This document provides information on carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), including its anatomy, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Some key points:
- CTS is caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Symptoms include pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand.
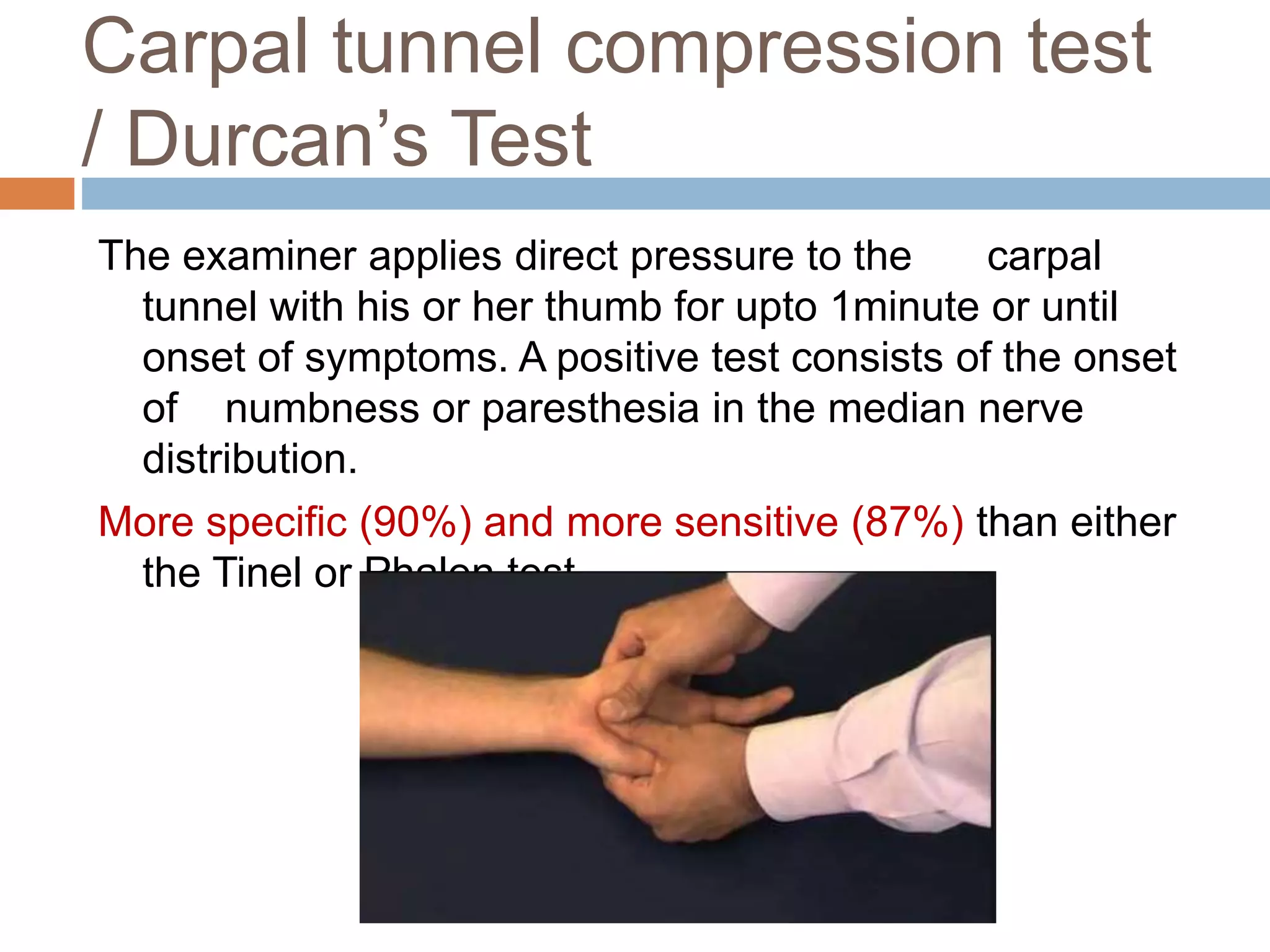
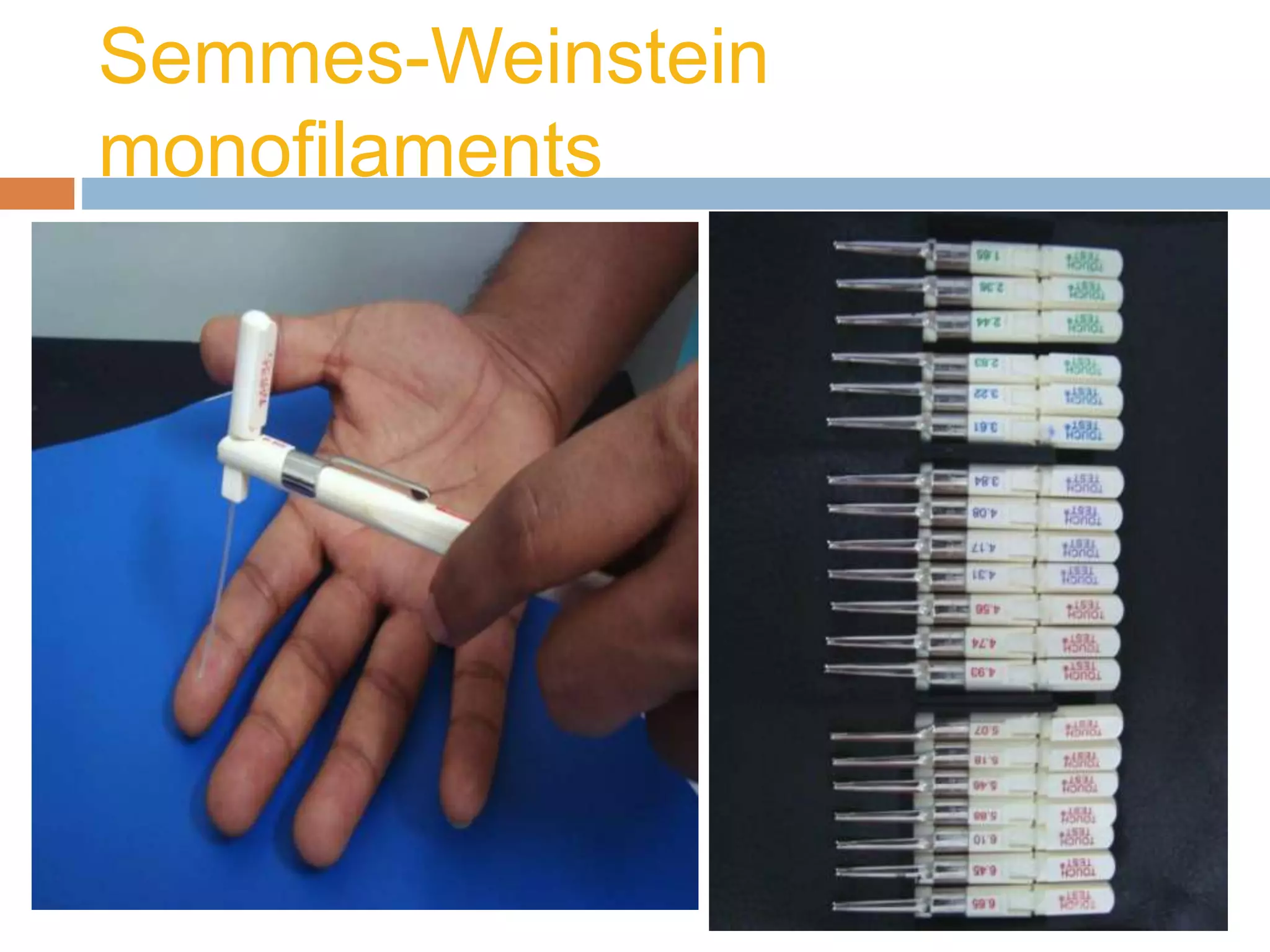
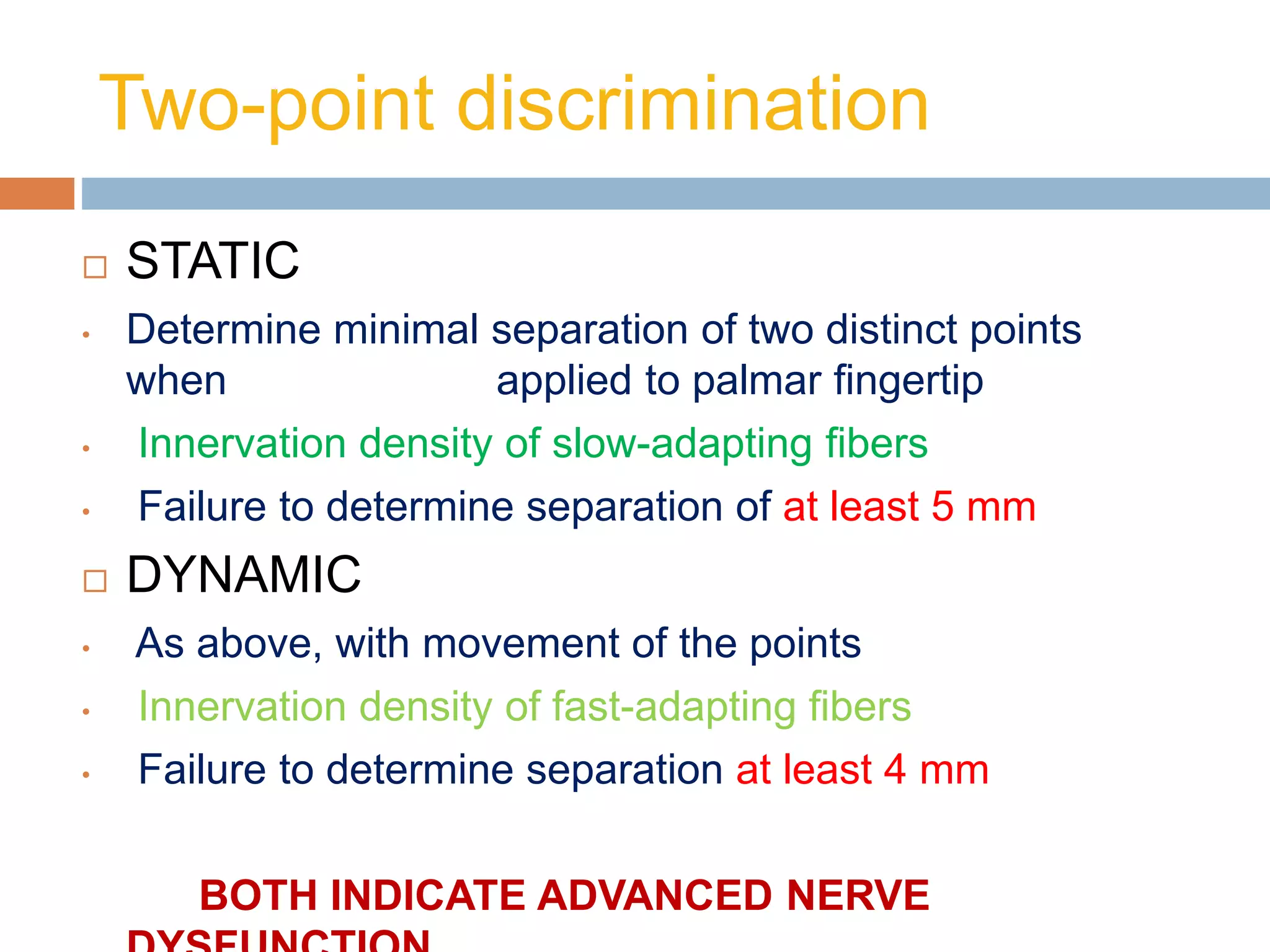
- Diagnosis is primarily clinical through tests like Tinel's sign and Phalen's maneuver. Electrodiagnostic tests like nerve conduction studies can help assess severity.
- Conservative treatments include splinting, injections, and exercises. Surgery (open or endoscopic release) is recommended if conservative options fail.
- The goals of any surgical technique are to completely