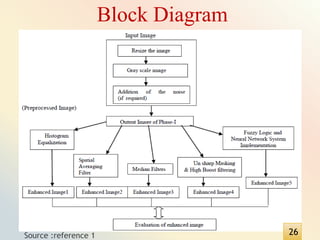
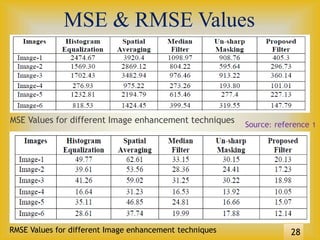
This document presents a method for image enhancement using artificial neural networks and fuzzy logic. It discusses existing image enhancement techniques, fuzzy logic concepts, and how fuzzy logic can be applied to image enhancement. It then introduces artificial neural networks and proposes a neuro-fuzzy system that integrates artificial neural networks and fuzzy inference systems. The document outlines the proposed model and ANFIS architecture. It compares different image enhancement techniques using parameters like mean squared error, root mean squared error, signal-to-noise ratio, and peak signal-to-noise ratio. Experimental results demonstrate improved performance using the proposed neuro-fuzzy approach.