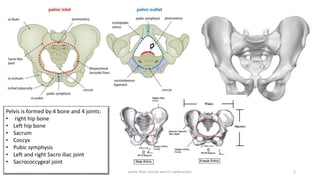
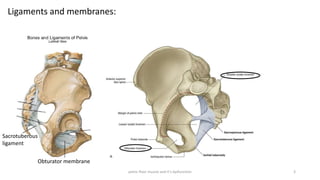
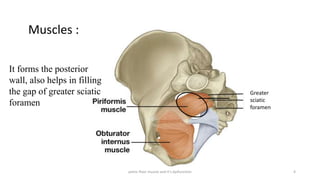
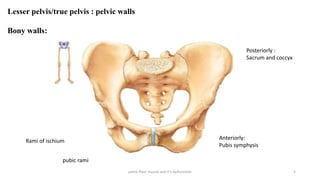
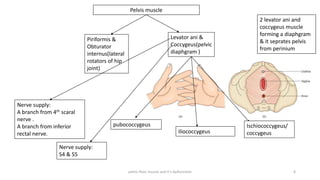
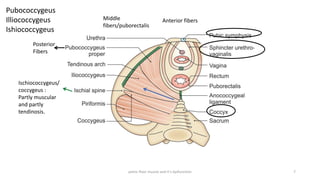
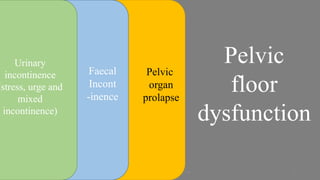
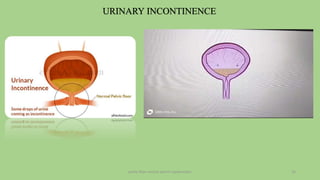
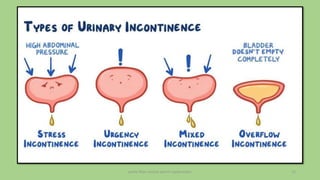
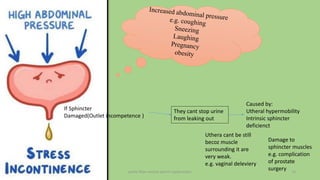
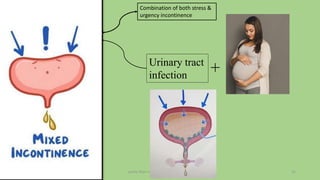
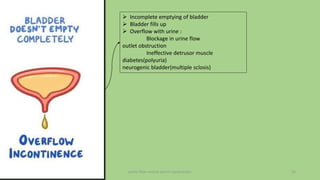
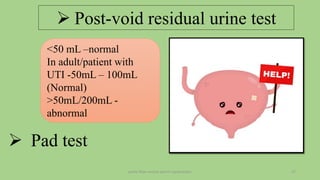
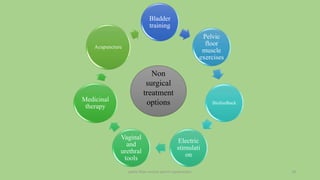
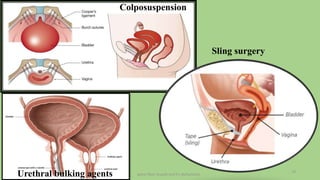
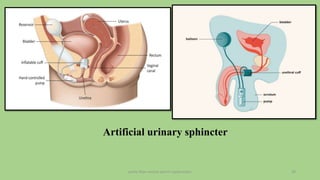
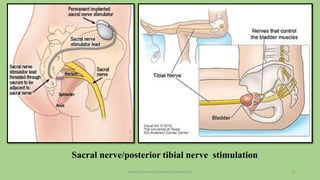
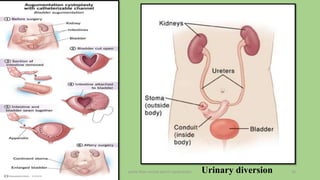
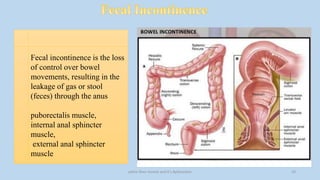
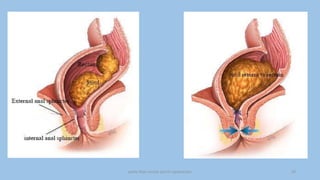
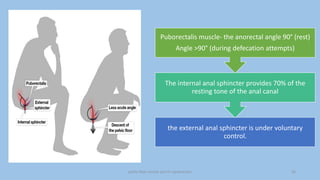
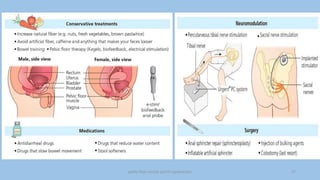
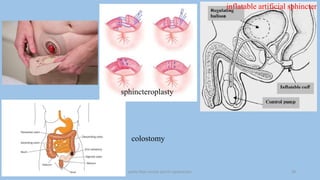
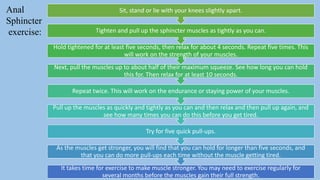
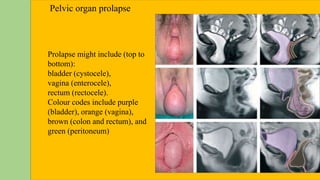
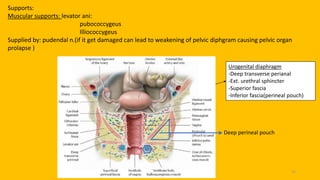
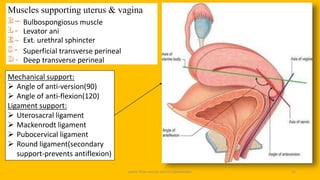
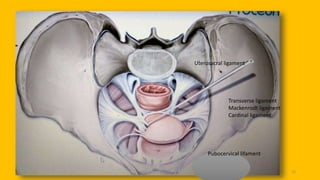
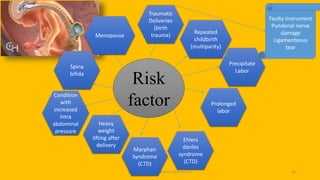
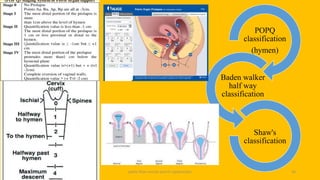
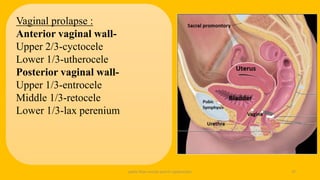
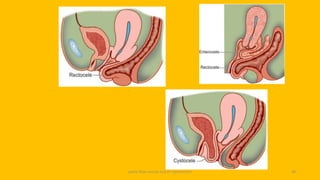
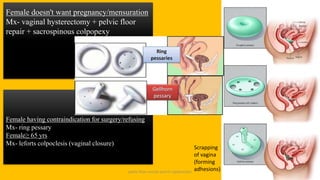
The document discusses the pelvic floor muscles and their dysfunctions. It describes the anatomy of the pelvis including bones, ligaments, and muscles like the levator ani. Dysfunctions of the pelvic floor muscles can cause urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and pelvic organ prolapse. Non-surgical and surgical treatment options are presented for each condition. Evaluation methods like pad tests and POPQ classification are also covered.