This document discusses the approach to evaluating a case of hemiplegia in a pediatric patient. It emphasizes taking a thorough history to determine the onset and any associated symptoms. The clinical examination involves a full neurological exam including cranial nerves and assessment of motor, sensory and reflex functions. Important investigations include CSF analysis, imaging studies like CT and MRI of the brain, and evoked potentials. The differential diagnosis includes conditions like cerebral palsy, vascular disorders, infections, demyelinating diseases and space occupying lesions. Management depends on the underlying etiology but may involve correcting fluid/electrolyte imbalances, reducing brain edema, and long-term rehabilitation.



































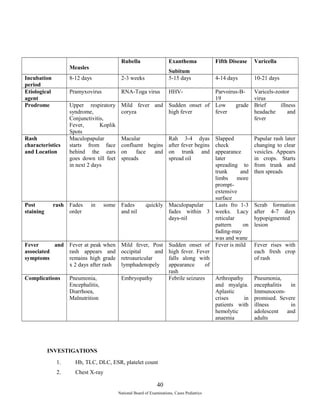
![Antacid/Ranitidine/Omeprazole
Treatment of causes-ITP etc
Treatment of variceal bleed
Vasopression/Nitroglycerin/
Glypression/Somatostatin
Octreotide
Beta blockers fro recurrent variceal bleed
Ballon tamponade
After patient is stabilized - Endoscopic sclerotherapy-every week for 3-6 wks
Observe for ulceration/stricture/disphagia
If bleeding continues emergency surgery-
Shunt surgery or
Portal decompressive surgery
Factory indicating poor prognosis-
[Massive hematemesis
Initial hematocrit<20o
HB<7gm%
Transfusion exceeding 85ml/kg
Failure to identify source of bleeding
Coexisting coagulation disorder
Associated liver disease of other systemic disease]
36
National Board of Examinations, Cases Pediatrics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricscasesbynatboard-141020142304-conversion-gate01/85/Pediatrics-cases-by-DNB-NATboard-36-320.jpg)