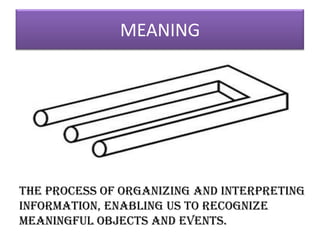
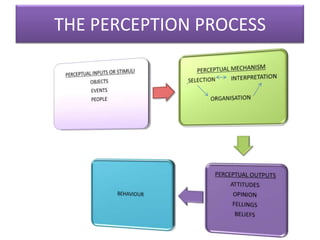
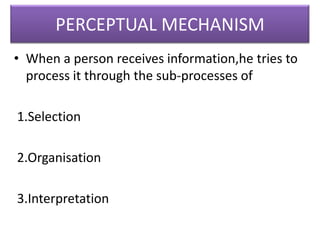
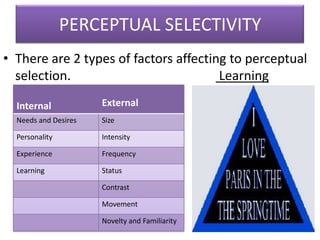
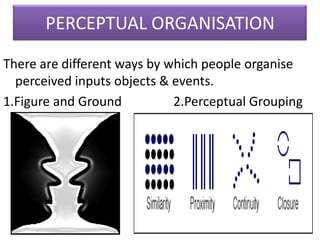
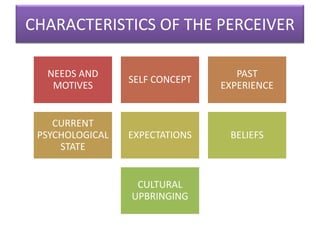
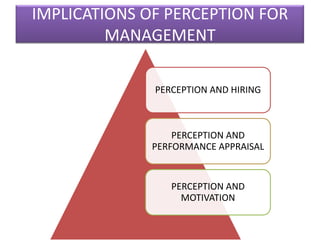
This document outlines a presentation on perception given by several presenters under the guidance of Ms. Priyanka Aneja. The presentation covers the meaning of perception, its significance, and the perceptual process. It discusses how internal and external factors influence perceptual selectivity. It also addresses perceptual organization, interpretation, and the characteristics of the perceiver. The presentation concludes by covering the implications of perception for management and guidelines for improving perception.