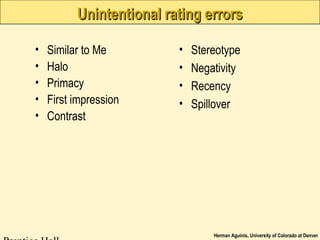
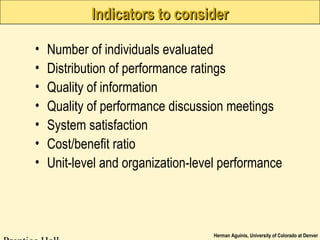
The document provides an overview of implementing a performance management system, outlining key components such as preparation, training programs, communication plans, and an appeals process. It emphasizes the importance of gaining buy-in from employees, reducing cognitive biases in communication, and includes strategies for rater training to improve evaluation accuracy. Additionally, it discusses pilot testing and ongoing evaluation to ensure the effectiveness of the performance management system.