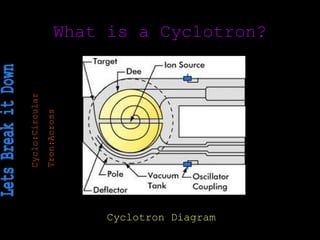
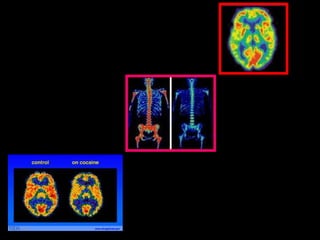
The cyclotron was invented by Leo Szilard in the early 1900s and accelerated the development of nuclear physics and particle accelerators. It allowed scientists to produce radionuclides for medical imaging like PET scans and treat cancer with proton therapy. Szilard later regretted his role in nuclear weapons and founded the Council for a Livable World to advocate for arms control. The cyclotron continues to be used for fundamental particle physics research and medical isotopes, influencing fields from astrophysics to medicine.



















































![Radiation Therapy
Involving Cyclotrons
• Accelerates [cyclotron] protons to high energies
• Proton beam is then sent down a beam line and into
a gantry
• Then directed to eradicate a portion of the
patient
Pros:
• Targets specific areas of the body
Cons:
• Range of protons of dependent on depth of body
– If body moves beams will miss targeted portion
• Can only be used on brain tumors
• Cost is 150 million](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecyclotron-120604120911-phpapp02/85/Pence-Cyclotron-55-320.jpg)



