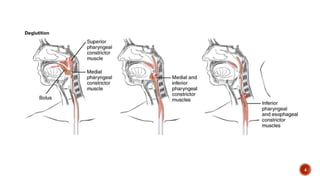
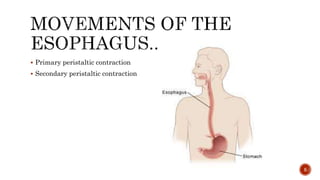
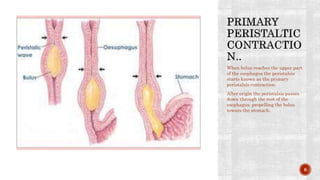
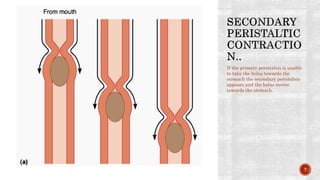
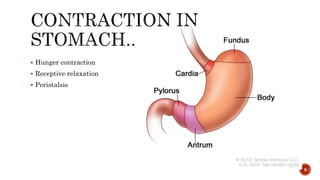
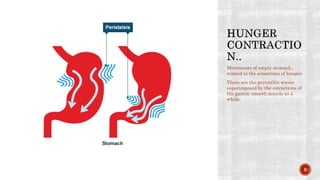
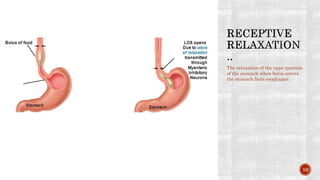
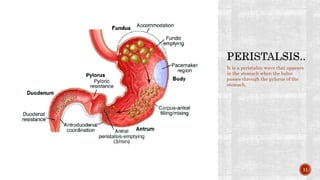
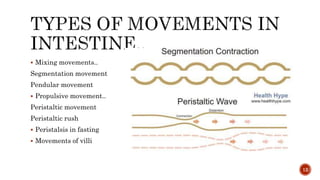
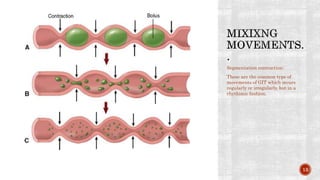
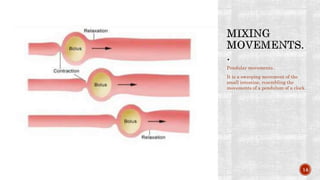
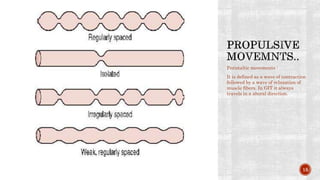
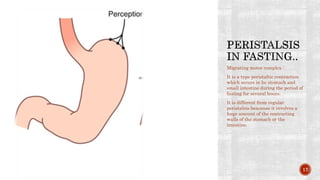
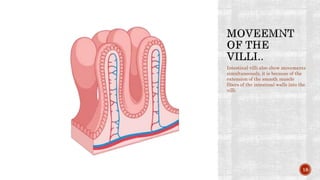
The document discusses the gastrointestinal tract's role in digestion, highlighting processes such as peristalsis, which involves wave-like contractions to move food from the mouth to the stomach. It describes stages of swallowing (deglutition), types of peristaltic contractions, and various movements of the stomach and intestines, including hunger contractions and migrating motor complexes during fasting. Additionally, it outlines how intestinal villi exhibit movement due to the contraction of smooth muscle fibers.