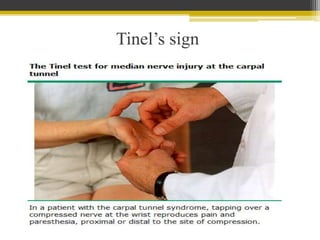
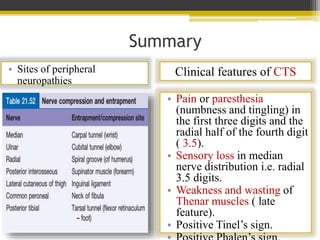
This document discusses peripheral neuropathy and carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). CTS is the most common entrapment neuropathy where the median nerve is compressed at the wrist by the transverse carpal ligament. CTS causes pain or paresthesia in the first three digits and radial half of the fourth digit, as well as sensory loss in the median nerve distribution. Other signs include weakness of the thenar muscles and positive Tinel's and Phalen's signs. Treatment options include rest, wrist splints, medications like NSAIDs, and surgery for cases that are unresponsive to conservative measures.