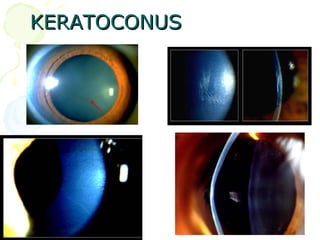
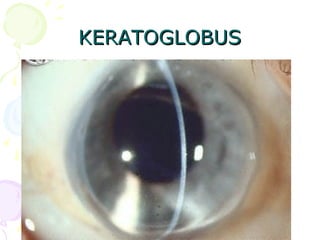
This document discusses the surgical management of Pellucid marginal degeneration (PMD), a non-inflammatory thinning of the cornea. It describes various surgical techniques used to treat PMD including INTACS inserts, eccentric penetrating keratoplasty, large diameter epikeratoplasty, lamellar crescentic keratoplasty, lamellar crescentic resection, and wedge resection. The goal of these surgeries is to reshape the cornea and reduce high astigmatism caused by PMD through techniques like inserting inserts, excising the thinned area, or using donor tissue grafts. Complications can include increased risk of rejection, vascularization, and long-term astigmatism changes.