This document contains information on various ultrasound findings including:
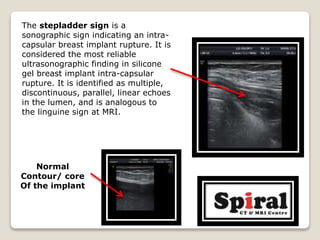
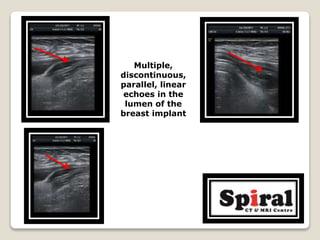
1. Intracapsular rupture of a breast implant seen as the "stepladder sign" of multiple parallel linear echoes within the implant lumen.
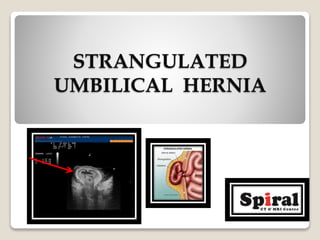
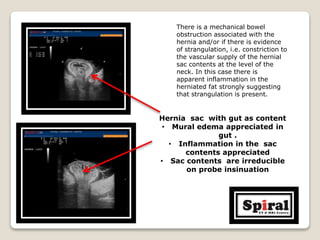
2. Strangulated umbilical hernia seen as inflammation and edema in herniated fat and gut suggesting vascular compromise.
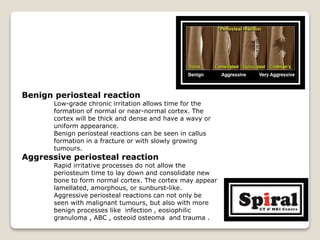
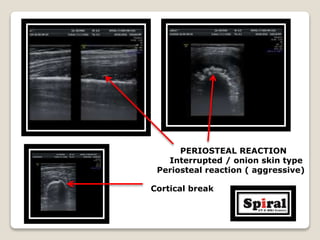
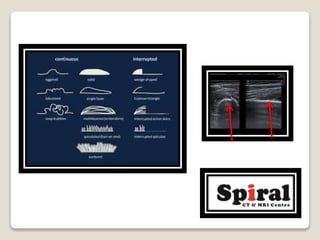
3. Aggressive periosteal reaction on bone seen as interrupted lamellated or "onion skin" patterns indicating rapid bone formation from infection or malignancy.
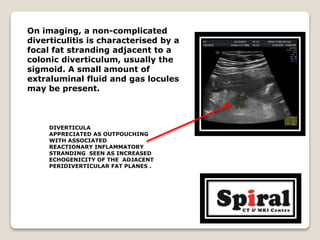
4. Diverticulitis seen as focal fat stranding next to a colonic diverticulum with possible fluid or gas locules.