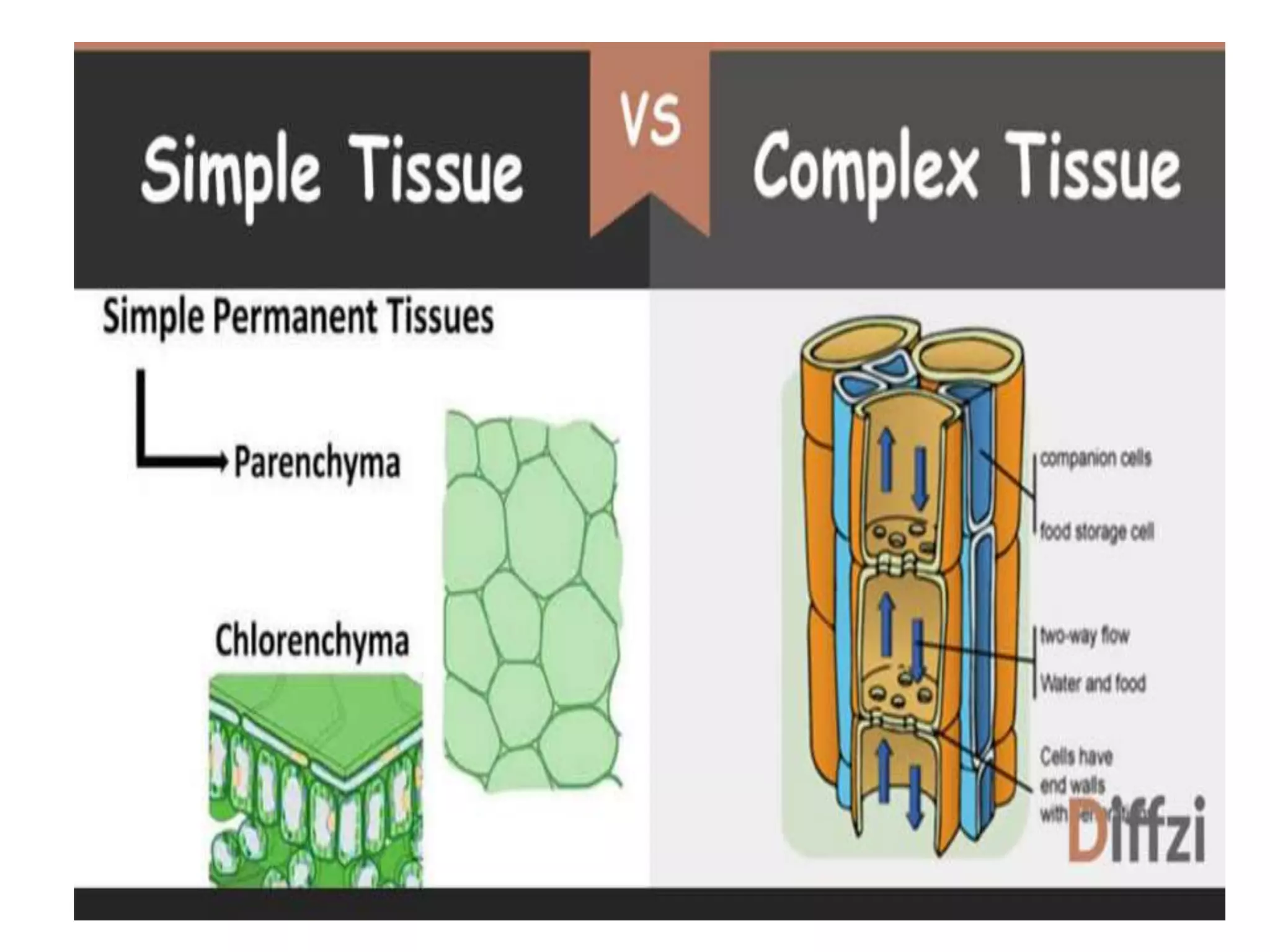
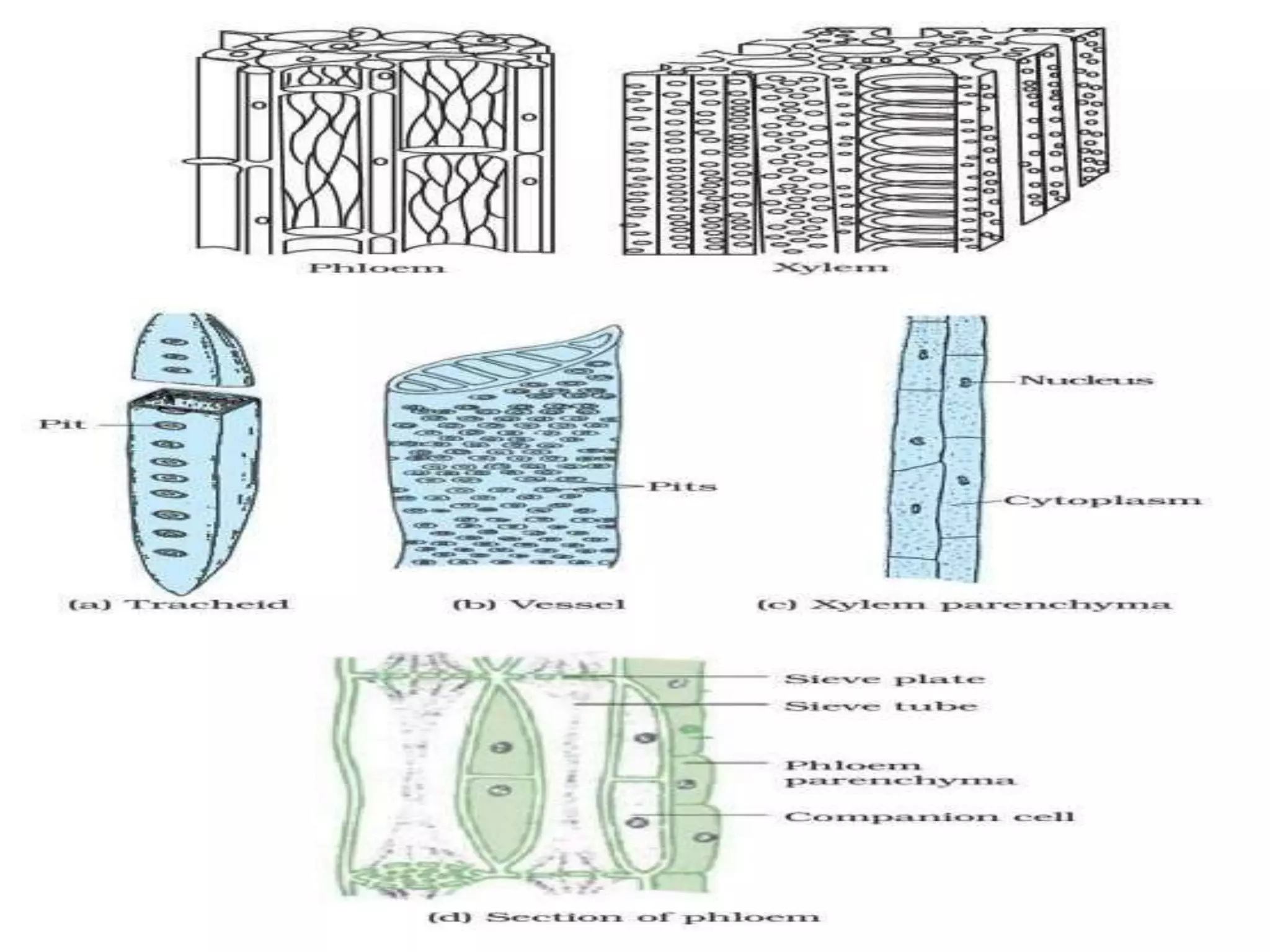
Permanent tissues in plants consist of non-dividing cells derived from meristematic tissues, responsible for specific functions such as support, protection, and transportation of nutrients. They are classified into simple permanent tissues (parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma) and complex permanent tissues (xylem and phloem), with each type having distinct characteristics and functions. Meristematic tissues, in contrast, are undifferentiated cells capable of division, promoting plant growth.