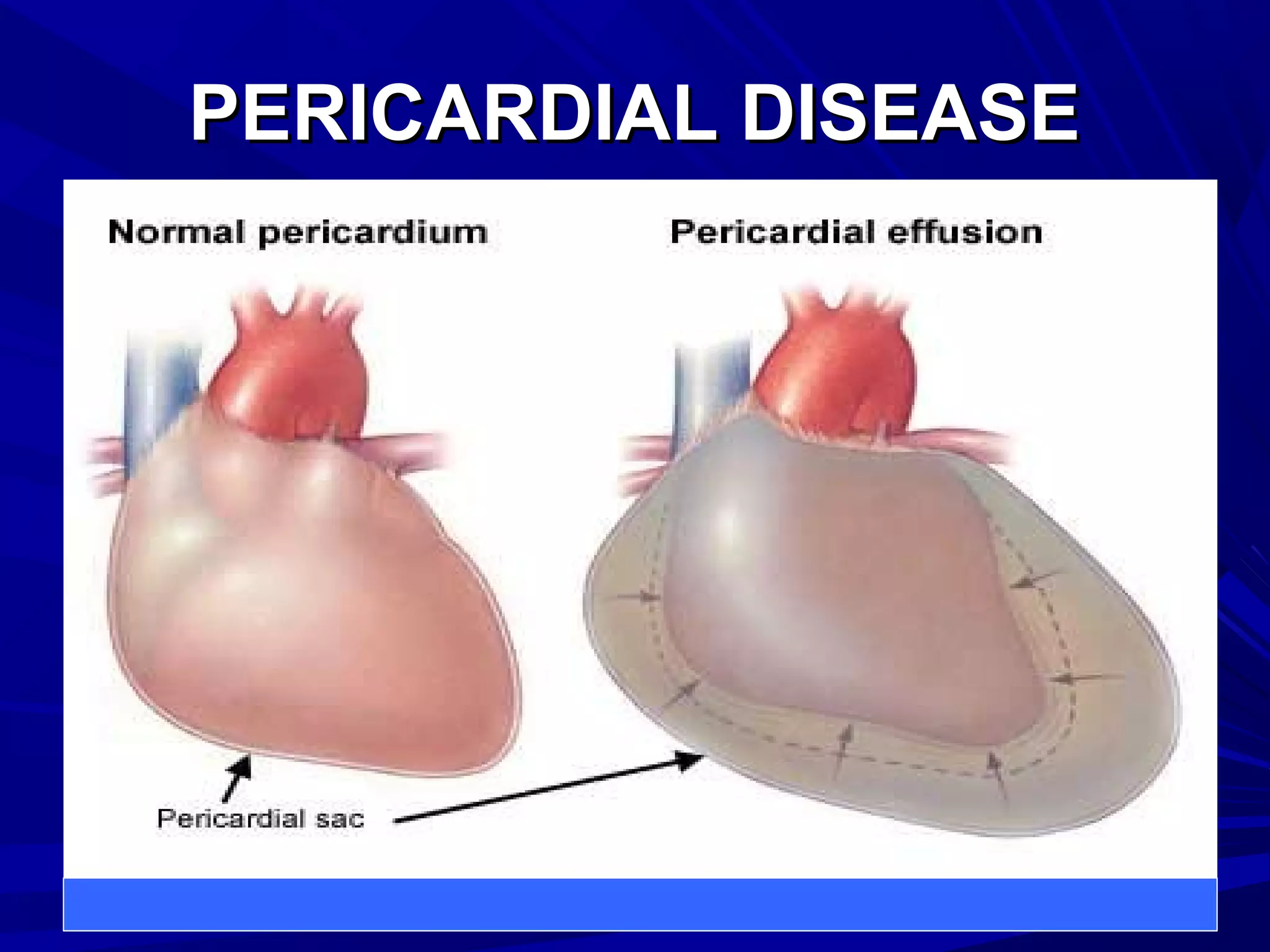
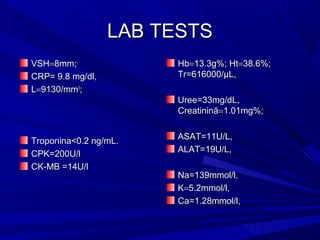
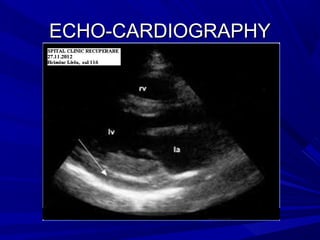
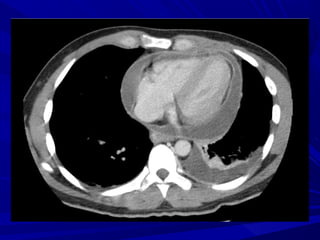
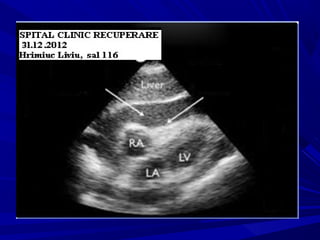
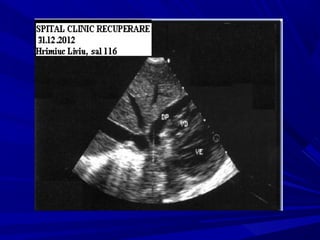
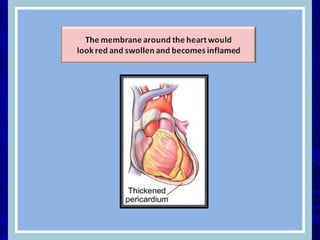
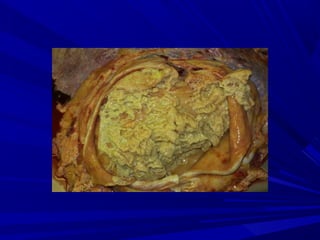
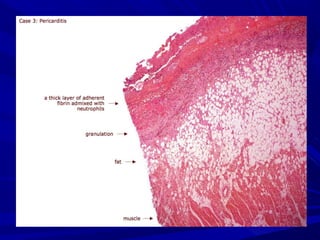
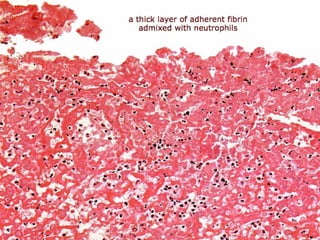
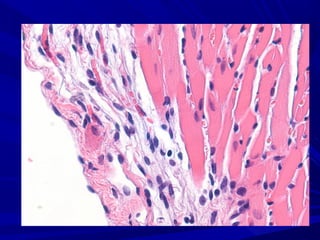
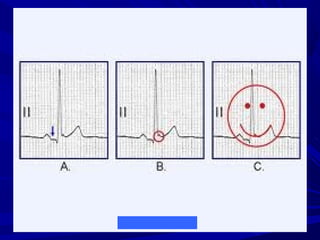
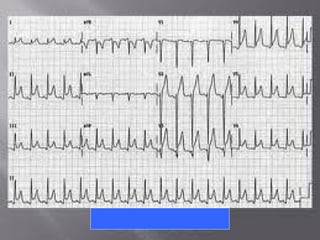
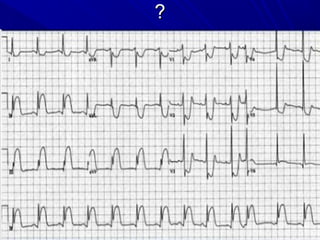
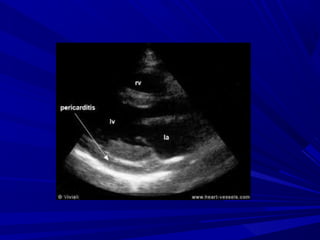
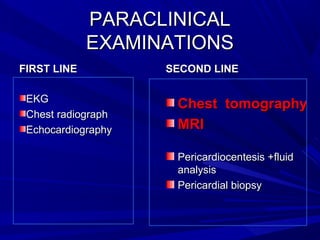
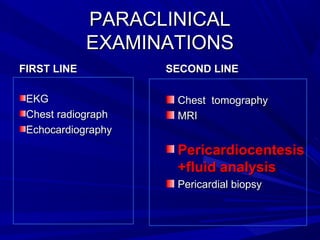
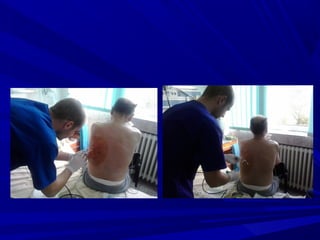
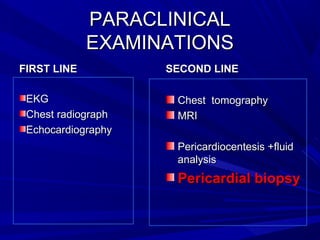
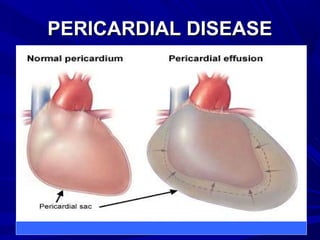
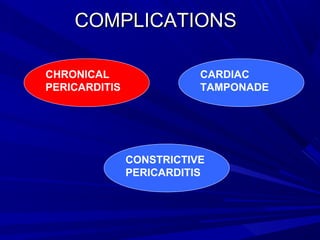
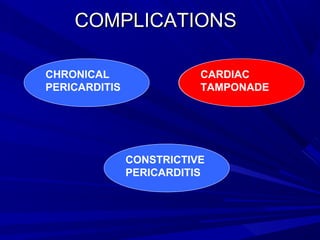
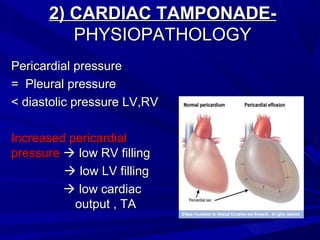
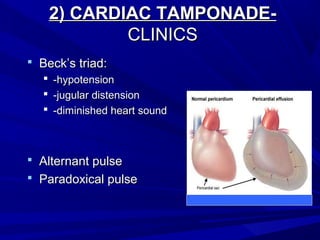
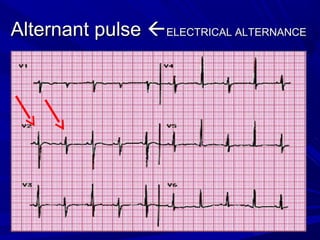
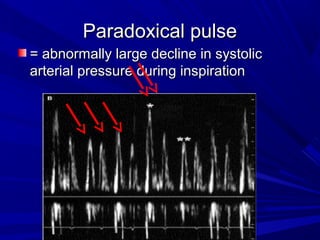
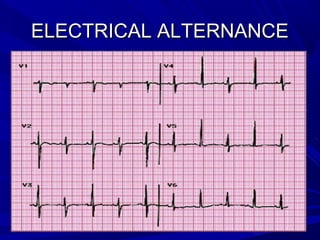
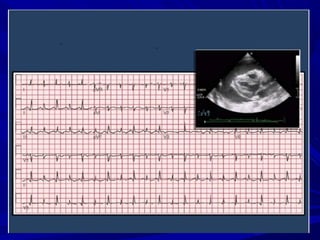
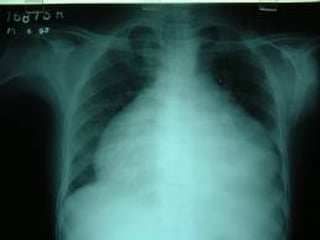
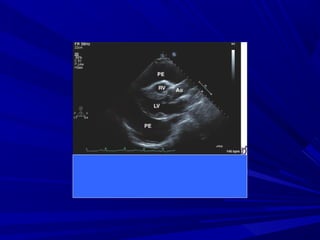
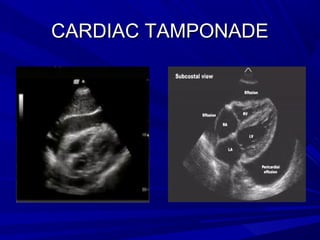
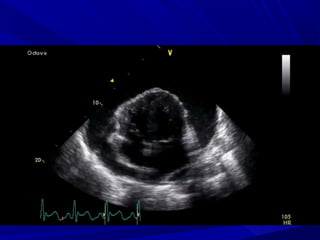
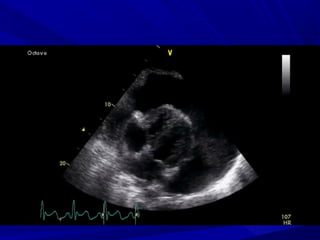
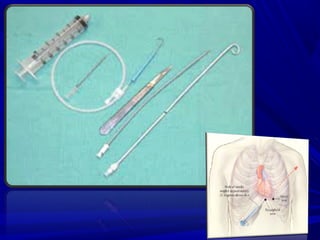
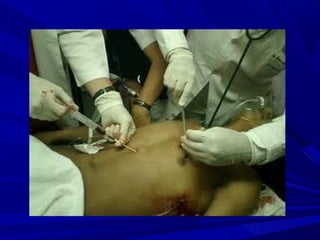
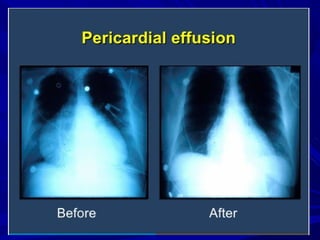
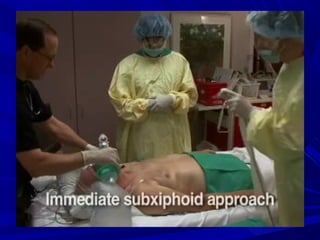
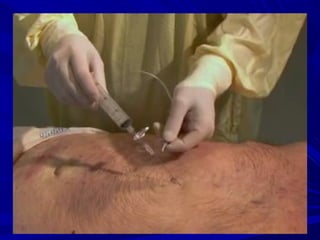
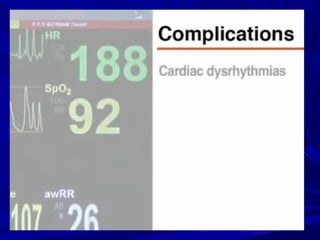
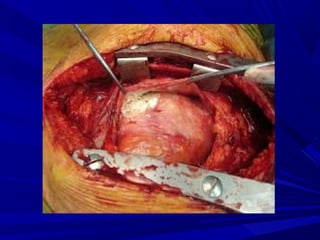
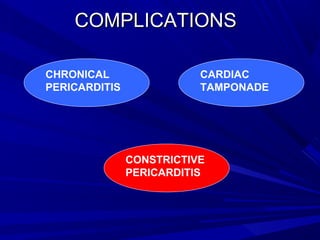
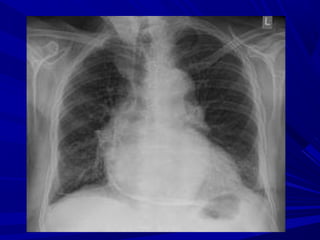
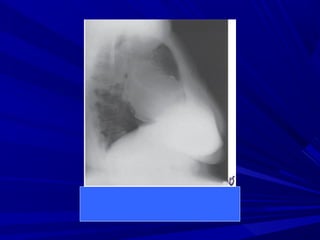
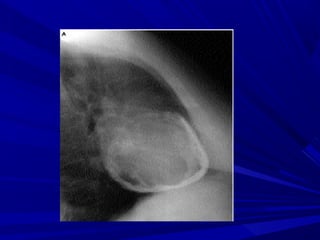
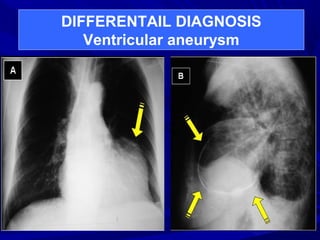
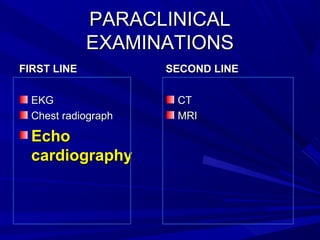
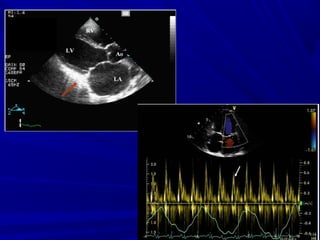
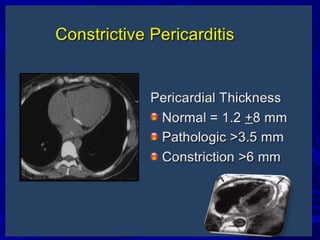
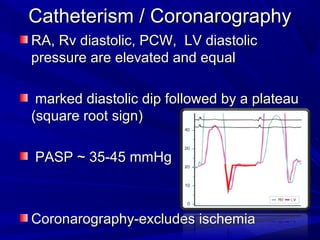
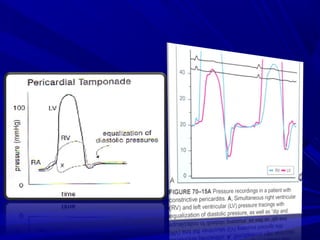
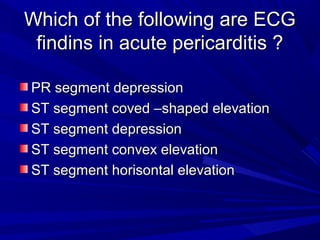
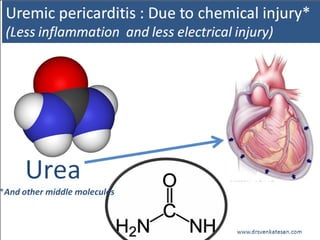
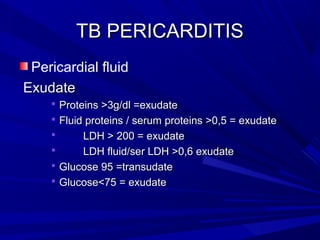
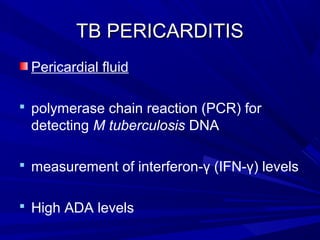
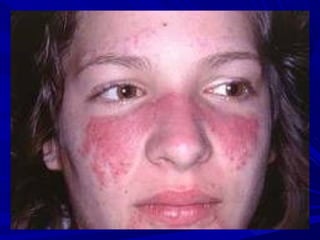
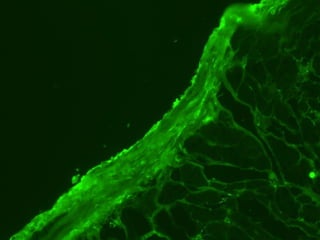
The document discusses pericardial disease and acute pericarditis. Acute pericarditis is defined as inflammation of the pericardium lasting less than 2 weeks. Common causes include viral or bacterial infections, tuberculosis, renal failure and idiopathic. Clinical features include chest pain relieved by sitting forward and pericardial rub. Investigations include EKG showing PR depression and ST elevation, echocardiogram detecting pericardial fluid, and pericardiocentesis if suspicion of infection or tamponade. Treatment involves NSAIDs or colchicine and complications can include recurrent pericarditis or constriction.