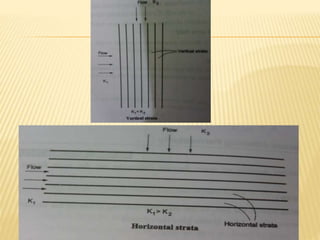
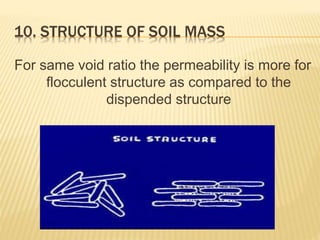
Permeability is the property of soil that allows water to flow through it, denoted by 'K'. Factors that affect permeability include grain size, properties of pore water, temperature, void ratio, stratification, entrapped air/organics, adsorbed water, degree of saturation, shape of particles, and structure of the soil mass. Permeability generally increases with larger grain size, higher temperatures, and void ratios, and decreases with stratified layers perpendicular to flow, entrapped air/organics, adsorbed water, partial saturation, angular particles, and dispersed soil structures.