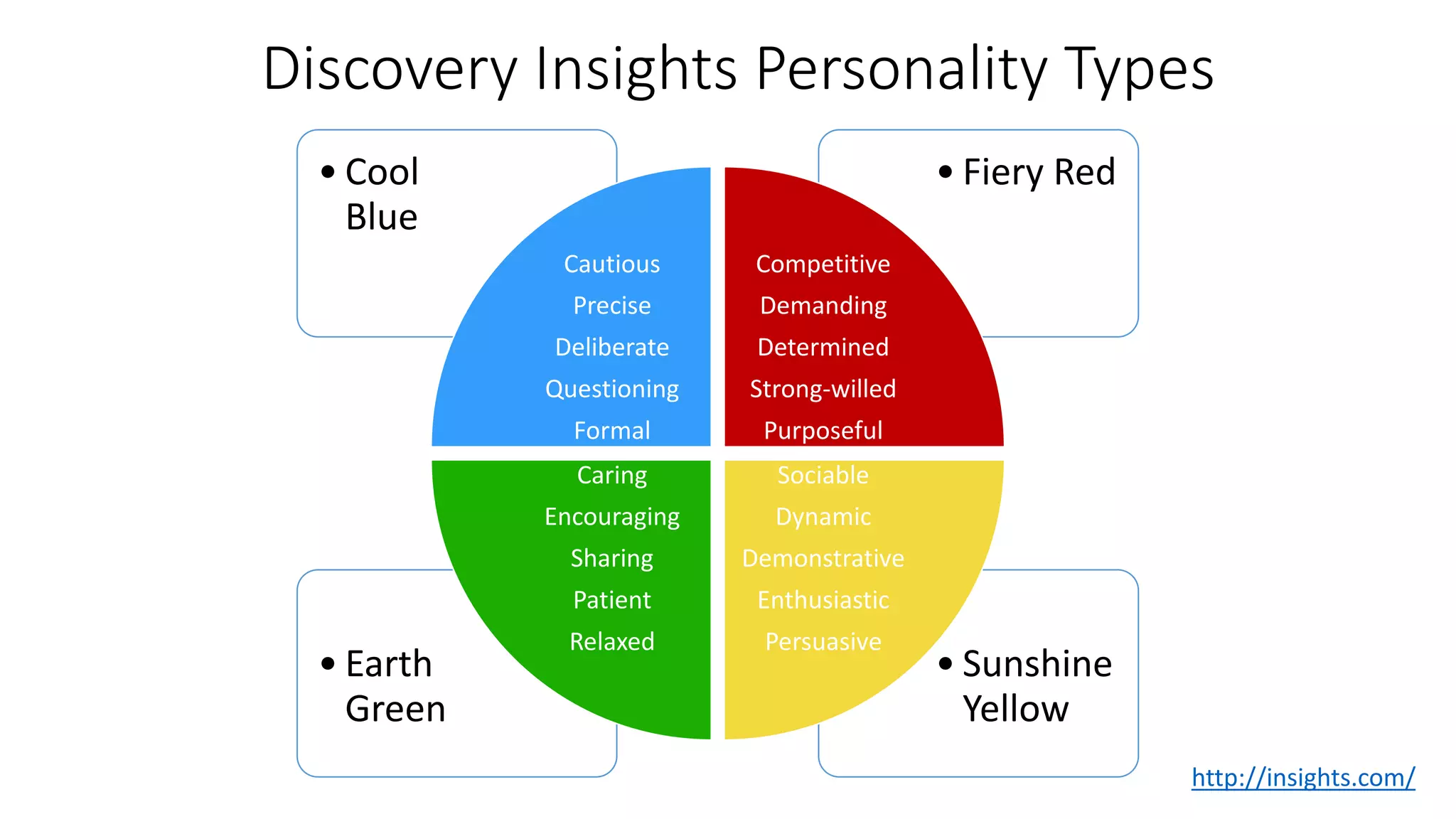
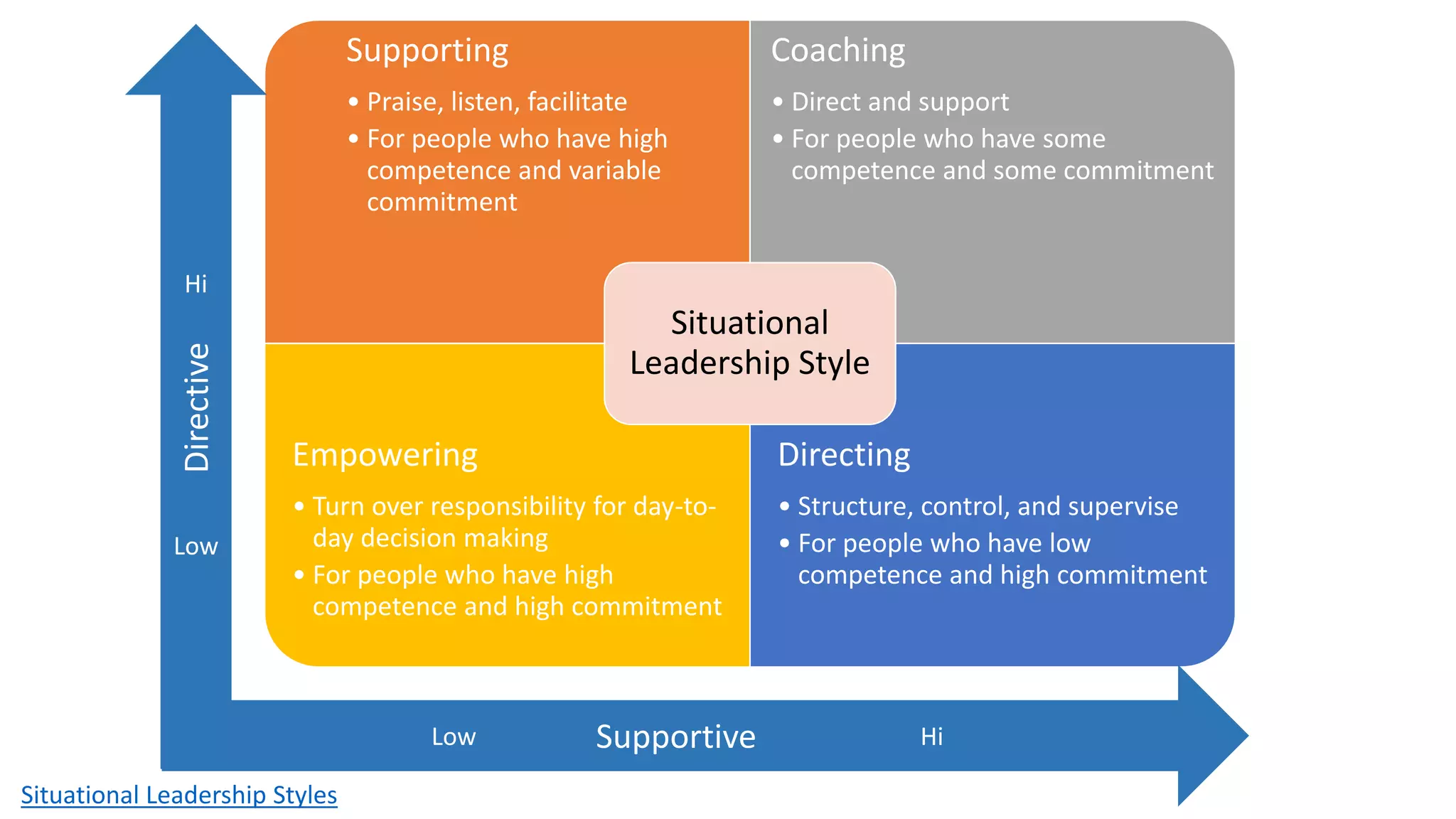
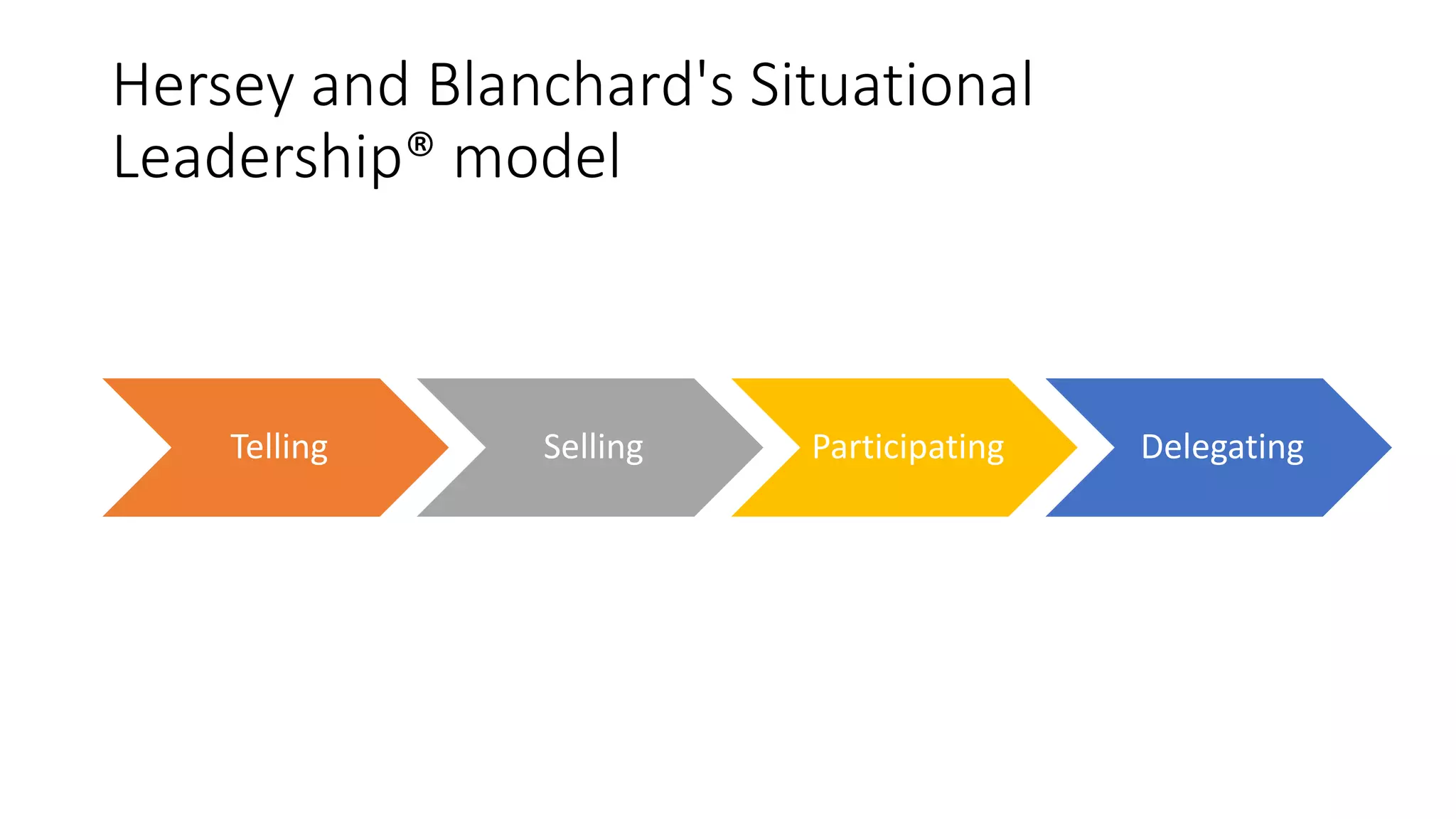
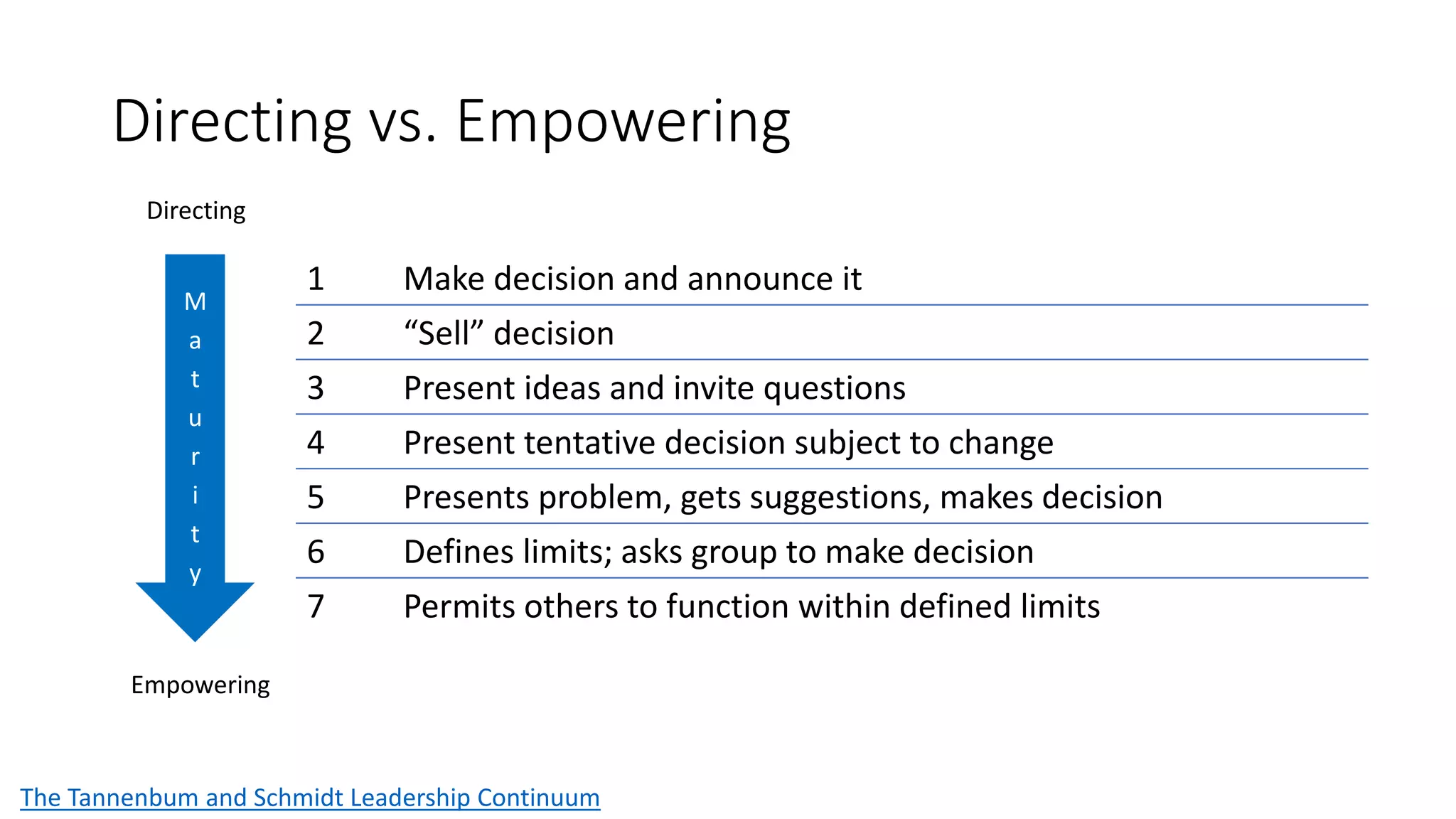
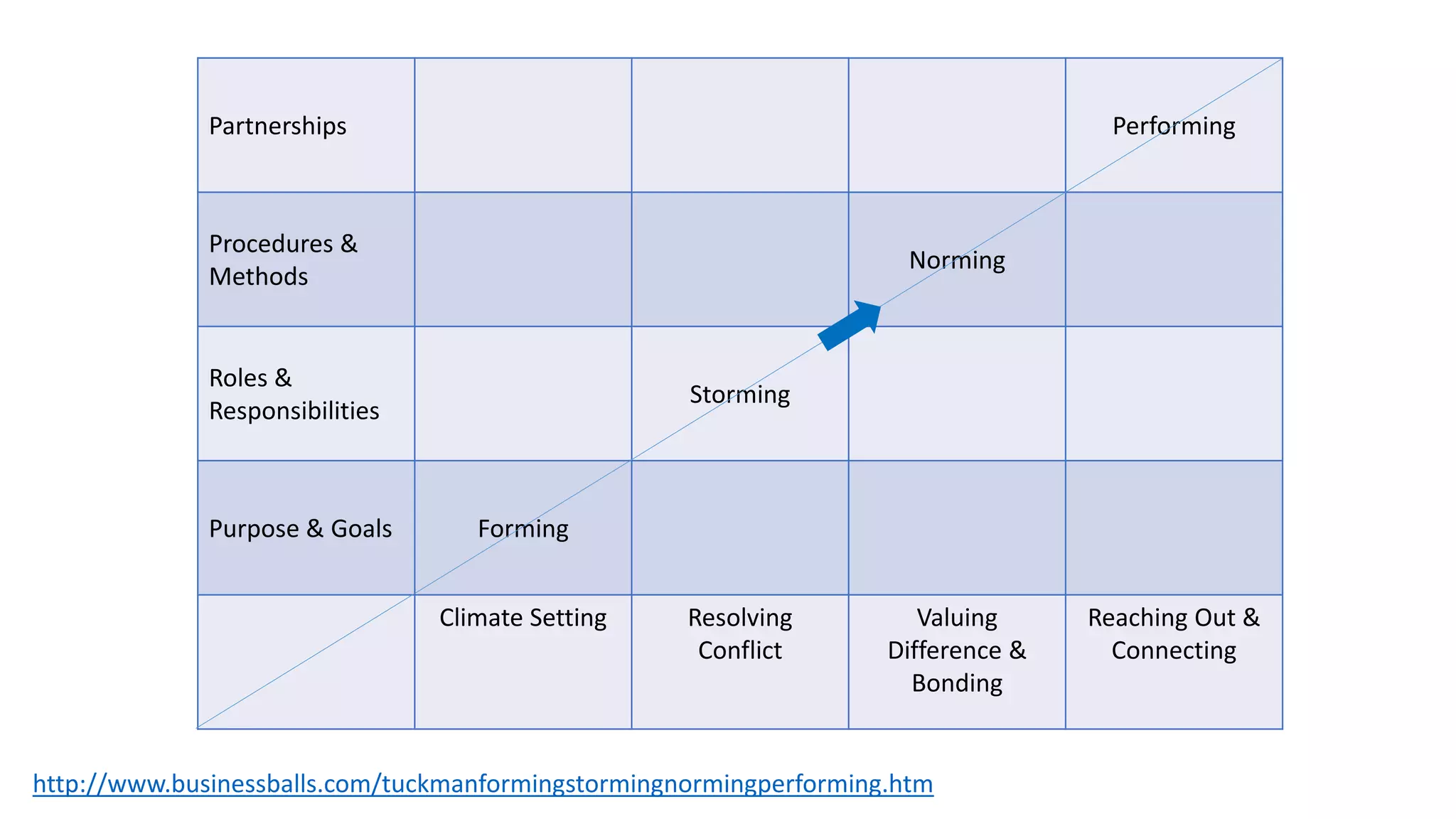
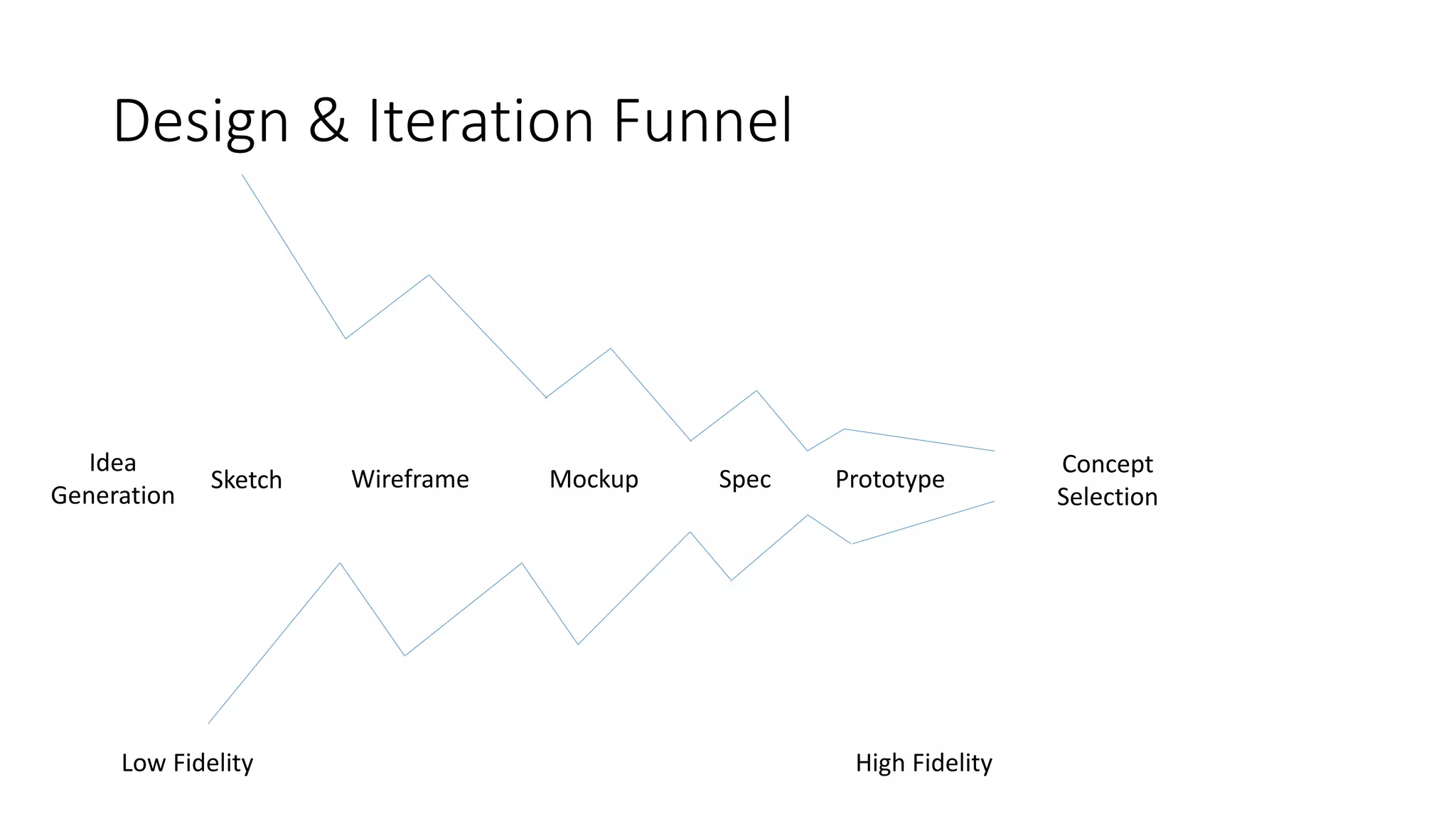
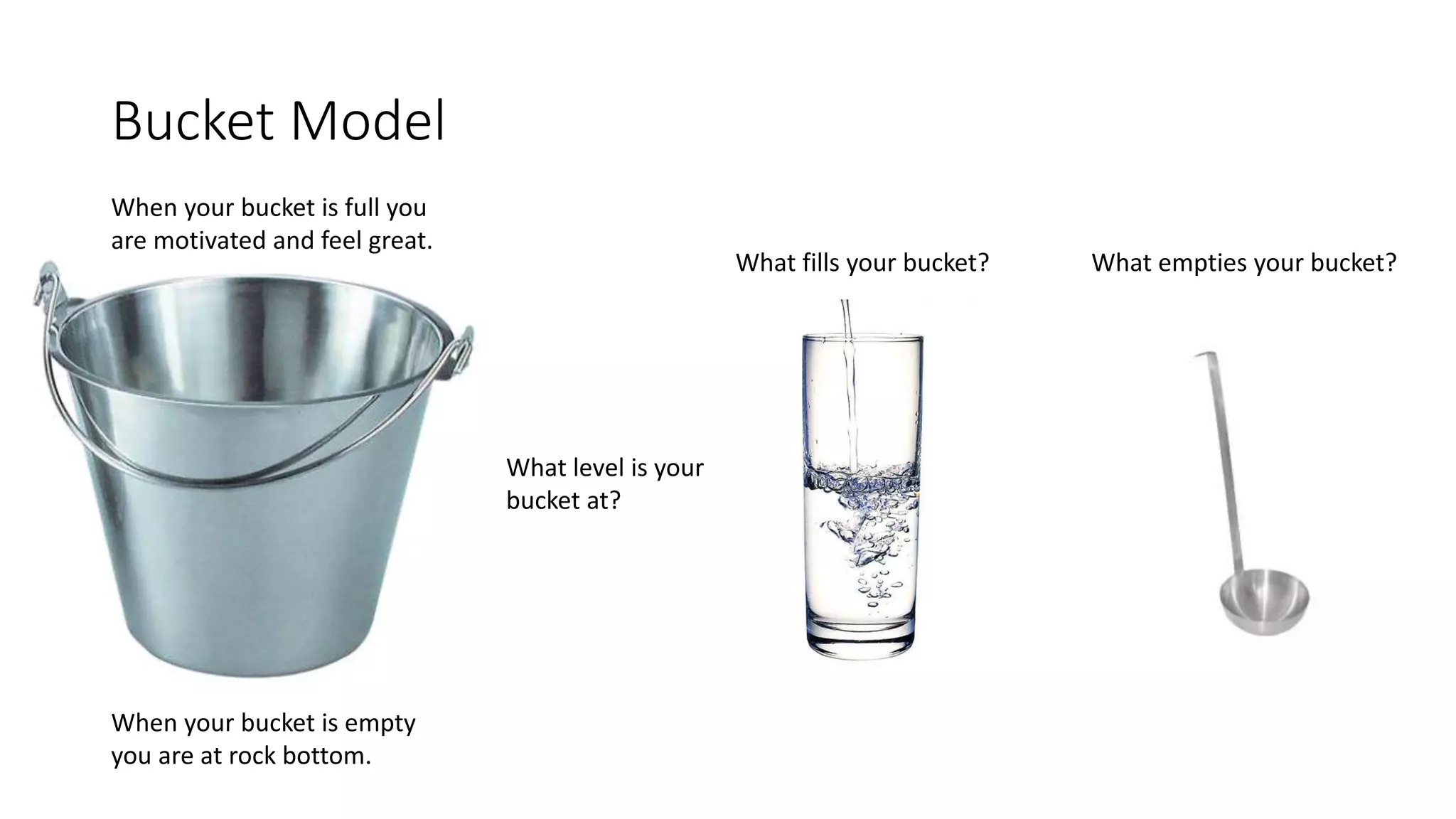
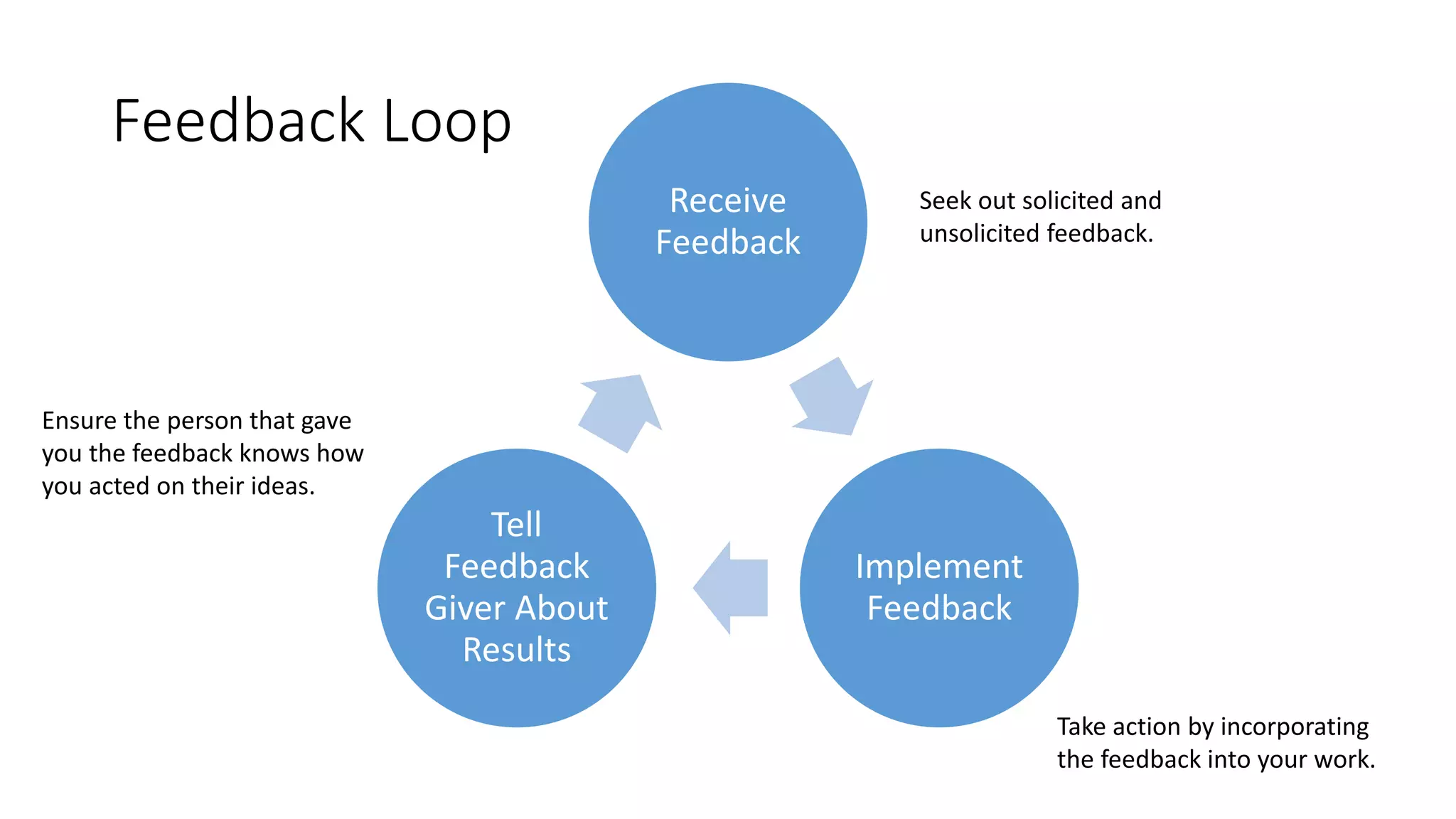
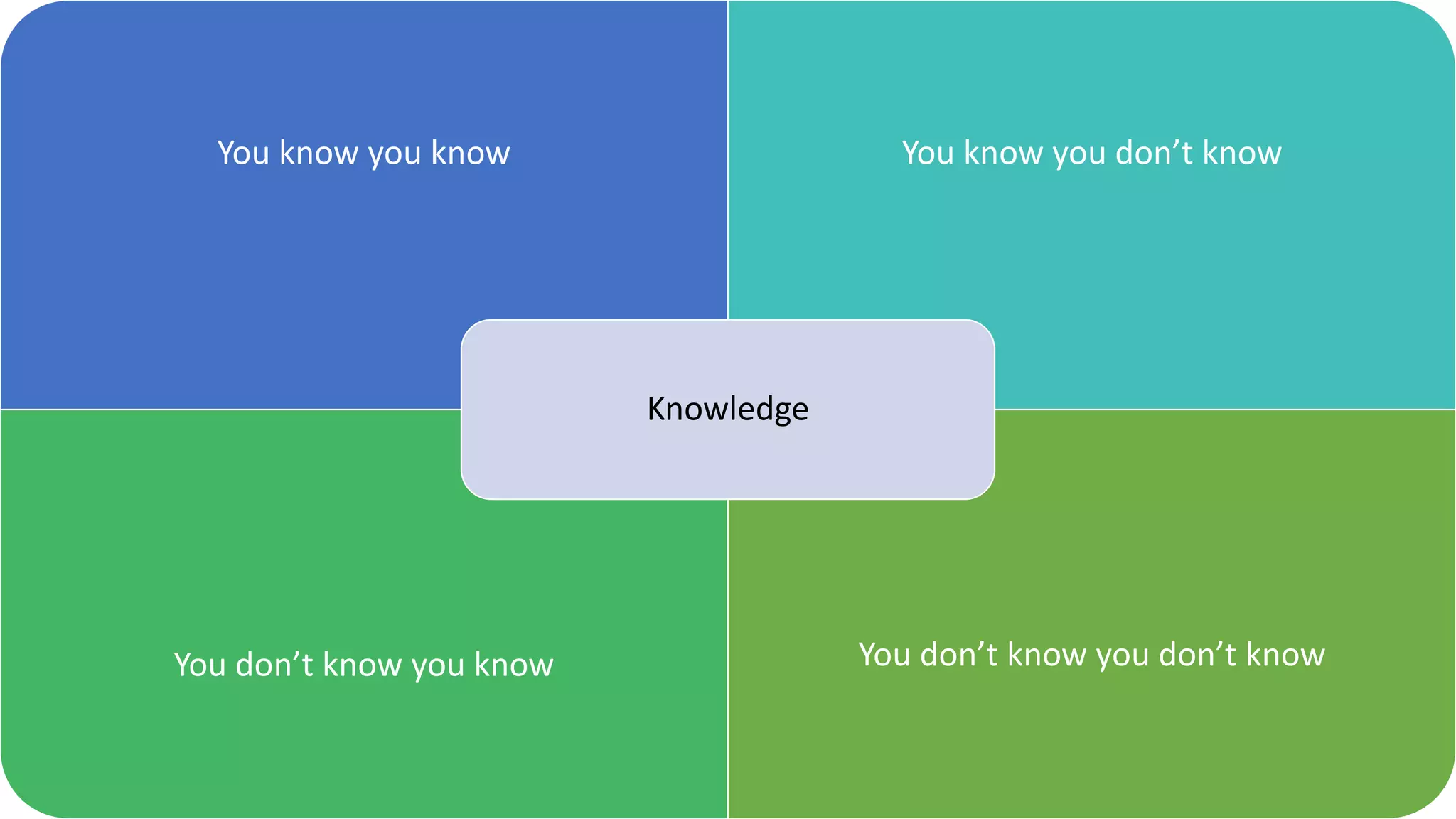
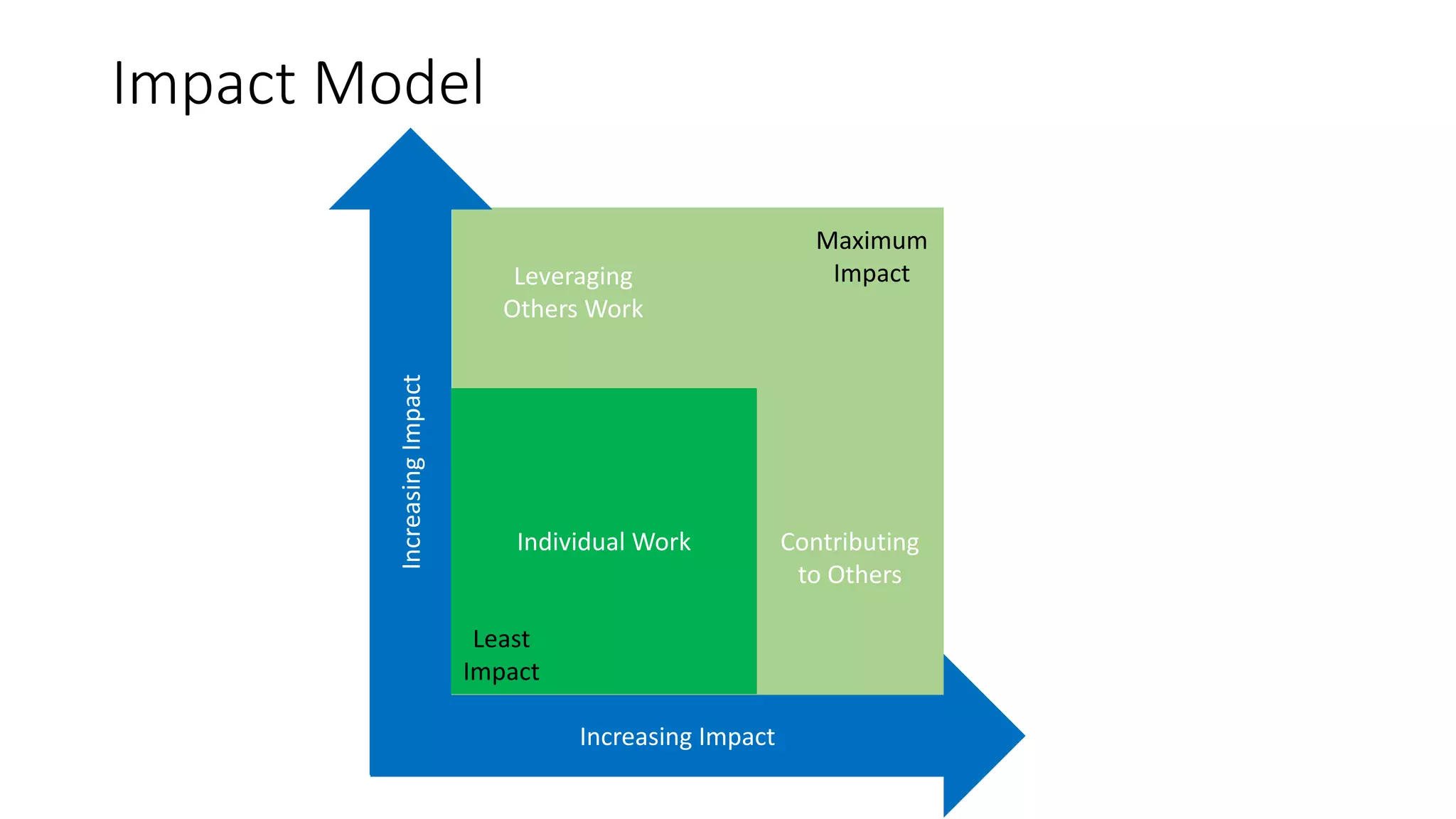
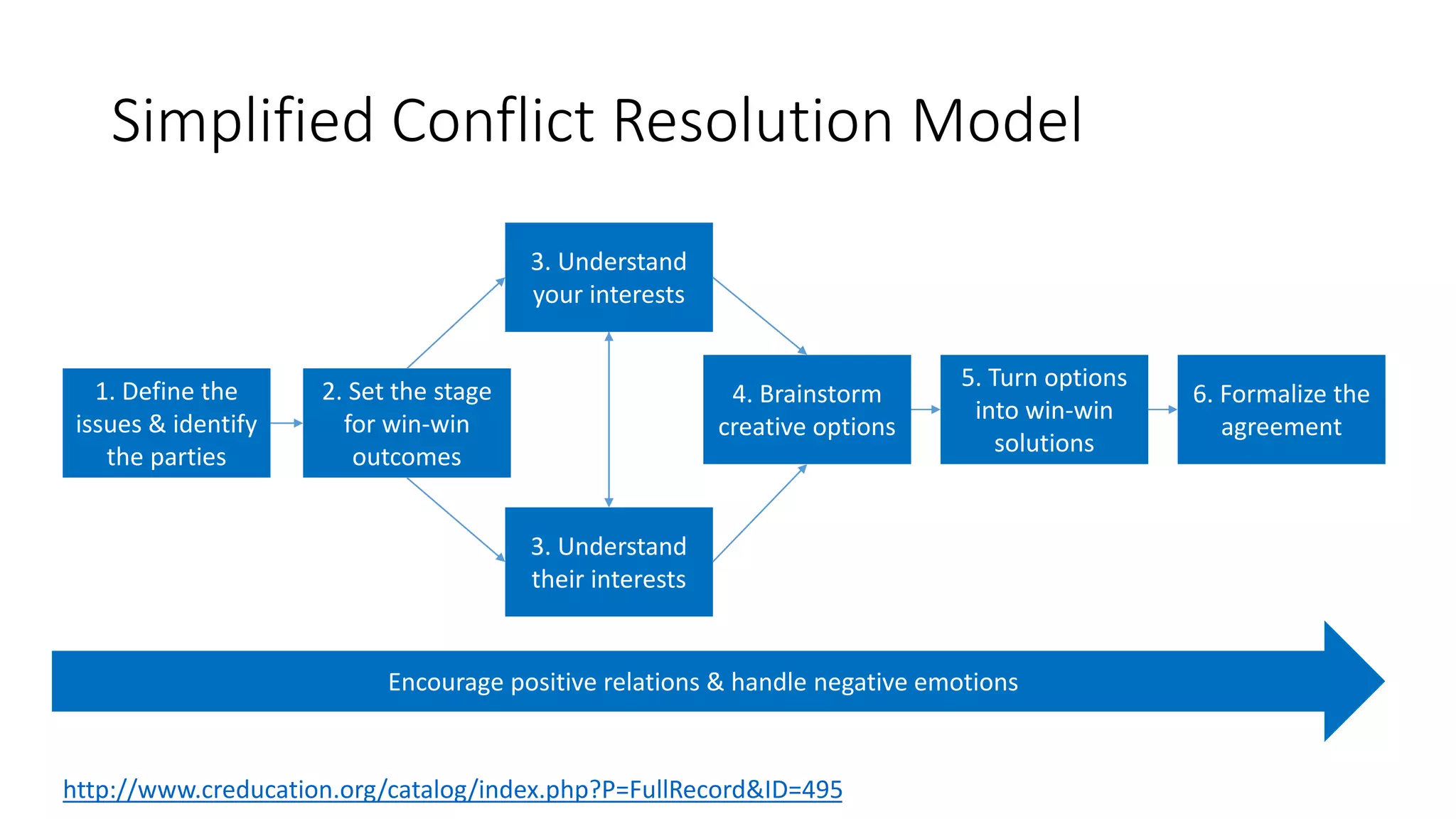
The document covers various aspects of personal and team development, focusing on the impact of instructional coaching and emotional intelligence in workplace dynamics. It outlines key models and frameworks, including the 'pit of success,' the five E's of coaching excellence, and situational leadership styles. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of adaptability, collaboration, and emotional intelligence in achieving professional growth and effective team performance.