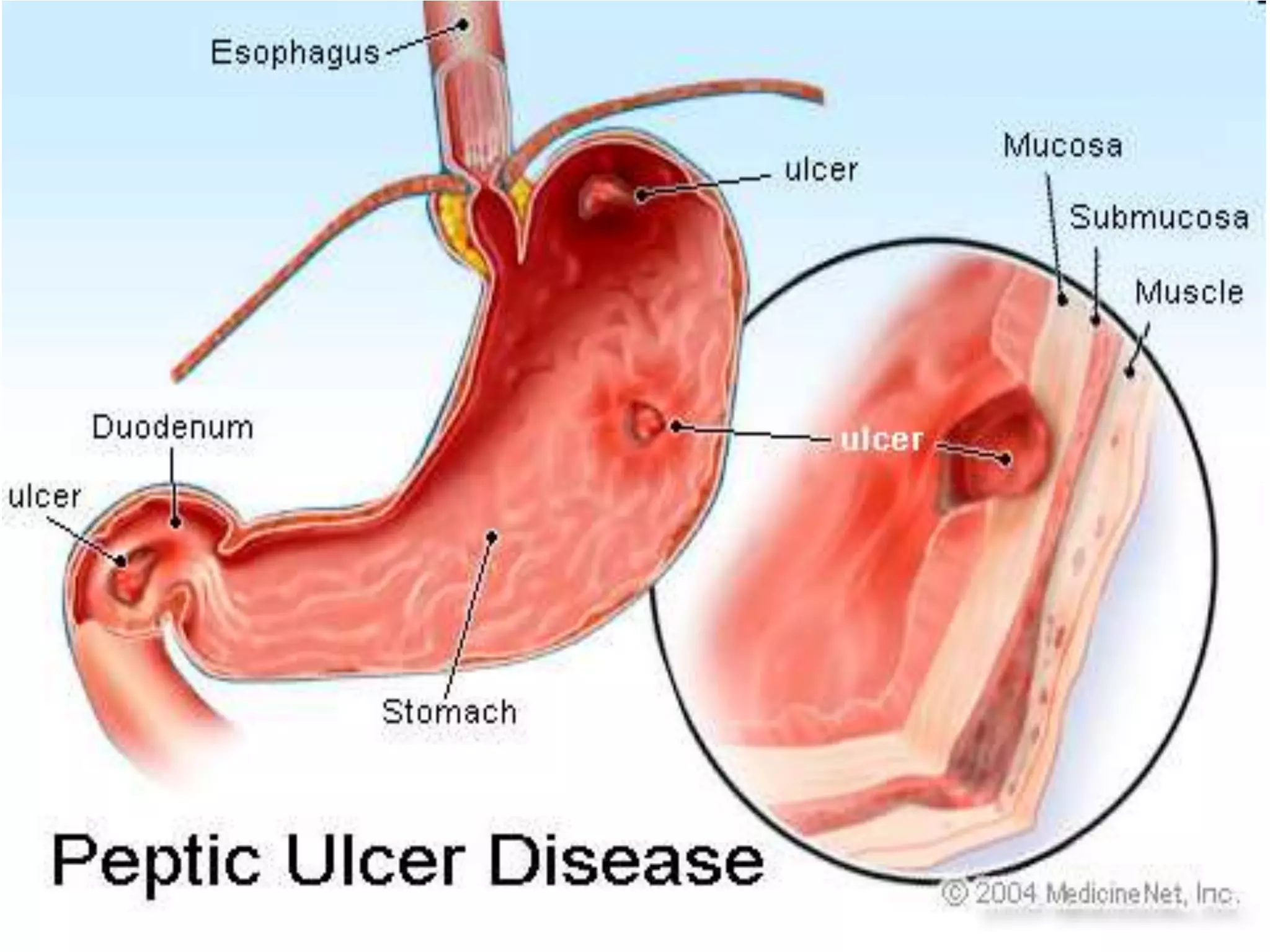
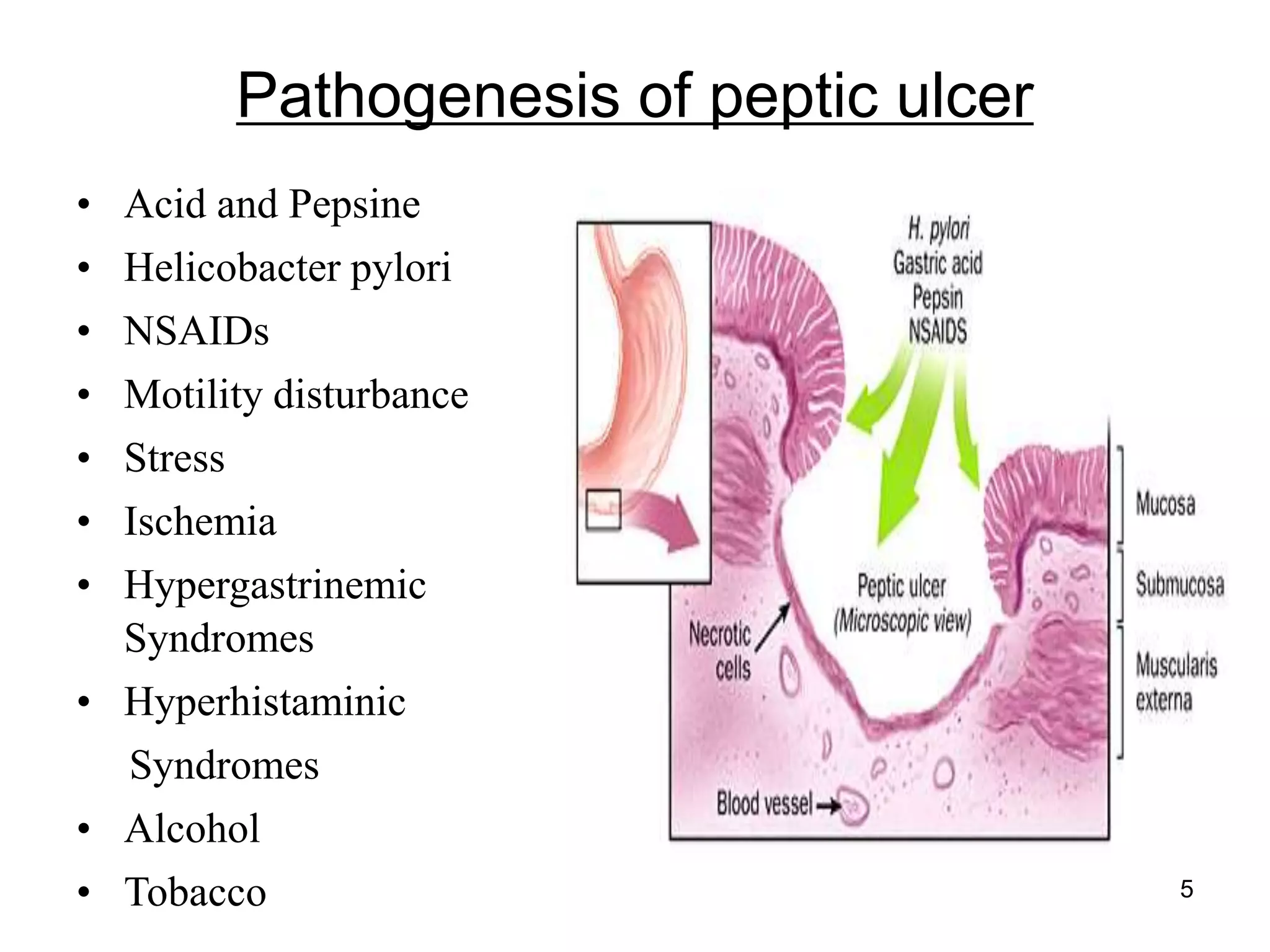
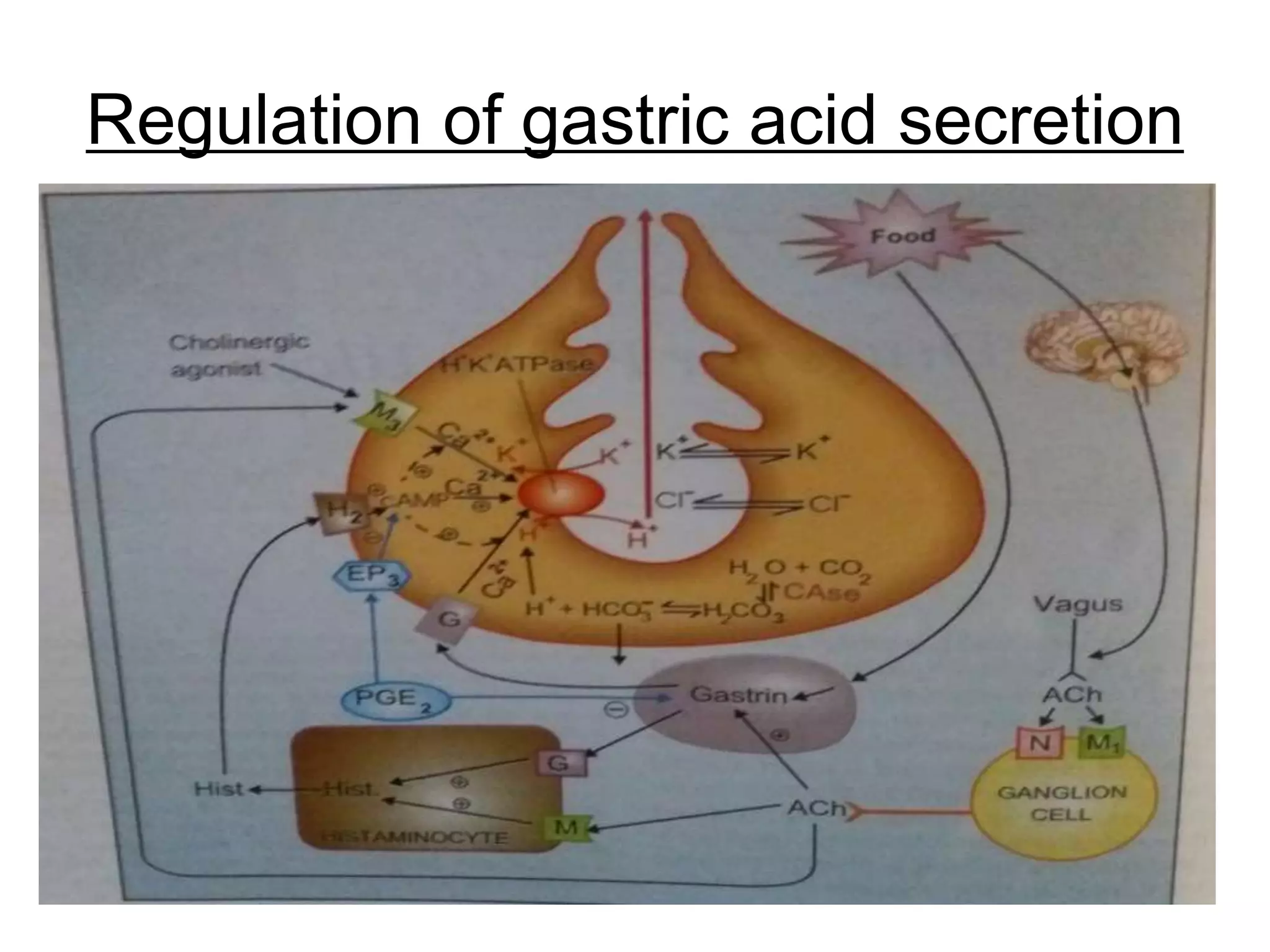
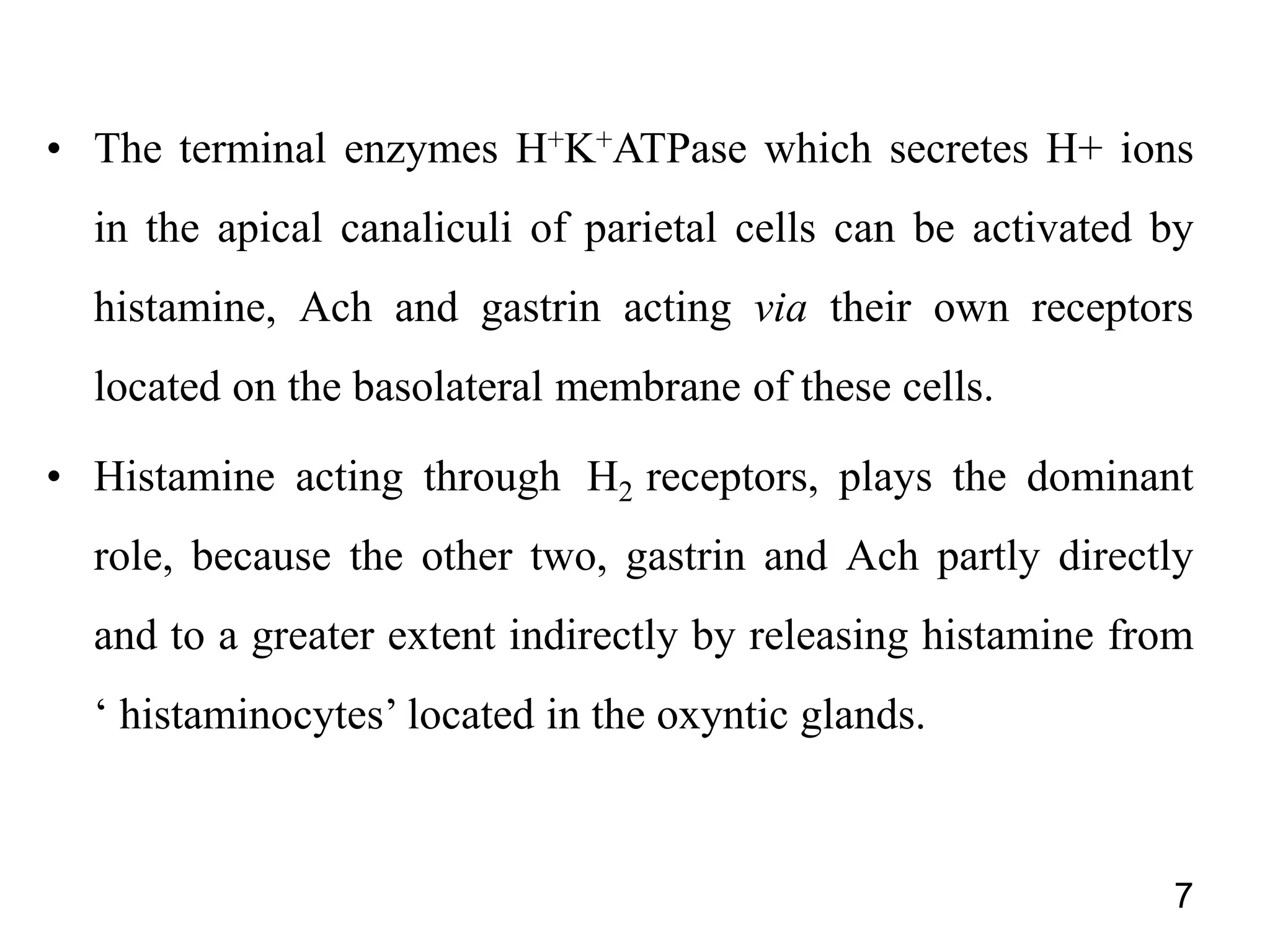
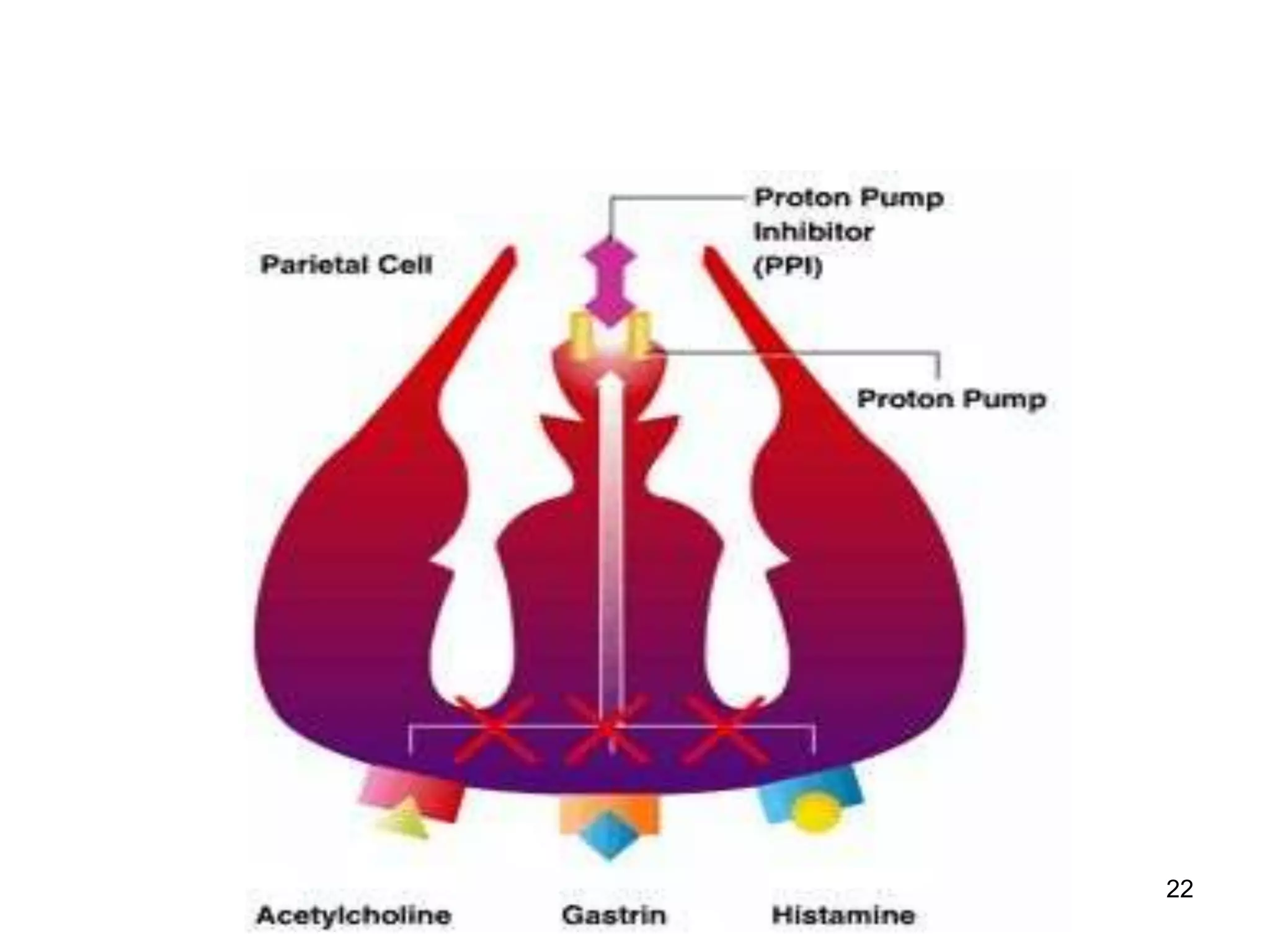
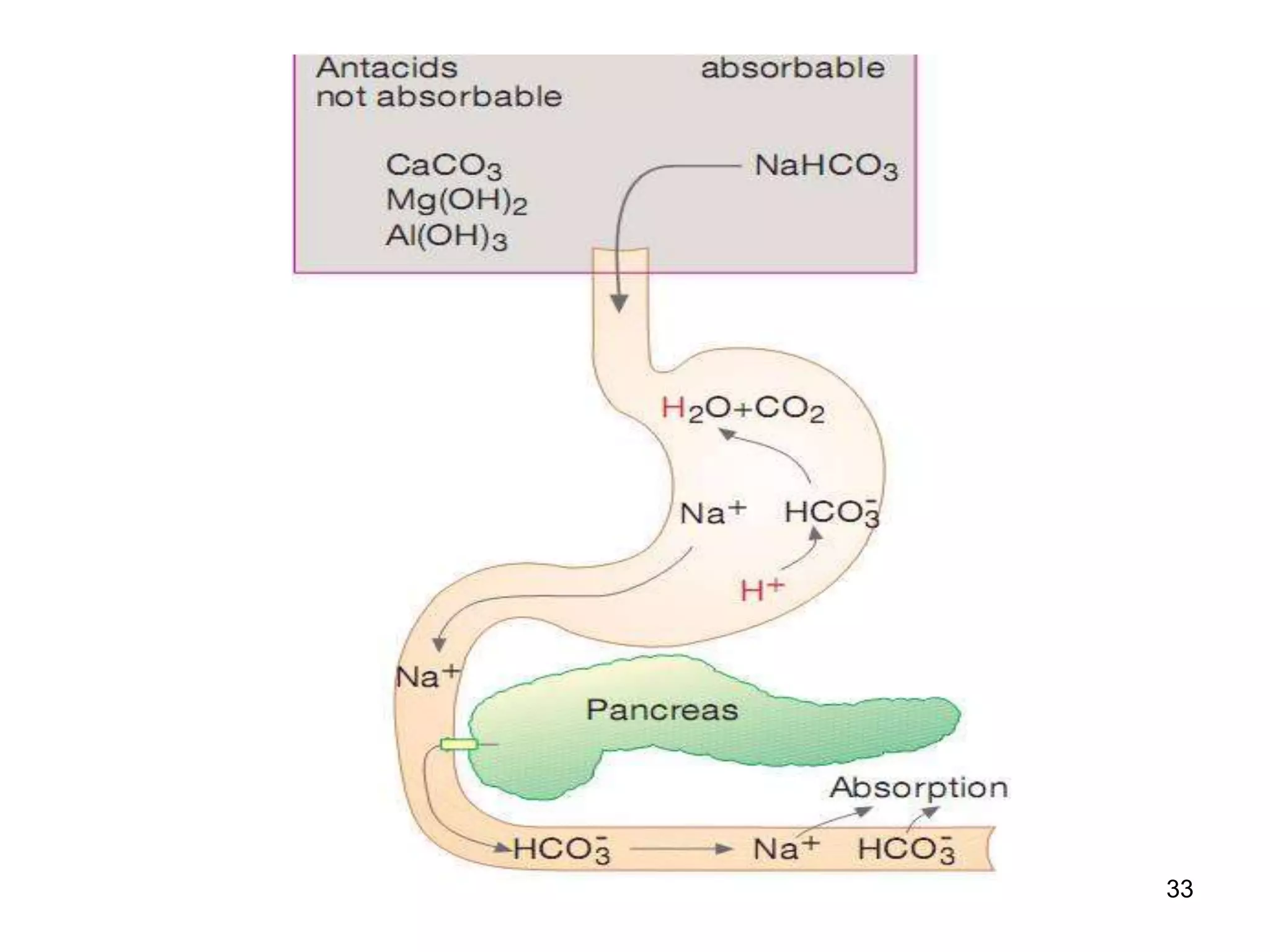
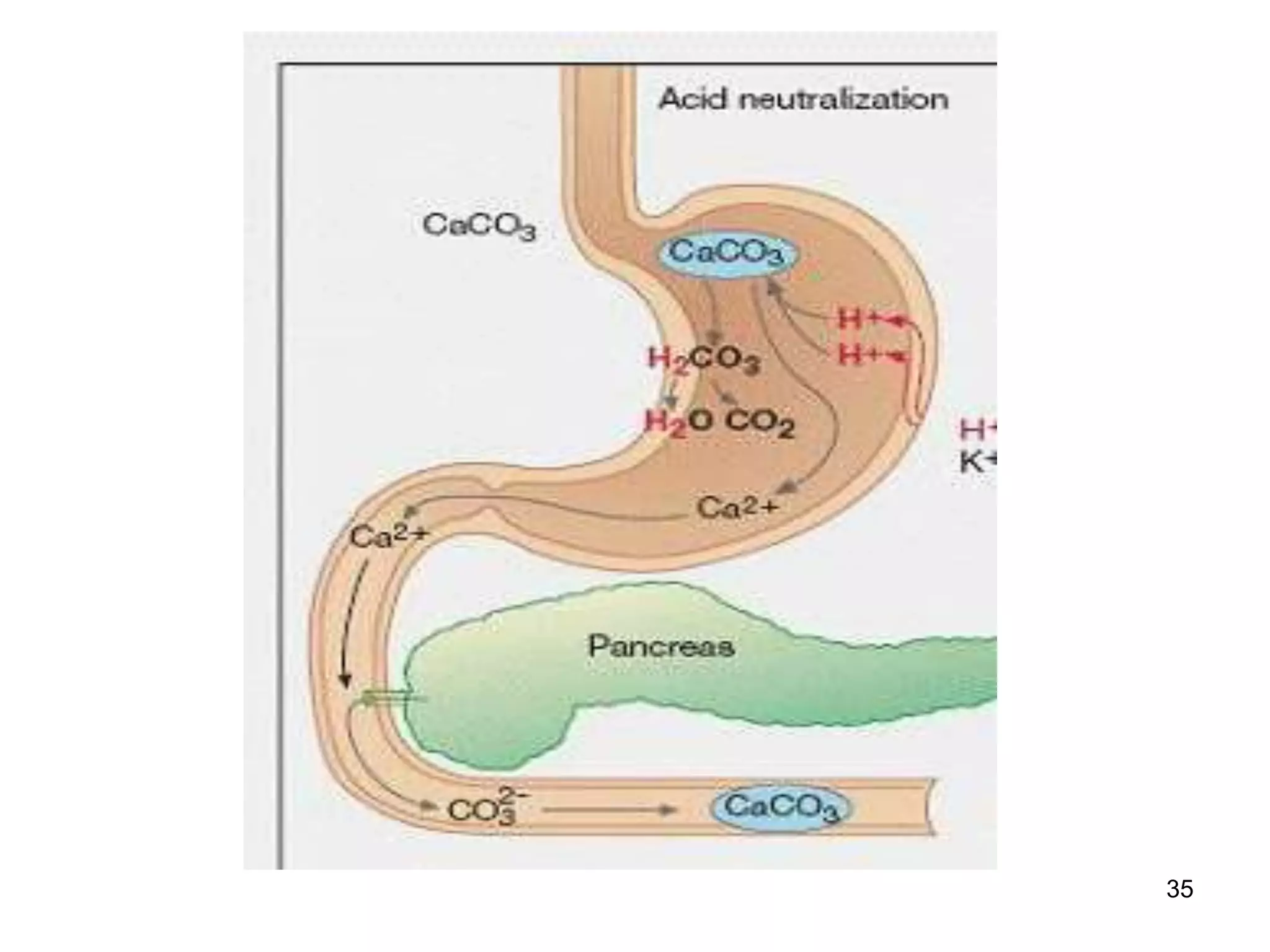
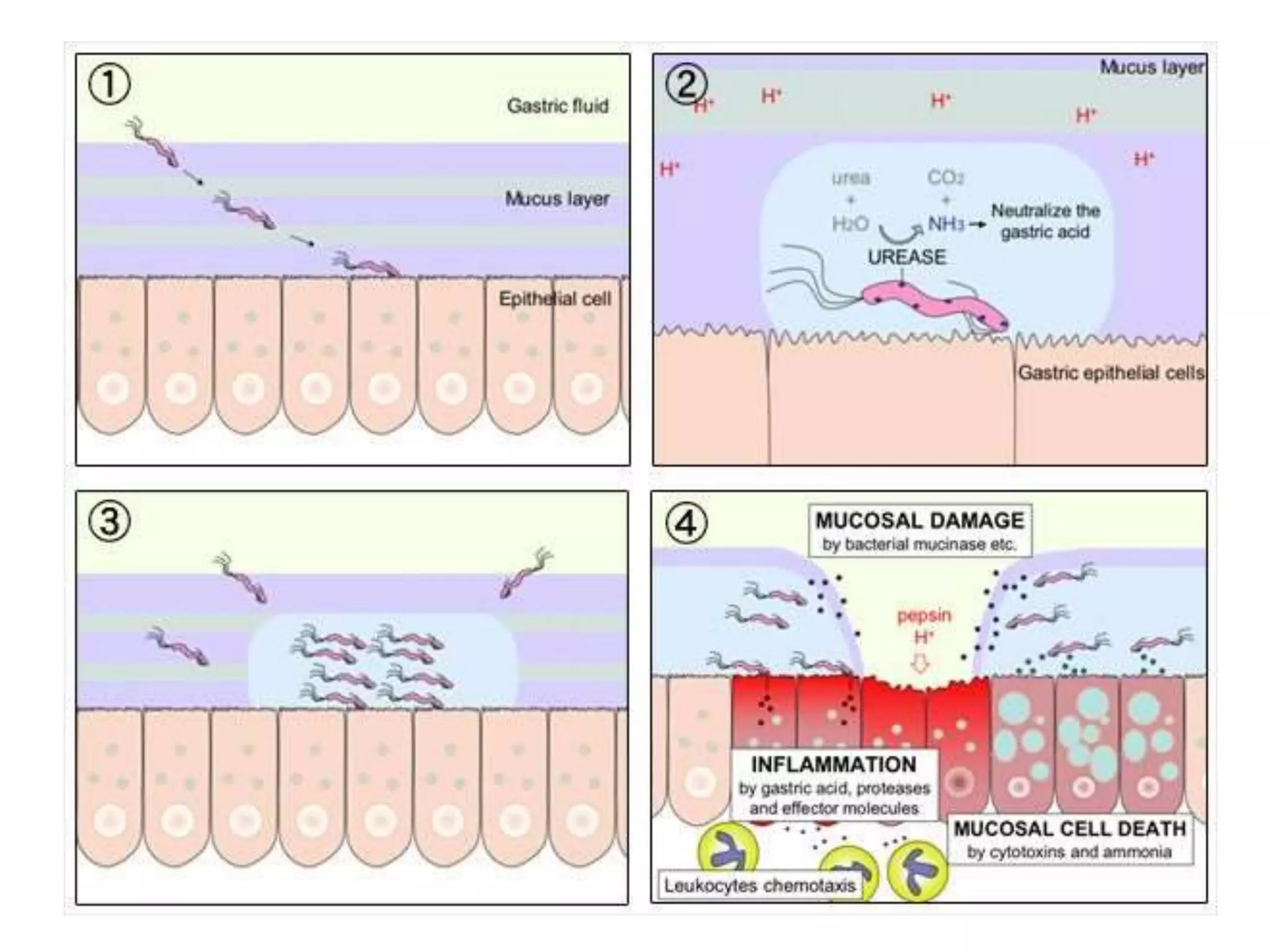
This document summarizes peptic ulcer disease. It begins by defining peptic ulcers as lesions in the stomach or duodenum caused by gastric acid and pepsin. Risk factors for peptic ulcers include an imbalance between aggressive factors like acid and protective mucosal defenses. Common symptoms are epigastric pain and weight loss. Treatment approaches aim to reduce acid secretion through H2 blockers, proton pump inhibitors, anticholinergics, and prostaglandin analogues. Other treatments include antacids to neutralize acid, ulcer protectives like sucralfate, and anti-H. pylori drugs to eradicate H. pylori infections which are a major cause of peptic ul