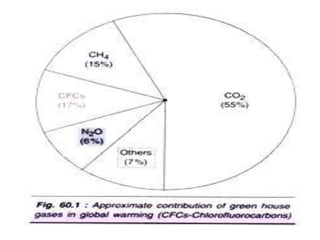
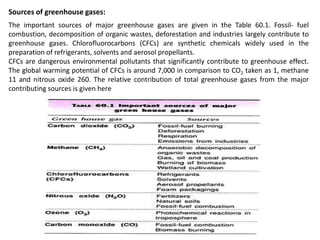
The document discusses three major global environmental problems: the greenhouse effect and global warming, ozone depletion, and acid rain, detailing their causes, effects, and potential solutions. It highlights the role of greenhouse gases in climate changes, the detrimental effects of ozone layer depletion, and the impacts of acid rain on various ecosystems. The document emphasizes the importance of environmental sustainability and biotechnology in combating these issues through pollution protection, clean-up, and control.