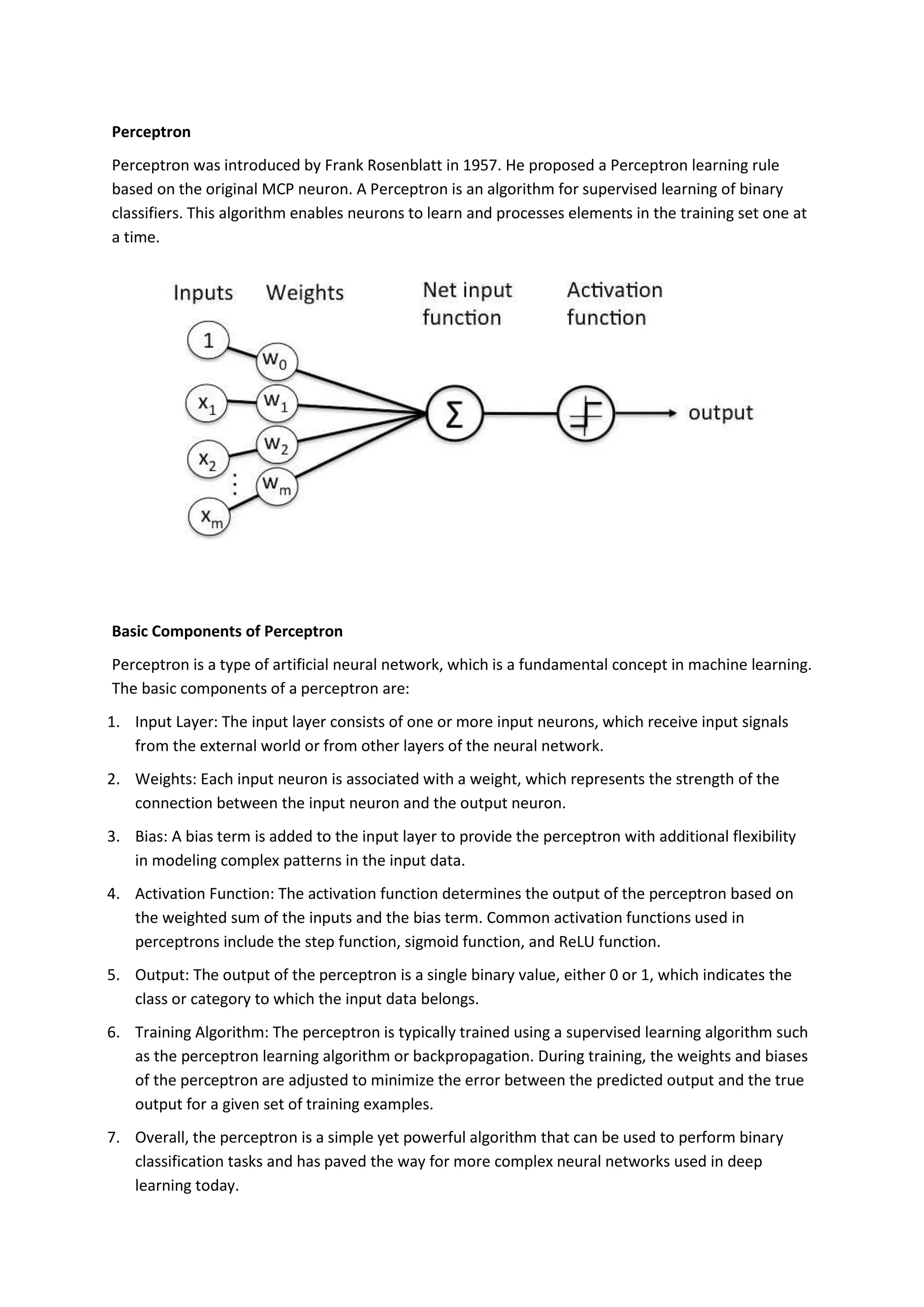
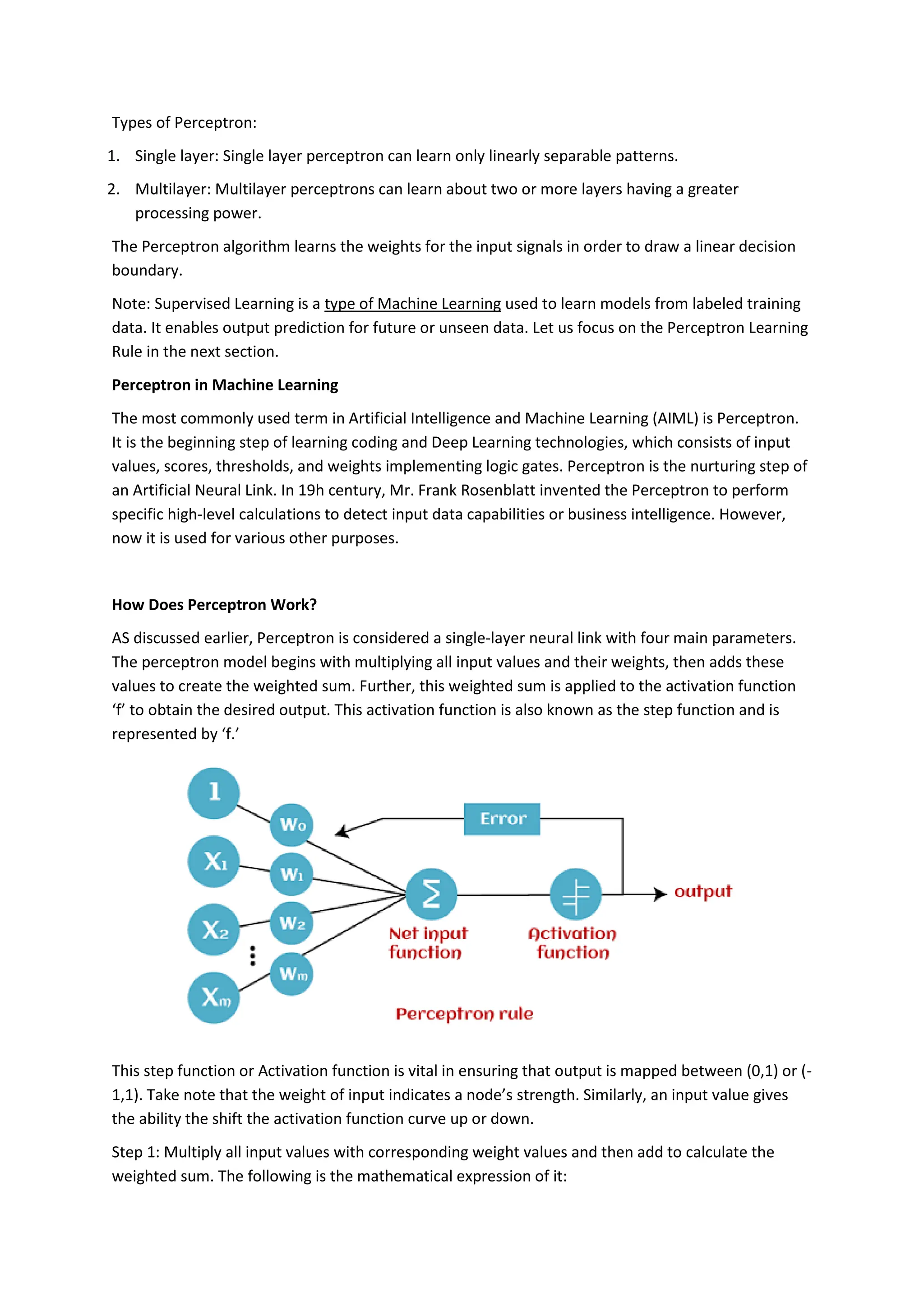
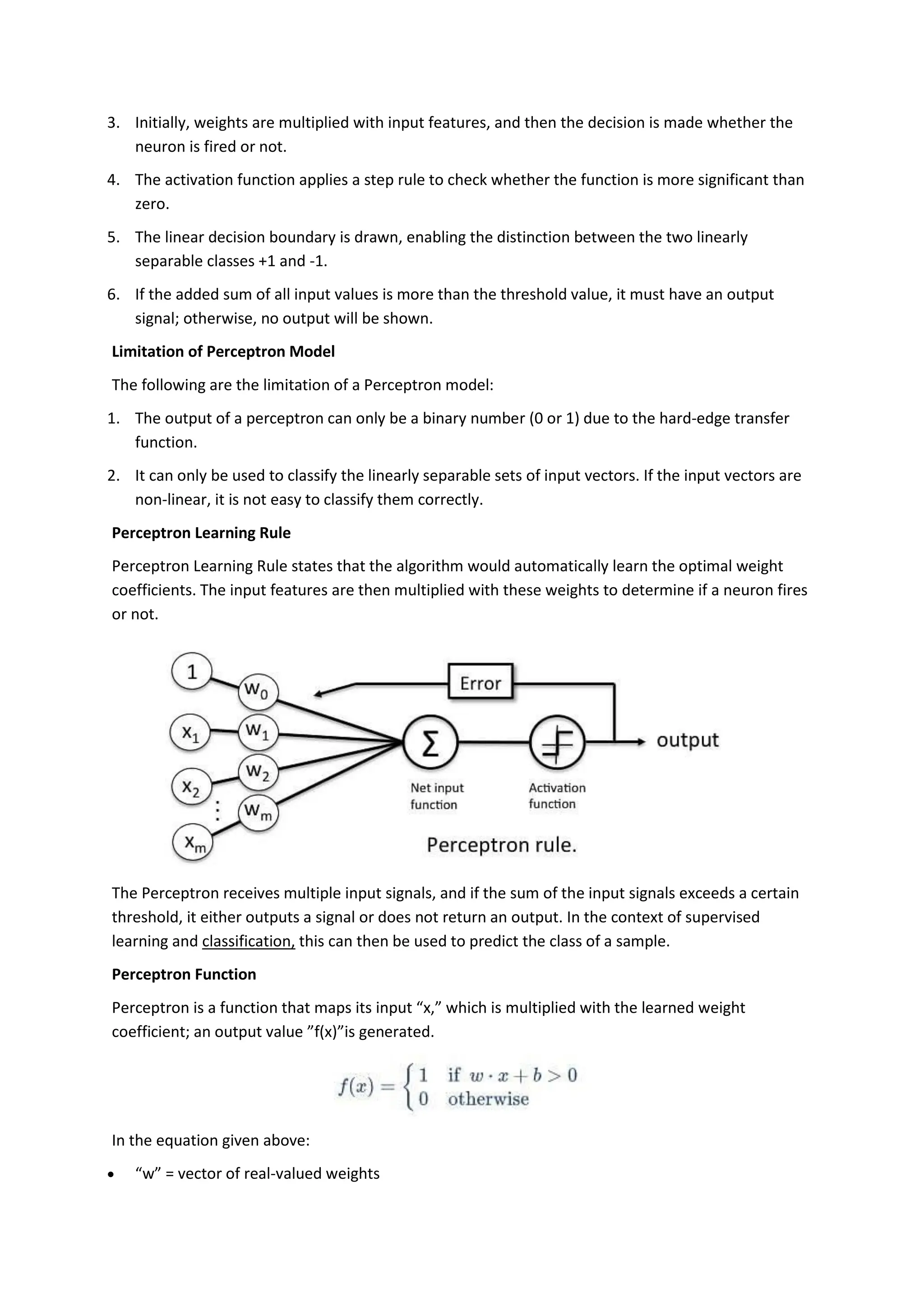
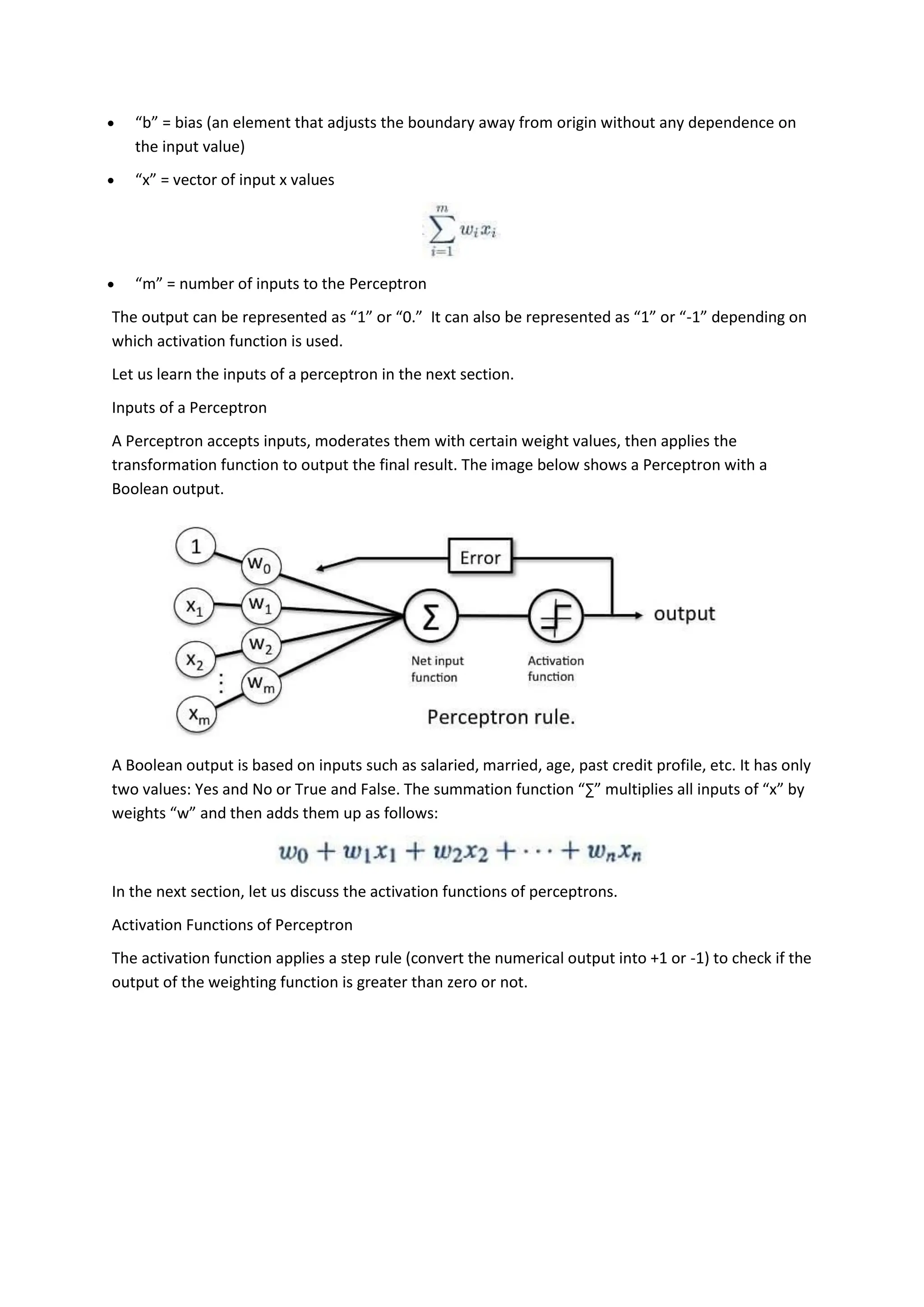
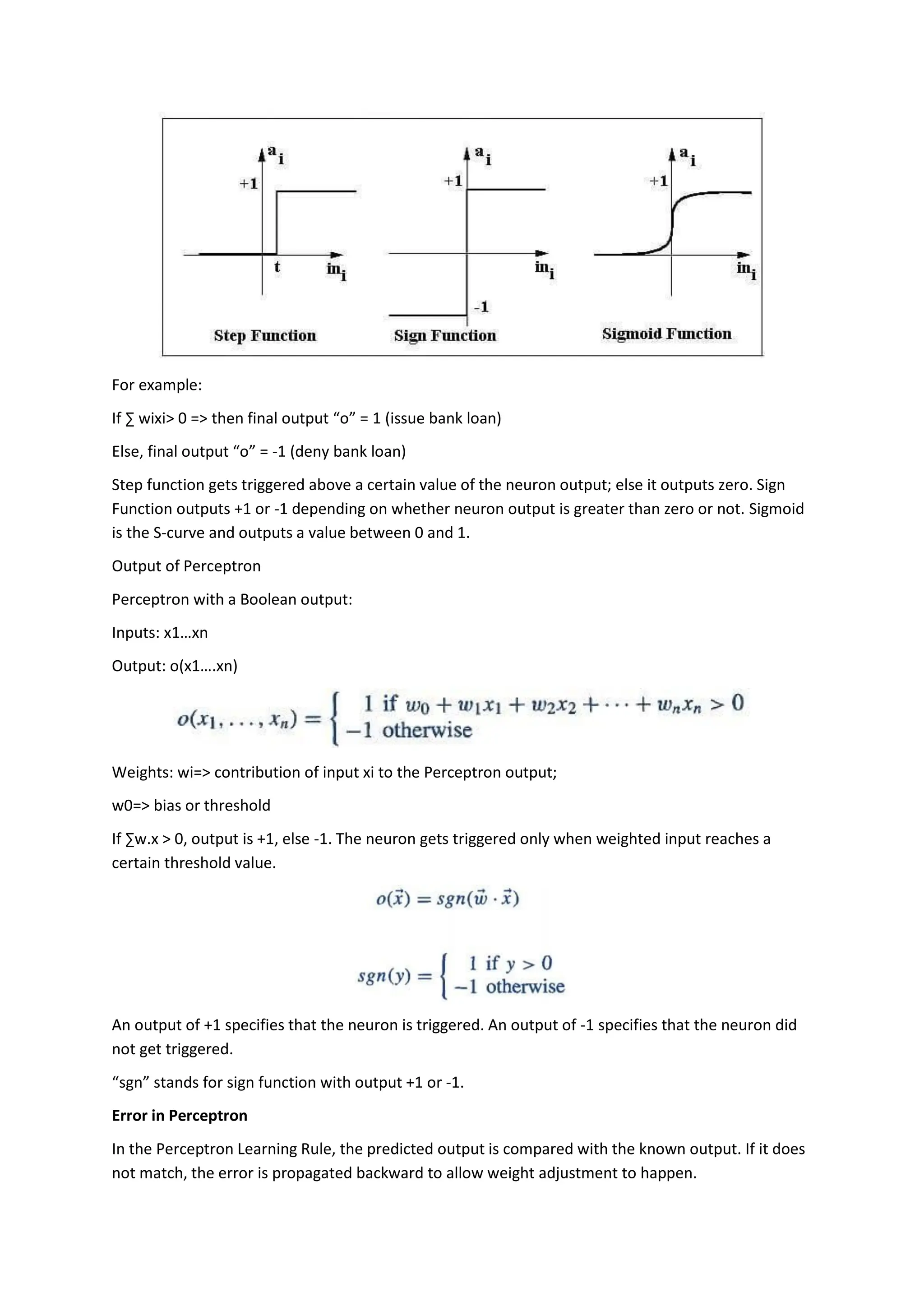
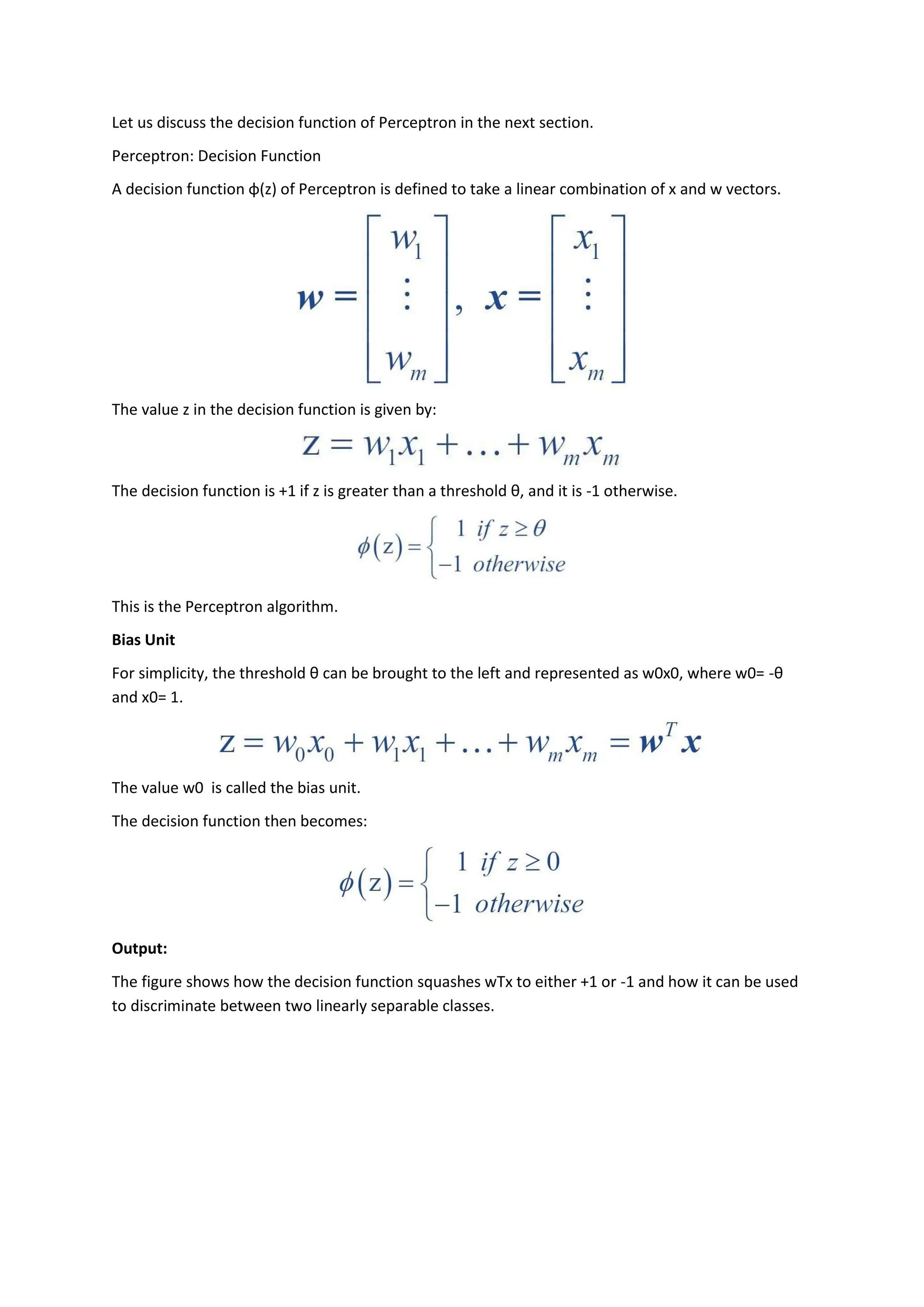
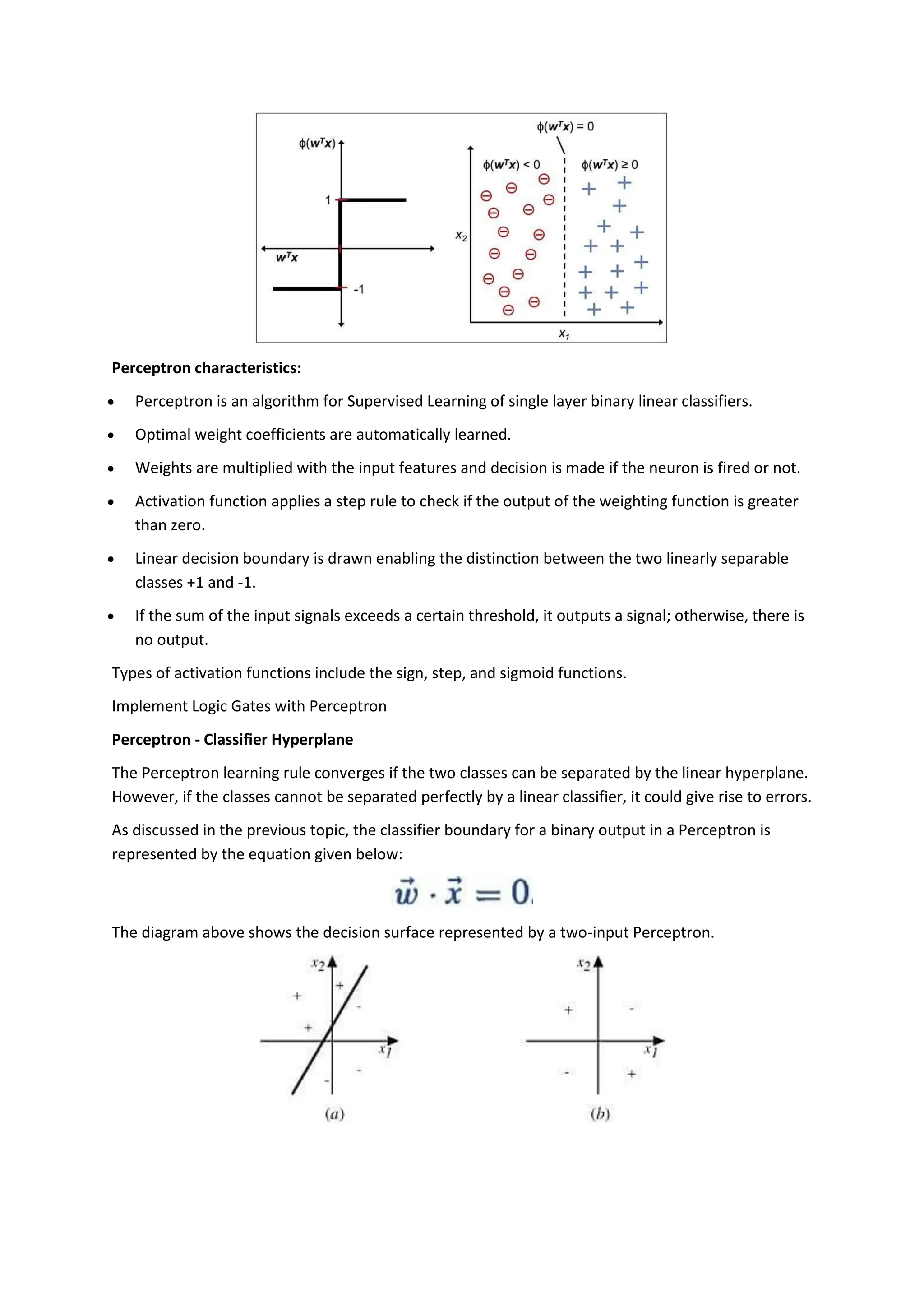
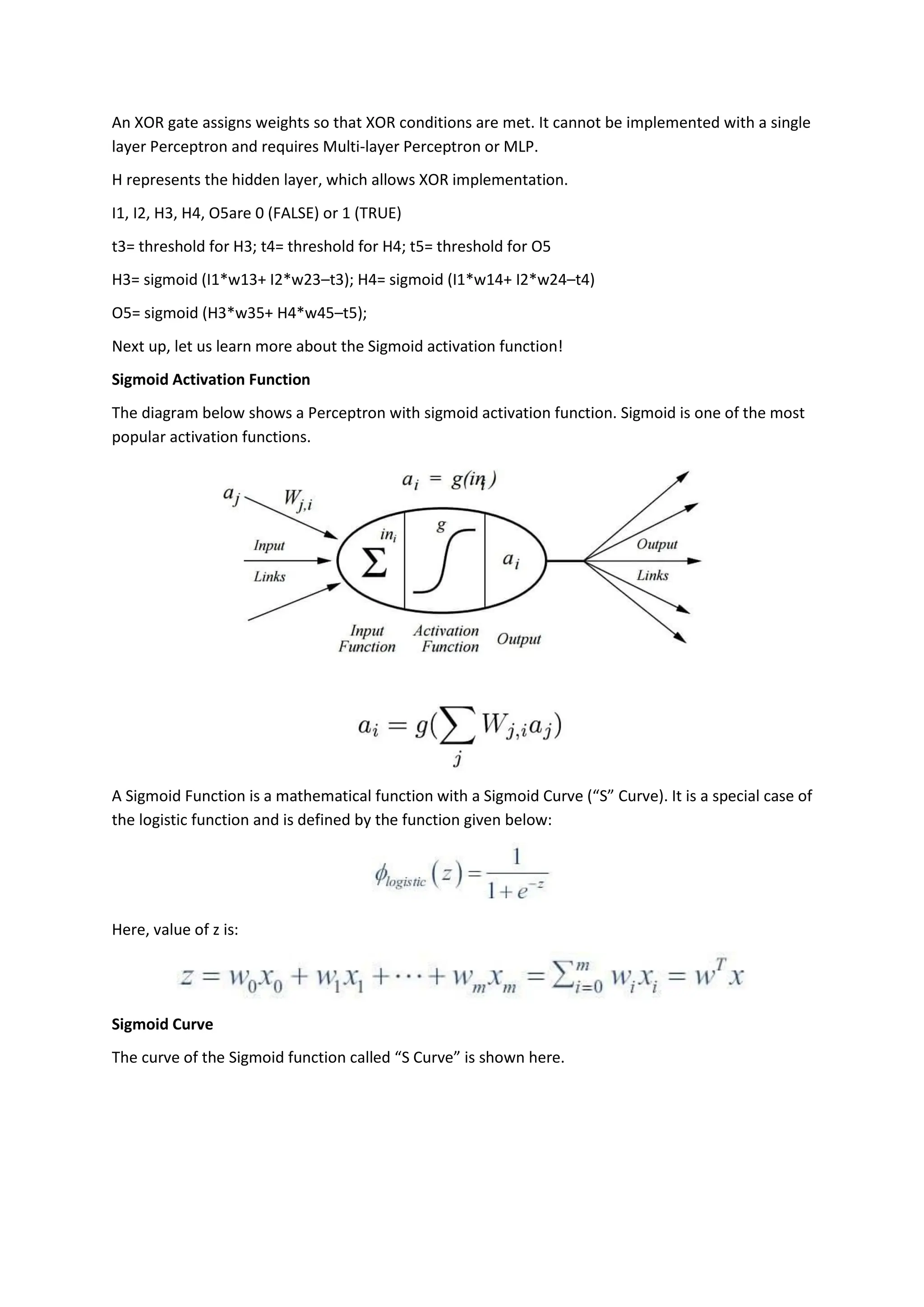
The perceptron, introduced by Frank Rosenblatt in 1957, is a supervised learning algorithm for binary classification, consisting of input neurons, weights, biases, an activation function, and an output that predicts class labels. It can be either a single-layer perceptron, which only learns linearly separable patterns, or a multi-layer perceptron, which possesses greater computational power and can handle non-linear problems. Key components include training rules for weight adjustment, activation functions such as step, sign, and sigmoid functions, and applications in logic gates.