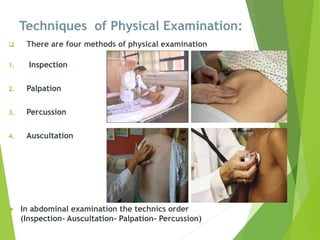
This document provides information on nursing history taking and physical examination. It discusses the importance of obtaining an accurate patient history, which is critical for diagnosis. The key components of history taking are identified as demographic data, chief complaint, history of present illness, past medical history, family history, drug history, review of systems, and physical examination. The principles and techniques of physical examination are outlined, including inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation. A head-to-toe assessment approach is recommended to perform a thorough physical exam.