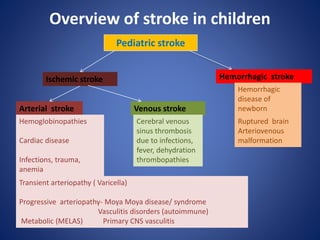
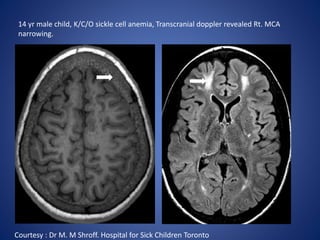
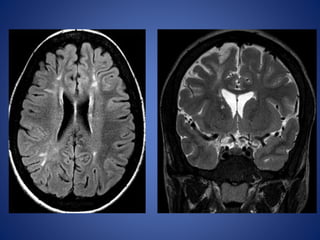
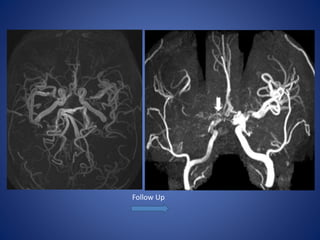
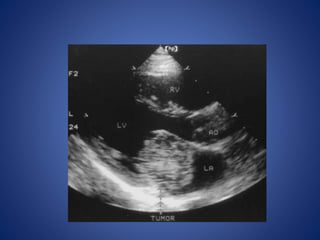
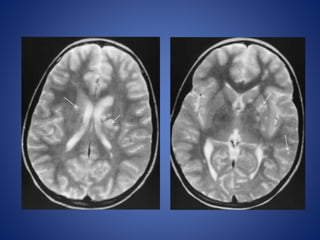
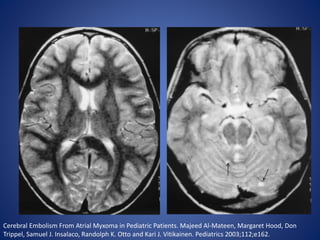
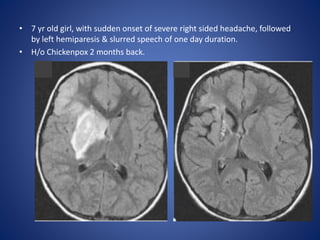
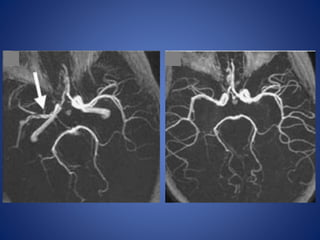
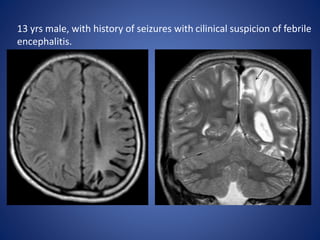
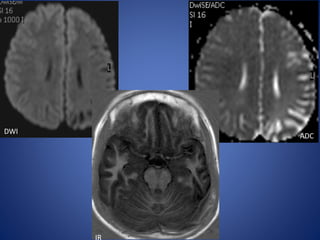
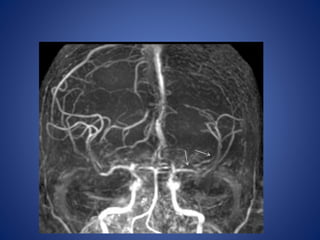
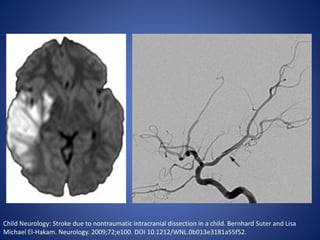
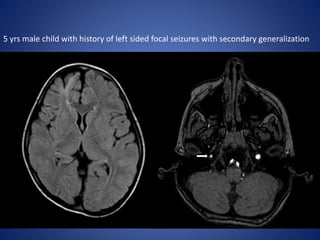
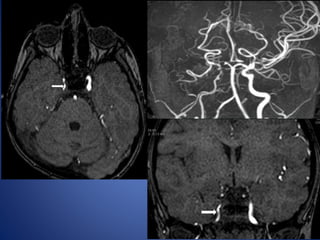
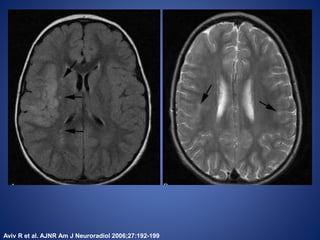
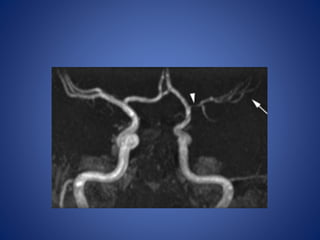
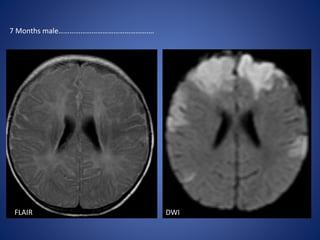
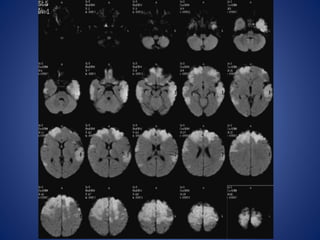
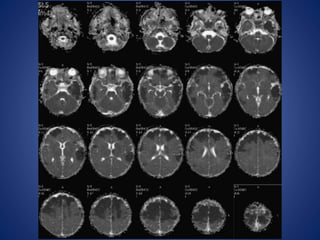
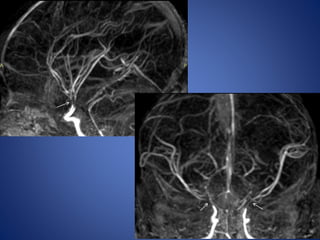
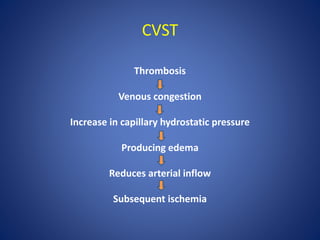
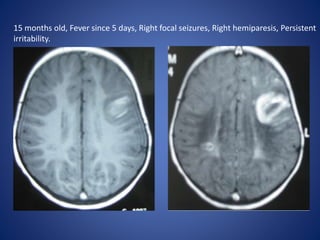
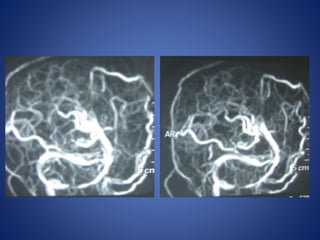
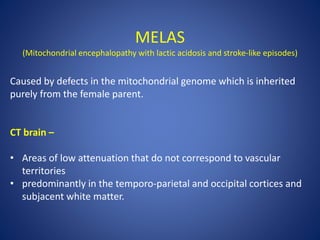
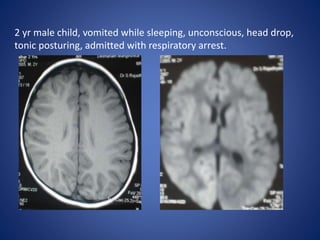
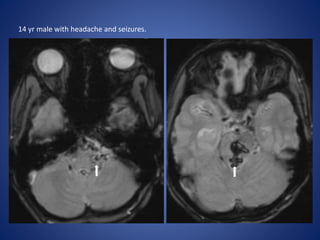
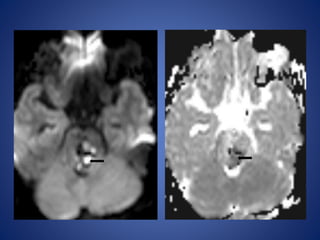
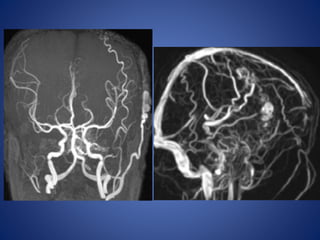
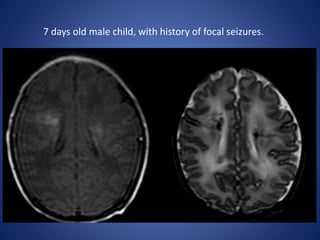
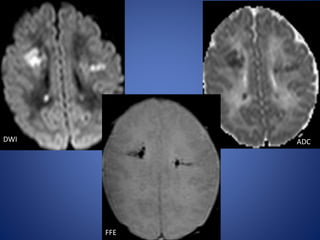
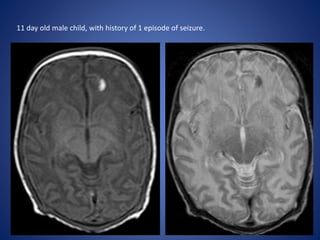
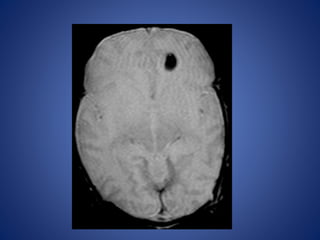
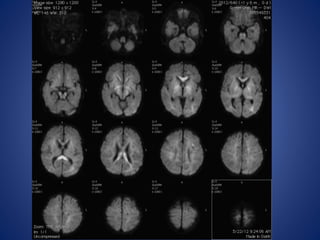
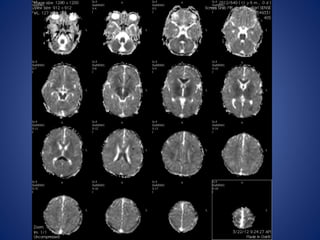
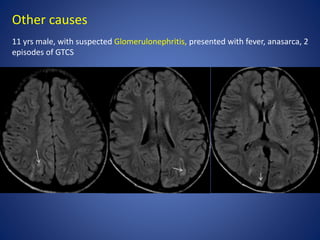
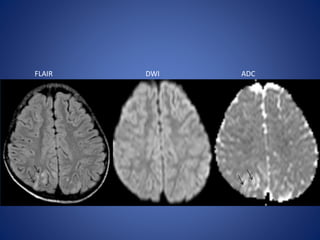
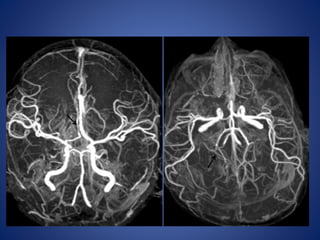
Pediatric stroke can be caused by a variety of conditions including sickle cell disease, infections like varicella, cardiac diseases, moyamoya disease, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, and vascular malformations. Diagnostic techniques like MRI, MRA, CT, and angiography are used to identify abnormalities and characterize the nature of the stroke. Common findings include lesions in the brain parenchyma that may involve gray or white matter or cross vascular territories, stenosis or occlusion of arteries, moyamoya vessels, and venous sinus thrombosis. Pediatric stroke requires identifying its underlying cause to provide appropriate treatment and management.