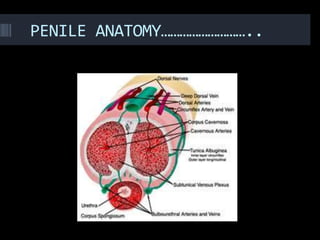
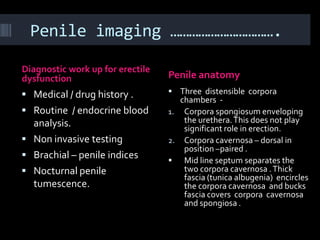
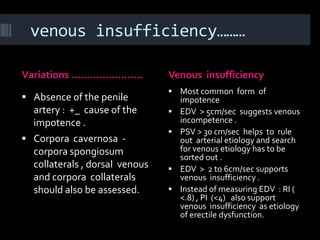
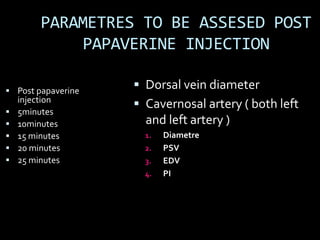
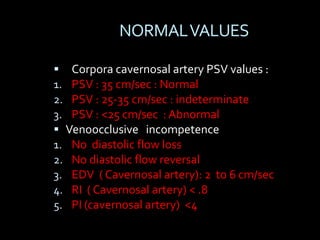
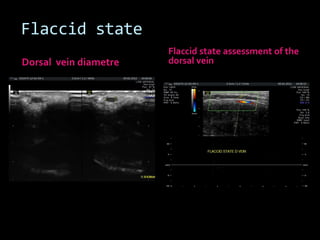
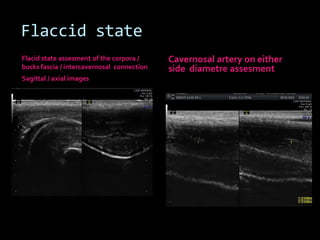
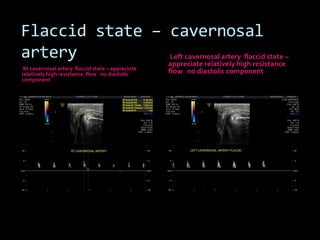
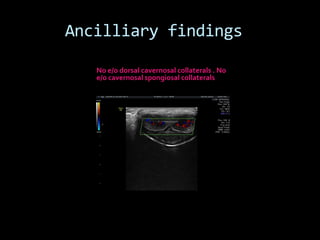
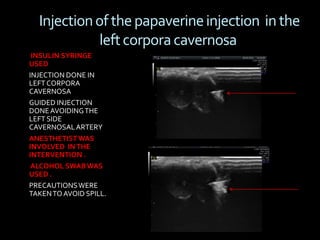
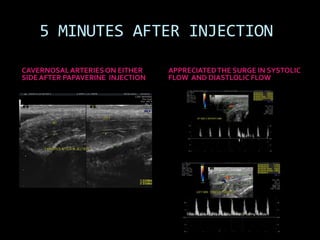
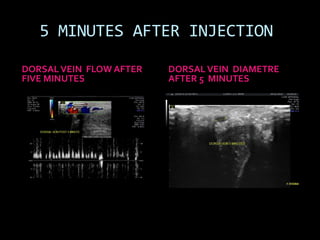
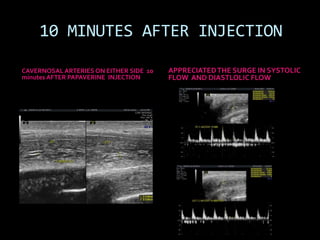
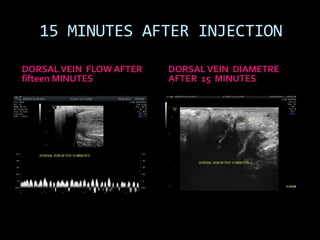
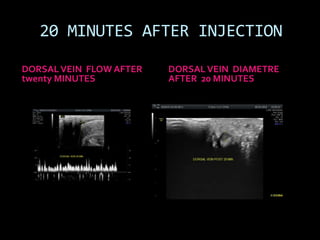
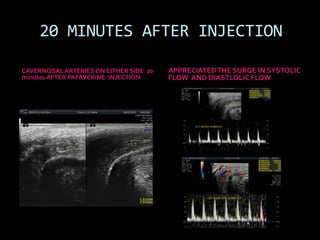
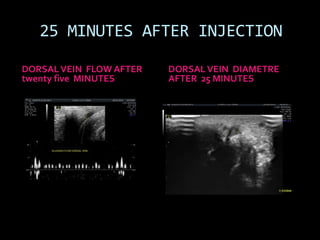
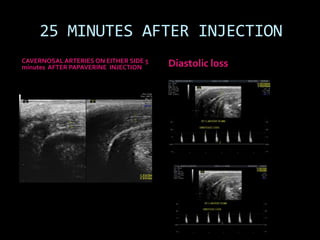
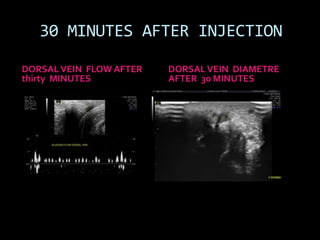
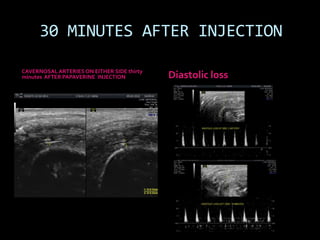
(1) A 35-year old male with depression and erectile dysfunction underwent penile Doppler ultrasound to assess the vasogenic cause of his erectile dysfunction. (2) The Doppler exam involved imaging of the penile arteries and veins in the flaccid state and at intervals after injection of papaverine into the corpora cavernosa. (3) Parameters like peak systolic velocity, end-diastolic velocity, and vein diameter were measured and compared to normal values to evaluate for vascular insufficiency as the cause of erectile dysfunction.