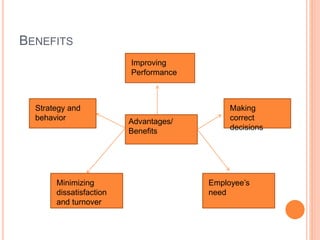
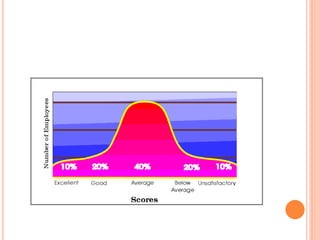
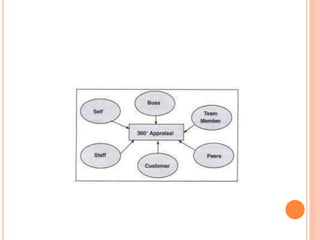
The document discusses performance appraisal, which is defined as the systematic evaluation of an employee's personality, traits, and job performance. It aims to determine an employee's contributions and value. Some key methods discussed include rating scales, checklists, forced distribution, and behavioral anchored rating scales. Performance appraisal provides benefits like improving performance, making correct decisions, and minimizing dissatisfaction. Future-oriented methods covered are management by objectives, psychological appraisal, and 360-degree feedback.